Alignment to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
Playing With Parachutes This lesson focuses on parachute design. Teams of students construct parachutes from everyday materials. They then test their parachutes to determine whether they can transport a metal washer to a target on the ground with the slowest possible rate of descent.
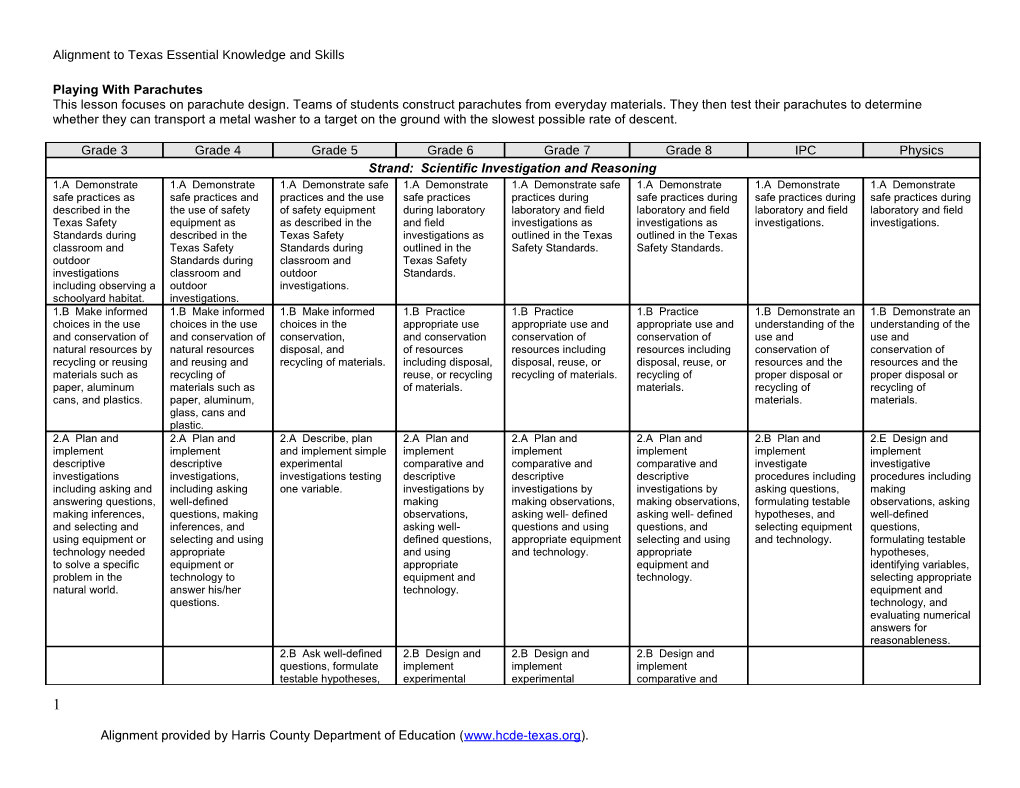
Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 IPC Physics Strand: Scientific Investigation and Reasoning 1.A Demonstrate 1.A Demonstrate 1.A Demonstrate safe 1.A Demonstrate 1.A Demonstrate safe 1.A Demonstrate 1.A Demonstrate 1.A Demonstrate safe practices as safe practices and practices and the use safe practices practices during safe practices during safe practices during safe practices during described in the the use of safety of safety equipment during laboratory laboratory and field laboratory and field laboratory and field laboratory and field Texas Safety equipment as as described in the and field investigations as investigations as investigations. investigations. Standards during described in the Texas Safety investigations as outlined in the Texas outlined in the Texas classroom and Texas Safety Standards during outlined in the Safety Standards. Safety Standards. outdoor Standards during classroom and Texas Safety investigations classroom and outdoor Standards. including observing a outdoor investigations. schoolyard habitat. investigations. 1.B Make informed 1.B Make informed 1.B Make informed 1.B Practice 1.B Practice 1.B Practice 1.B Demonstrate an 1.B Demonstrate an choices in the use choices in the use choices in the appropriate use appropriate use and appropriate use and understanding of the understanding of the and conservation of and conservation of conservation, and conservation conservation of conservation of use and use and natural resources by natural resources disposal, and of resources resources including resources including conservation of conservation of recycling or reusing and reusing and recycling of materials. including disposal, disposal, reuse, or disposal, reuse, or resources and the resources and the materials such as recycling of reuse, or recycling recycling of materials. recycling of proper disposal or proper disposal or paper, aluminum materials such as of materials. materials. recycling of recycling of cans, and plastics. paper, aluminum, materials. materials. glass, cans and plastic. 2.A Plan and 2.A Plan and 2.A Describe, plan 2.A Plan and 2.A Plan and 2.A Plan and 2.B Plan and 2.E Design and implement implement and implement simple implement implement implement implement implement descriptive descriptive experimental comparative and comparative and comparative and investigate investigative investigations investigations, investigations testing descriptive descriptive descriptive procedures including procedures including including asking and including asking one variable. investigations by investigations by investigations by asking questions, making answering questions, well-defined making making observations, making observations, formulating testable observations, asking making inferences, questions, making observations, asking well- defined asking well- defined hypotheses, and well-defined and selecting and inferences, and asking well- questions and using questions, and selecting equipment questions, using equipment or selecting and using defined questions, appropriate equipment selecting and using and technology. formulating testable technology needed appropriate and using and technology. appropriate hypotheses, to solve a specific equipment or appropriate equipment and identifying variables, problem in the technology to equipment and technology. selecting appropriate natural world. answer his/her technology. equipment and questions. technology, and evaluating numerical answers for reasonableness. 2.B Ask well-defined 2.B Design and 2.B Design and 2.B Design and questions, formulate implement implement implement testable hypotheses, experimental experimental comparative and 1
