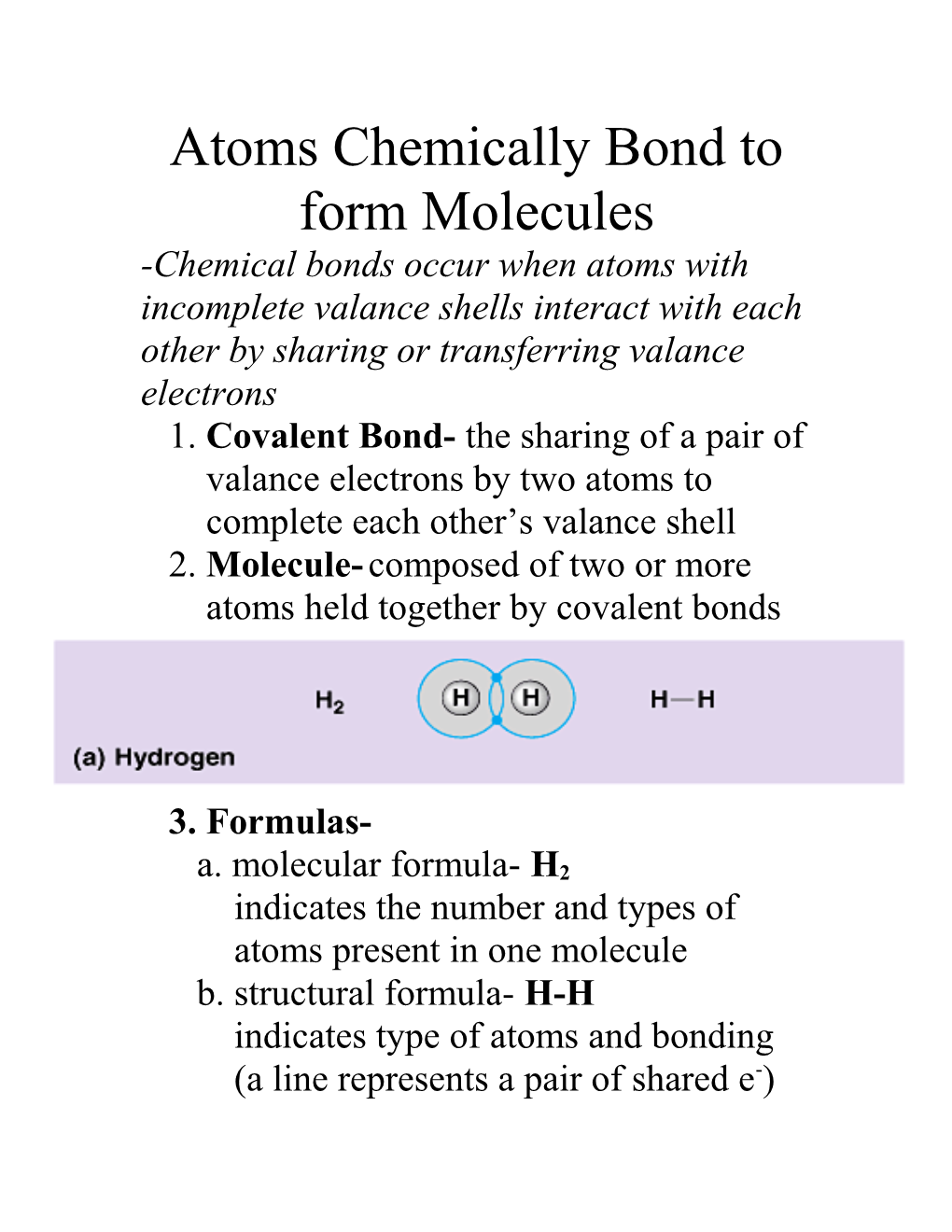
Atoms Chemically Bond to form Molecules -Chemical bonds occur when atoms with incomplete valance shells interact with each other by sharing or transferring valance electrons 1. Covalent Bond- the sharing of a pair of valance electrons by two atoms to complete each other’s valance shell 2. Molecule- composed of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
3. Formulas- a. molecular formula- H2 indicates the number and types of atoms present in one molecule b. structural formula- H-H indicates type of atoms and bonding (a line represents a pair of shared e-) 4. Double Covalent Bond-the sharing of two electron pairs between two atoms
5. Valence- total # of covalent bonds that an atom characteristically forms ex. Hydrogen =1 Oxygen = 2 Nitrogen = 3 Carbon = 4 Phosphorus = 5 (Should have a valence of 3 based on the three unpaired electrons, but it forms 3 single covalent bonds and one double bond) 6. Compound- atoms of different elements bound by covalent bonds 7. Electronegativity- the attraction of an atom for the electrons of a covalent bond a. strongly electronegative atoms pull the shared electrons toward themselves b. nonpolar covalent bond- equal sharing of electrons in a covalent bond 1. covalent bonds between atoms with similar electronegativities are nonpolar c. polar covalent bond- electrons not shared equally by the atoms in a covalent bond ex. H2O Oxygen has a stronger electronegativity and the electrons are closer to it, therefore, it has a partial negative charge. Hydrogen has weak electronegativity, so the electrons are less near, therefore, it has a partial positive charge 8. Ionic Bond- form when the electronegativity of two atoms is very unequal and one atom strips an electron completely away from the other. a. after the transfer of electrons, both atom are no longer neutral, but have charges and are called Ions 1. Cations- atoms with positive charges 2. Anions- atoms with negastive charges b. because of the difference in charge, cations and anions are attracted and form ionic bonds c. salts- compounds formed by ionic bonding 1. the formula for an ionic compound indicates the ratio of elements in a crystal of that salt. ex. NaCl 9. Hydrogen Bond- weak electrostatic bond a. Formed between an H atom that is already covalently bonded to a strongly electronegative atom and is attracted to another strongly electronegative atom. b. Usually occur with N & C c. Common in polar covalent situations d. The partially + charged H is attracted to – charged atoms, molecules, or regions Areas with opposite charges are attracted. 10. van der Waals interactions- weak electrostatic bonds a. created as a result of random, ever- changing areas of charge differences due to electron motion -Collectively, weak bonds have strength