7th Grade Mastery Learning Document: Natural Selection
Major Beginner Partially Proficient Proficient Advanced Concept
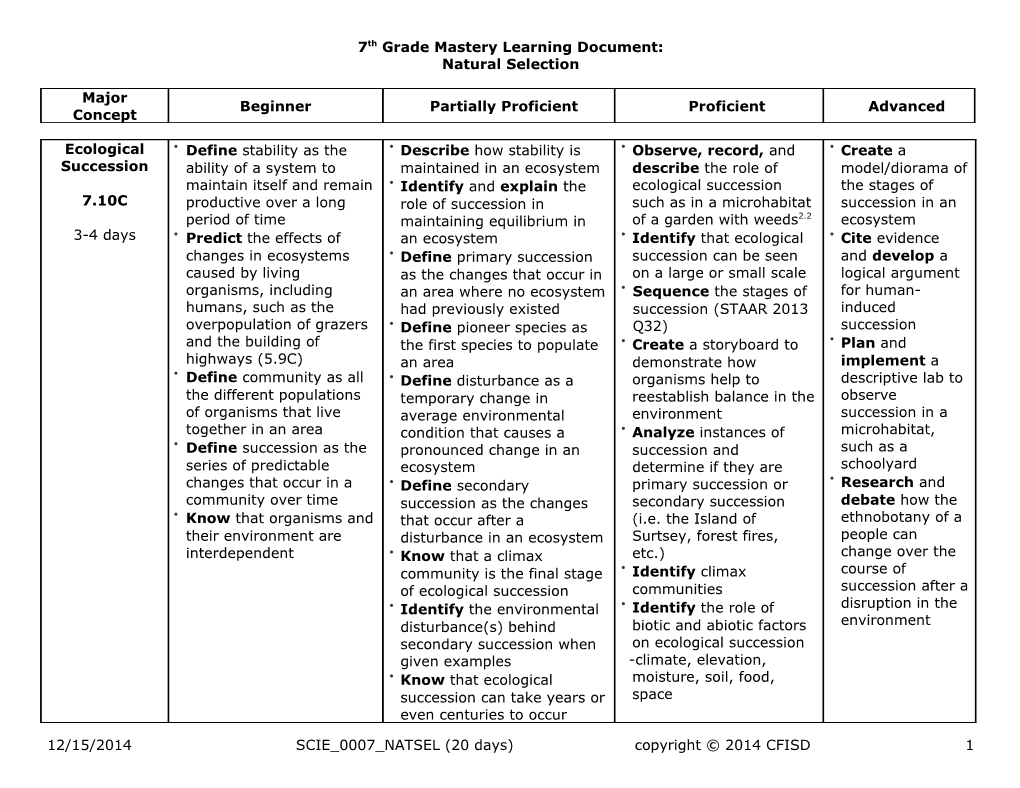
Ecological Define stability as the Describe how stability is Observe, record, and Create a Succession ability of a system to maintained in an ecosystem describe the role of model/diorama of maintain itself and remain Identify and explain the ecological succession the stages of 7.10C productive over a long role of succession in such as in a microhabitat succession in an period of time maintaining equilibrium in of a garden with weeds2.2 ecosystem 3-4 days Predict the effects of an ecosystem Identify that ecological Cite evidence changes in ecosystems Define primary succession succession can be seen and develop a caused by living as the changes that occur in on a large or small scale logical argument organisms, including an area where no ecosystem Sequence the stages of for human- humans, such as the had previously existed succession (STAAR 2013 induced overpopulation of grazers Define pioneer species as Q32) succession and the building of the first species to populate Create a storyboard to Plan and highways (5.9C) an area demonstrate how implement a Define community as all Define disturbance as a organisms help to descriptive lab to the different populations temporary change in reestablish balance in the observe of organisms that live average environmental environment succession in a together in an area condition that causes a Analyze instances of microhabitat, Define succession as the pronounced change in an succession and such as a series of predictable ecosystem determine if they are schoolyard changes that occur in a Define secondary primary succession or Research and community over time succession as the changes secondary succession debate how the Know that organisms and that occur after a (i.e. the Island of ethnobotany of a their environment are disturbance in an ecosystem Surtsey, forest fires, people can interdependent Know that a climax etc.) change over the community is the final stage Identify climax course of of ecological succession communities succession after a Identify the environmental Identify the role of disruption in the disturbance(s) behind biotic and abiotic factors environment secondary succession when on ecological succession given examples -climate, elevation, Know that ecological moisture, soil, food, succession can take years or space even centuries to occur
12/15/2014 SCIE_0007_NATSEL (20 days) copyright © 2014 CFISD 1 7th Grade Mastery Learning Document: Natural Selection
Major Beginner Partially Proficient Proficient Advanced Concept
Explore how structures Define variation as a Explain variation within Investigate and and functions of plants difference among individuals a population or species develop a and animals allow them to of the same species by comparing external regional map survive in a particular Define physiology as the features, behaviors, or depicting the environment (3.10A) way an organism’s parts or physiology that enhance variation among Compare the structures processes function together survival, including, not different and functions of different limited to: populations of a species that help them External features: given species live and survive (5.10A) animal examples: Research and Define genetic trait as a appendages, mouth create a Venn characteristic that an structures, and/or diagram on the organism can pass on to camouflage difference its offspring through its plant examples: between species Variation and genes roots, leaves, fruits, and breeds Changes in Define heredity as the and/or flowers Research and Genetic Traits passage of genetic Behaviors: create a story instructions from one Migration, hibernation board on how 7.11B, 7.11C generation to the next and other survival mutations can generation (7.14A) strategies used by cause genetic 6-8 days 2.4 Know that genetic organisms variation within a material is found in genes Physiology: population within chromosomes in a storage of food in a cell (7.14C) bulb, seed dispersal Compare results of and/or fruiting plants offspring from sexual and Investigate variation in asexual reproduction a population of similar (7.14B) organisms and consider how this may lead to some individuals being better adapted to their environment (Explore 12/15/2014 SCIE_0007_NATSEL (20 days) copyright © 2014 CFISD 2 7th Grade Mastery Learning Document: Natural Selection
