The Spread of Human Civilizations: The Great River Valleys
OVERVIEW 3.1 Population Growth and Cultural Divergence: 5000 B.C.E. – 2500 B.C.E.
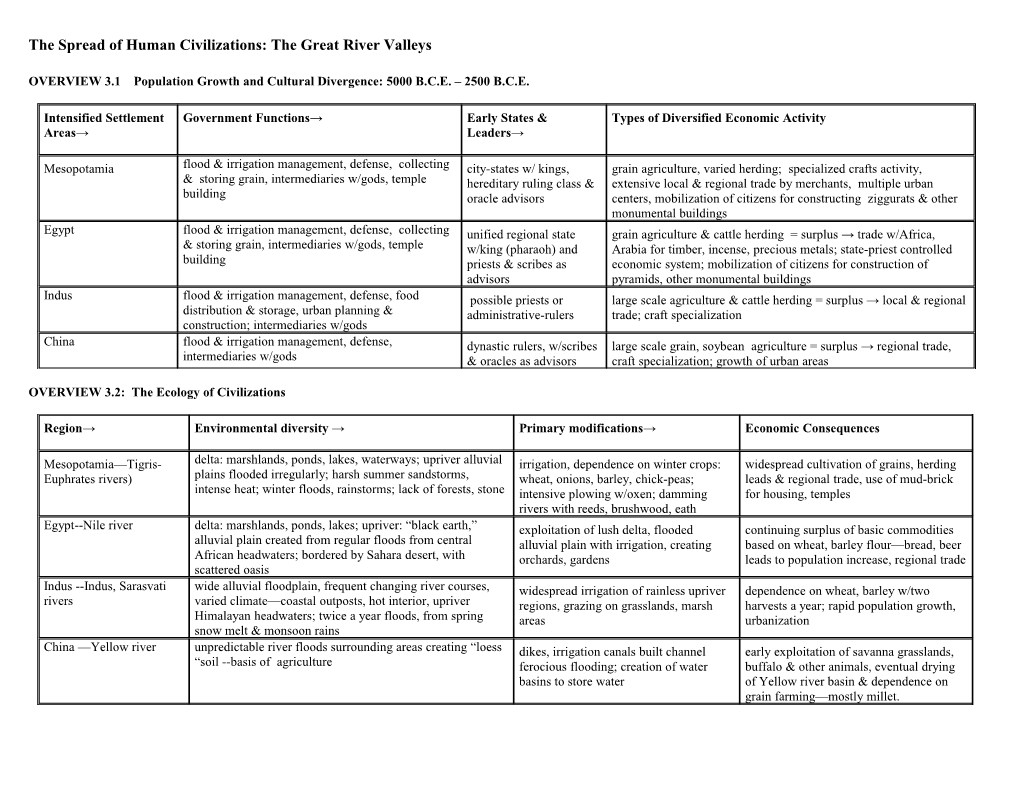
Intensified Settlement Government Functions→ Early States & Types of Diversified Economic Activity Areas→ Leaders→
Mesopotamia flood & irrigation management, defense, collecting city-states w/ kings, grain agriculture, varied herding; specialized crafts activity, & storing grain, intermediaries w/gods, temple hereditary ruling class & extensive local & regional trade by merchants, multiple urban building oracle advisors centers, mobilization of citizens for constructing ziggurats & other monumental buildings Egypt flood & irrigation management, defense, collecting unified regional state grain agriculture & cattle herding = surplus → trade w/Africa, & storing grain, intermediaries w/gods, temple w/king (pharaoh) and Arabia for timber, incense, precious metals; state-priest controlled building priests & scribes as economic system; mobilization of citizens for construction of advisors pyramids, other monumental buildings Indus flood & irrigation management, defense, food possible priests or large scale agriculture & cattle herding = surplus → local & regional distribution & storage, urban planning & administrative-rulers trade; craft specialization construction; intermediaries w/gods China flood & irrigation management, defense, dynastic rulers, w/scribes large scale grain, soybean agriculture = surplus → regional trade, intermediaries w/gods & oracles as advisors craft specialization; growth of urban areas
OVERVIEW 3.2: The Ecology of Civilizations
Region→ Environmental diversity → Primary modifications→ Economic Consequences
Mesopotamia—Tigris- delta: marshlands, ponds, lakes, waterways; upriver alluvial irrigation, dependence on winter crops: widespread cultivation of grains, herding Euphrates rivers) plains flooded irregularly; harsh summer sandstorms, wheat, onions, barley, chick-peas; leads & regional trade, use of mud-brick intense heat; winter floods, rainstorms; lack of forests, stone intensive plowing w/oxen; damming for housing, temples rivers with reeds, brushwood, eath Egypt--Nile river delta: marshlands, ponds, lakes; upriver: “black earth,” exploitation of lush delta, flooded continuing surplus of basic commodities alluvial plain created from regular floods from central alluvial plain with irrigation, creating based on wheat, barley flour—bread, beer African headwaters; bordered by Sahara desert, with orchards, gardens leads to population increase, regional trade scattered oasis Indus --Indus, Sarasvati wide alluvial floodplain, frequent changing river courses, widespread irrigation of rainless upriver dependence on wheat, barley w/two rivers varied climate—coastal outposts, hot interior, upriver regions, grazing on grasslands, marsh harvests a year; rapid population growth, Himalayan headwaters; twice a year floods, from spring areas urbanization snow melt & monsoon rains China —Yellow river unpredictable river floods surrounding areas creating “loess dikes, irrigation canals built channel early exploitation of savanna grasslands, “soil --basis of agriculture ferocious flooding; creation of water buffalo & other animals, eventual drying basins to store water of Yellow river basin & dependence on grain farming—mostly millet. OVERVIEW 3.3: Politics and State Power in River Valley Societies
State Leader & Symbolic Role Method of Unification Ruler’s Means of Control Egypt state Pharaoh (herdsman) sometimes organizing labor to manage floods; distributing Pharaoh’s commands, policies function as function as god food; use of Nile river as highway to unify, law, regarded as divine control Mesopotamia city Kings/Royal magicians emulate organizing labor; distributing food; competition earliest law codes; rituals performed by states gods with other city-states oracles guide decisionmaking Chinese state (starting Emperor/engineer, builder, organizing dike-building, irrigation, use of Yellow Ritual divination using oracle bones— with Shang dynasty) hunter river as highway to unify, control foretelling future, interpreting will of spirits Indus Civilization uncertain if singular ruler or harnessing river, irrigation; distributing food; unknown; widespread standardization of priest dominated ruling class engineering & construction of complex urban measurements, trade point to coordination, systems leadership