Math Pacing Guide for Fourth Grade 2012-2013 Course: 4th grade 3rd Nine Weeks(47days)
Grade TNCore Focus Standards Extend understanding of fraction equivalence and ordering 4th Grade Build fractions from unit fractions by applying and extending previous understanding of operations on whole numbers
Unit/Theme: Data – Line Plots Estimated Time: 1 week
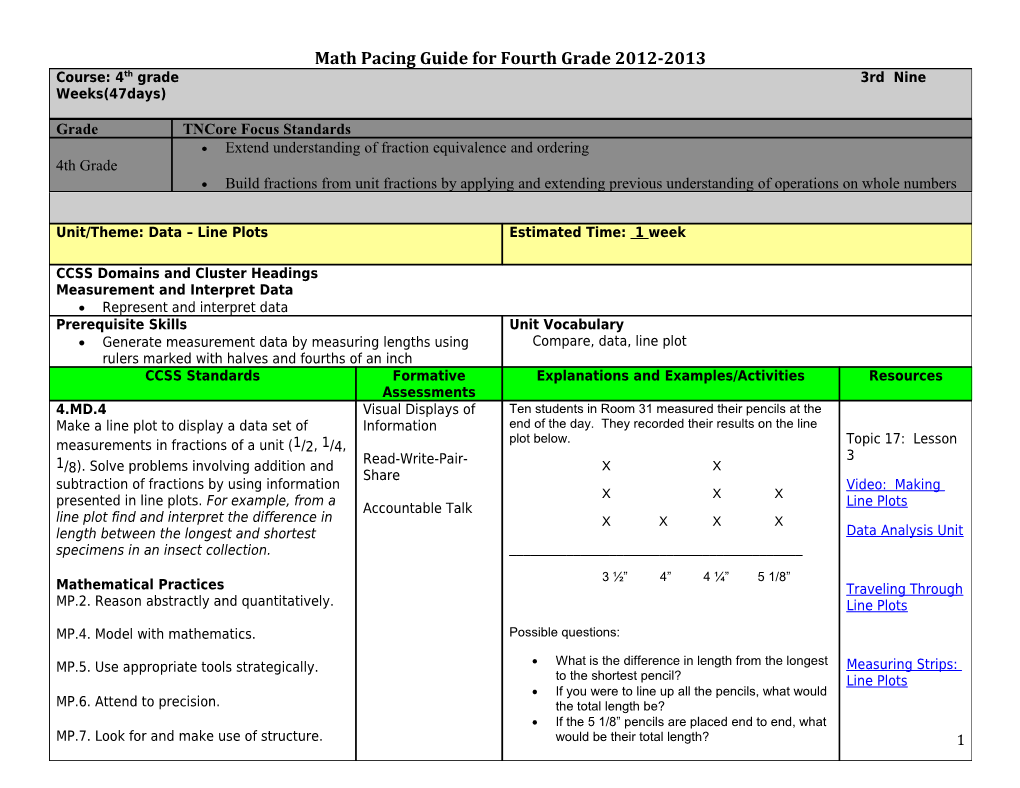
CCSS Domains and Cluster Headings Measurement and Interpret Data Represent and interpret data Prerequisite Skills Unit Vocabulary Generate measurement data by measuring lengths using Compare, data, line plot rulers marked with halves and fourths of an inch CCSS Standards Formative Explanations and Examples/Activities Resources Assessments 4.MD.4 Visual Displays of Ten students in Room 31 measured their pencils at the Make a line plot to display a data set of Information end of the day. They recorded their results on the line plot below. Topic 17: Lesson measurements in fractions of a unit (1/2, 1/4, Read-Write-Pair- 3 1/8). Solve problems involving addition and X X Share subtraction of fractions by using information Video: Making X X X presented in line plots. For example, from a Line Plots Accountable Talk line plot find and interpret the difference in X X X X length between the longest and shortest Data Analysis Unit specimens in an insect collection. ______3 ½” 4” 4 ¼” 5 1/8” Mathematical Practices Traveling Through MP.2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Line Plots
MP.4. Model with mathematics. Possible questions:
MP.5. Use appropriate tools strategically. What is the difference in length from the longest Measuring Strips: to the shortest pencil? Line Plots If you were to line up all the pencils, what would MP.6. Attend to precision. the total length be? If the 5 1/8” pencils are placed end to end, what MP.7. Look for and make use of structure. would be their total length? 1 Math Pacing Guide for Fourth Grade 2012-2013
2 Math Pacing Guide for Fourth Grade 2012-2013
Unit/Theme: Measurement - Conversions Estimated Time: 2 weeks
CCSS Domains and Cluster Headings Measurement and Data Solve problems involving measurement and conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit Prerequisite Skills Unit Vocabulary Know units of measurement: km, m, c; kg, g; lb, oz; hr, Capacity, centimeter, cup, customary system, foot, gallon, gram, min, sec inch, kilogram, kilometer, liter, mass, meter, metric system, mile, milliliter, millimeter, minute, ounce, pint, quart, second, weight CCSS Standards Formative Explanations and Examples/Activities Resources Assessments 4.MD.1 The units of measure that have not been addressed in prior Know relative sizes of measurement Visual Display of years are pounds, ounces, kilometers, milliliters, and seconds. Students’ prior experiences were limited to measuring length, Topic 16: units within one system of units Information mass, liquid volume, and elapsed time. Students did not including km, m, cm; kg, g; lb, oz.; l, convert measurements. Students need ample opportunities to Lessons 1- 10 