Major Beginner Partially Proficient Proficient Advanced Concept
Learning: “Rainfall and Bird Beaks”; STAAR 2014 Q7) Model and explain how genetic diversity can give some organisms added advantages leading to a greater chance of survival in certain catastrophic events and environments (7.3B) Relate adaptations that Variation and enhance survival given a Changes in description or image of a Genetic Traits specific environment
7.11B, 7.11C Understand that sexual Identify and explain Predict and (continued) Define species as any reproduction maintains or changes in genetic traits justify the group of organisms that increases diversity of a that have occurred over impact that 6-8 days can mate to reproduce species generations through environmental fertile offspring Define natural selection as natural selection within a stressors may Define population as a the process by which population and a species have on species group of individuals of the individuals that are adapted Explain that adaptations and populations same species living in a to their environment are enhance survival within a in the far future particular area more likely to survive and population or species Define adaptation as a reproduce than other (STAAR 2014 Q7) characteristic that helps members of the same Relate Darwin’s an organism survive in its species contributions to the environment and Know that natural selection understanding of natural reproduce affects multiple species selection(7.3D) Define theory as a simultaneously Analyze population data scientific explanation Know that natural selection for organisms over time supported by much affects a population not an and represent changes in evidence collected over a individual a trait with models 12/15/2014 SCIE_0007_NATSEL (20 days) copyright © 2014 CFISD 3 7th Grade Mastery Learning Document: Natural Selection
Major Beginner Partially Proficient Proficient Advanced Concept
long period of time Know how natural selection (Explore Learning affect species over time “Natural Selection”) Identify factors that are (7.2E) involved in natural selection (i.e. environmental changes (long or short-term), genetic variation, competition among organisms, etc.) Define reproductive “success” as organism passing its genes to the next generation
Define selective breeding as Know how selective Research the Know that organisms of the process of selecting a breeding affects species advancement of the same species are not few organisms with desired over time (STAAR 2013 creating hybrids Variation and always identical traits to serve as parents of Q1) organisms Changes in the next generation (STAAR Describe how humans Research and Genetic Traits 2013 Q1) used selective breeding create an Understand that to domesticate animals infographic 7.11B, 7.11C domestication is the process Identify and explain highlighting the (continued) of changing plants or changes in genetic traits success rate of animals to make them more that have occurred over captive breeding 6-8 days useful to humans (i.e. generations through of different selective breeding and/or selective breeding endangered train) Discuss the advantages species and disadvantages of selective breeding Identify the basic Explain how internal Investigate how Investigate the characteristics of structures of organisms are internal structures of internal Internal organisms, including adaptations that allow organisms have structures of Structures of prokaryotic or eukaryotic, specific functions such as adaptations that allow whales that allow Organisms unicellular or multicellular, gills in fish, hollow bones in specific functions such as them to adapt to autotrophic or birds, or xylem in plants gills in fish, hollow bones cold ocean water 12/15/2014 SCIE_0007_NATSEL (20 days) copyright © 2014 CFISD 4 7th Grade Mastery Learning Document: Natural Selection