Alignment provided by Harris County Department of Education (www.hcde-texas.org). Alignment to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 IPC Physics and select and use investigations by investigations by experimental appropriate making making observations, investigations by equipment and observations, asking well-defined making observations, technology. asking well-defined questions, formulating asking well-defined questions, testable hypotheses, questions, formulating and using appropriate formulating testable testable equipment and hypotheses and hypotheses, and technology. selecting and using using appropriate appropriate equipment and equipment and technology. technology.
2.B Collect data by 2.B Collect and 2.C Collect 2.C Collect and 2.C Collect and 2.C Collect and 2.C Collect data 2.H Make observing and record data by information by record data using record data using the record data using the and make measurements with measuring using the observing and detailed observations the International International System International System measurements with accuracy and metric system and measuring, using and accurate System of Units of Units (SI) and of Units (SI) and precision. precision and record recognize the metric system, measuring. (SI) and qualitative qualitative means qualitative means data using scientific differences between and using means such as such as labeled such as labeled notation and observed and descriptive words labeled drawings, drawings, writing, and drawings, writing, International System measured data. and numerals, such writing, and graphic organizers. and graphic (SI) units. as labeled graphic organizers. organizers. drawings, writing, and concept maps. 2.C Construct maps, 2.C Construct 2.D Construct 2.D Construct tables 2.D Construct tables graphic organizers, simple tables, tables, using and graphs, using and graphs, using simple tables, charts, charts, bar graphs, repeated trials and repeated trials and repeated trials and and bar graphs using and maps using means to organize means to organize means, to organize tools and current tools and current data and identify data and identify data and identify technology to technology to patterns. patterns. patterns. organize, examine, organize, examine, and evaluate and evaluate data. measured data. 2.D Analyze and 2.D Analyze data 2.D Analyze and 2.E Analyze data 2.E Analyze data to 2.E Analyze data to 2.D Organize, 2.J Organize and interpret patterns in and interpret interpret information to formulate formulate reasonable formulate reasonable analyze, evaluate, evaluate data and data to construct patterns to to construct reasonable explanations, explanations, make inferences, make inferences reasonable construct reasonable explanations, communicate valid communicate valid and predict trends from data including explanations based reasonable explanations from communicate valid conclusions supported conclusions from data. the use of tables, on evidence from explanations from direct (observable) conclusions by the data, and supported by the charts, and graphs. investigations. data that can be and indirect (inferred) supported by the predict trends. data, and predict observed and evidence. data, and predict trends. measured. trends. 2.E Demonstrate 2.E Perform 2.E Demonstrate that that repeated repeated repeated investigations may investigations to investigations may increase the increase the increase the reliability reliability of results. reliability of results. of results. 2.F Communicate 2.F Communicate 2.F Communicate 2.E Communicate 2.K Communicate valid conclusions valid, oral and valid conclusions in valid conclusions. valid conclusions
2 Alignment to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 IPC Physics supported by data in written results both written and supported by the writing, by drawing supported by data. verbal forms. data through various pictures, and through methods such as lab verbal discussion. reports, labeled drawings, graphic organizers, journals, summaries, oral reports, and technology-based reports. 3.B Use models to 3.B Use models to 3.B Use models to represent aspects represent aspects of represent aspects of of the natural world the natural world such the natural world such as a model of as human body such as an atom, a Earth’s layers. systems, and plant molecule, space or a and animal cells. geologic feature.