Major Beginner Partially Proficient Proficient Advanced Concept
heterotrophic, and mode in birds, or xylem in Compare 7.12A, 6.12D of reproduction that plants structures in further classify them in plants from 1-2 days the currently organized various biomes Kingdoms (6.12D)(STAAR that allow them 2013 Q47) to adapt to a Know how internal and particular external structure is environment(i.e. related to function in desert plants vs. Internal organisms tundra plants) Structures of Observe internal Organisms structures of organisms 7.12A, 6.12D that allow them to survive (continued) in a particular environment given 1-2 days pictures of diagrams
Embryology, homologous structures, and vestigial structures will be covered in Limits and boundaries: Biology Biodiversity Define biodiversity as the Give examples of Understand that Research and number of different biodiversity in marine, populations of organisms invasive species Sustainability species in an area freshwater, and terrestrial live in a variety of and their effect Understand that ecosystems habitats, and change in on the ecosystem 7.10B biodiversity is often used Describe the importance of those habitats affects the Create a as a measure of the biodiversity in an ecosystem organisms living there4.4 campaign poster 5-7 days stability of an ecosystem (Explore Learning: “Food Describe how to promote Define sustainability of Chain”) biodiversity contributes biodiversity and an ecosystem as the Identify limiting factors in a to the sustainability of an conservation in ability to support, variety of ecosystems that ecosystem local maintain, or endure would restrict the growth of ecosystems4.5 Define limiting factor as a population Give examples in an abiotic or biotic factor Use collecting nets and which biodiversity that restricts the growth insect traps to collect data contributed to of a population 12/15/2014 SCIE_0007_NATSEL (20 days) copyright © 2014 CFISD 5 7th Grade Mastery Learning Document: Natural Selection
Major Beginner Partially Proficient Proficient Advanced Concept
about the biodiversity in a the sustainability particular area(7.4B) of an ecosystem in a biome
12/15/2014 SCIE_0007_NATSEL (20 days) copyright © 2014 CFISD 6 7th Grade Mastery Learning Document: Natural Selection
Resilient Planet Curricula 7th Grade Science Required JASON Lessons
Mission Lesson Lesson Name Overview
Students will meet Bob Ballard and begin understanding ecological succession. Hook Article: Securing a Niche pg 30 Securing a 2 Mission Briefing Video (2:17) Niche Mission Briefing Article: Ecological Succession pgs 30-31 2 Lab 1: Competing Adaptations pg 32
Students will explore survival strategies used by ocean organisms. Survival 4 Diagram: Survival Strategies pgs 38-39 Strategies Activity: Critical Thinking Activity pg 38 (TE)
Students will explore the effects of geography on biodiversity to understand its importance to ecology. Geography and Reading: Geography and Biodiversity pg 78 4 4 Biodiversity Reading: "Islands" of Life pgs 79 - 80 Lab 3: Field Trip to an Island pg 81
MLD statements covered by the required JASON lessons are referenced with decimal number such as 2.3. The first number refers to the JASON expedition and the second to the expedition lesson. Teachers can add additional activities from the JASON Terminal Velocity to supplement the required lessons. Teachers can add additional activities from the JASON Resilient Planet Curricula to supplement the required lessons. (8th grade will teach Mission 2: Lesson 3 and 5, Mission 3: Lesson 1- 3 and Mission 4: Lesson 1 in their ECOSYSTEM unit) *7E Lesson: SCIE_0007_NATSEL_LES_7.11CADAPT_AL incorporates required lesson 4 over TEKS 7.11B/C into a 7E lesson format. **7E Lesson: SCIE_0007_NATSEL_LES_7.10BBIODIV_AL incorporates required lesson 4 over TEKS 7.10B into a 7E lesson format.
12/15/2014 SCIE_0007_NATSEL (20 days) copyright © 2014 CFISD 7