3.D Connect grade 3.D Connect 3.D Connect grade- 3.D Relate the 3.D Relate the impact 3.D Relate the 3.D Evaluate the 3.D Explain the level appropriate grade-level level appropriate impact of research of research on impact of research impact of research impacts of the science concepts appropriate science science concepts with on scientific scientific thought and on scientific thought on scientific thought, scientific with the history of concepts with the the history of science, thought and society, including and society including society, and the contributions of a science, science history of science, science careers, and society including history of science and the history of science environment. variety of historical careers and science careers, contributions of the history of contributions of and contributions of and contemporary contributions of and contributions of scientists. science and scientists as related to scientists as related scientists on scientists. scientists. contributions of the content. to the content. scientific thought and scientists as society. related to the content. 3.E Describe 3.E Research and connections describe the between physics connections between and chemistry and physics and future future careers. careers. Strand: Matter and Energy 5.A Measure, test, 5.A Measure, 6.C Analyze and record physical compare, and physical and properties of matter contrast physical chemical properties including properties of matter of elements and temperature, mass, including size, compounds such as, magnetism, and the mass, volume, color, density, ability to sink or float. states (solid, liquid, viscosity, buoyancy, gas), temperature, boiling point, magnetism, and the freezing point, ability to sink or conductivity, and float. reactivity. Strand: Force, Motion and Energy 3
Alignment provided by Harris County Department of Education (www.hcde-texas.org). Alignment to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 IPC Physics 6.A Explore different 6.A Differentiate 6.A Explore the uses 8.A Compare and 6.A Demonstrate 4.A Describe and 4.B Describe and forms of energy among forms of of energy including contrast potential and calculate how calculate an object’s analyze motion in including energy including mechanical, light, and kinetic energy. unbalanced forces motion in terms of one dimension using mechanical, light, mechanical, sound, thermal, electrical, change the speed or position, equations with the sound, and electrical, light, and and sound energy. direction of an displacement, speed concepts of distance, heat/thermal in heat/thermal. object's motion. and acceleration. displacement, everyday life. speed, average velocity, instantaneous velocity, and acceleration. 6.B Demonstrate 6.D Design an 6.D Design an 8.B Identify and 6.B Differentiate 4.B Measure and 4.D Calculate the and observe how experiment to test experiment that tests describe the between speed, graph distance and effect of forces on position and motion the effect of force the effect of force on changes in velocity and speed as a function objects including the can be changed by on an object such an object. position, direction, acceleration. of time using moving law of inertia, the pushing and pulling as a push or a pull, and speed of an toys. relationship between objects to show work gravity, friction, or object when acted force and being done such as magnetism. upon by acceleration, and the swings, balls, unbalanced forces. nature of force pairs pulleys, and wagons. between objects. 6.C Observe forces 8.C Calculate 6.C Investigate and 4.C Investigate how 6.B Investigate such as magnetism average speed describe applications an object’s motion examples of kinetic and gravity acting on using distance and of Newton’s law of changes only when and potential energy objects. time inertia, law of force a net force is and their measurements. and acceleration and applied, including transformations. law of action- activities and reaction, such as in equipment such as vehicle restraints, toy cars, vehicle sports activities, restraints, sports amusement park activities and rides, Earth’s classroom objects. tectonic activities, and rocket launches. 8.D Measure and 4.D Assess the graph changes in relationship between motion. force, mass and acceleration, noting the relationship is independent of the nature of the force, using equipment such as dynamic carts, moving toys, vehicles and falling objects. 5.A Recognize and demonstrate that objects and
4 Alignment to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 IPC Physics substances in motion have kinetic energy such as vibration of atoms, water flowing down a stream moving pebbles, and bowling balls knocking down pins. 5.B Demonstrate common forms of potential energy including gravitational, elastic, and chemical, such as a ball on an inclined plane, springs and batteries.
5
Alignment provided by Harris County Department of Education (www.hcde-texas.org).