ml; hr, min, sec. Within a single Accountable Talk become familiar with these new units of measure. system of measurement, express Students may use a two-column chart to convert from larger to Video: Metric measurements in a larger unit in Place Value Line-Up smaller units and record equivalent measurements. They Conversions terms of a smaller unit. Record make statements such as, if one foot is 12 inches, then 3 feet measurement equivalents in a two- Hand Signals has to be 36 inches because there are 3 groups of 12. Conversion Word column table. For example, know that Problems 1 ft is 12 times as long as 1 in. kg g ft in lb oz Express the length of a 4 ft snake as Measurement 48 in. Generate a conversion table for 1 1000 1 12 1 16 Concentration feet and inches listing the number 2 2000 2 24 2 32 pairs (1, 12), (2, 24), (3, 36) Metric 3 3000 3 36 3 48 Relationships Mathematical Practices Capacity Creature MP.2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
MP.5. Use appropriate tools strategically.
MP.6. Attend to precision
3 Unit/Theme: Geometry Estimated Time: 5 weeks
CCSS Domains and Cluster Headings Geometry Math Pacing Guide for Fourth Grade 2012-2013 Draw and Identify lines and angles and classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles. Measurement Solve problems involving measurement and conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit Geometric measurement: understand concepts of angel and measure angles Prerequisite Skills Unit Vocabulary Classify 2-D & 3-D shapes by their attributes Acute angle, angle, angle measure, arc, congruent, degree (angle Convert measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit measure), endpoint, intersecting lines, line of symmetry, line segment, line symmetric figures, obtuse angle, parallel line, perpendicular lines, plane figure, point, protractor, right angle, right triangle CCSS Standards Formative Explanations and Examples/Activities Resources Assessments Examples of points, line segments, lines, angles, enVision 4.G.1 Visual Display of parallelism, and perpendicularity can be seen daily. Draw points, lines, line segments, Information Students do not easily identify lines and rays because 9-1, 9-2 rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), they are more abstract. and perpendicular and parallel lines. Right angle Identify these in two-dimensional http://www.learnin figures. gwave.com/lwonli Acute angle ne/geometry_secti Mathematical Practices on1/lessons/lines1 MP.5. Use appropriate tools strategically. .html
MP.6. Attend to precision. Obtuse angle Geoboard Line Segments
Angles on the Geoboard
Straight angle
4 Math Pacing Guide for Fourth Grade 2012-2013
5 Math Pacing Guide for Fourth Grade 2012-2013
Unit/Theme: Measurement – Area & Perimeter Estimated Time: 1 week & 2 days
CCSS Domains and Cluster Headings Measurement and Data Solve problems involving measurement and conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit Prerequisite Skills Unit Vocabulary Recognize and understand area/perimeter area, area model, perimeter Know square unit CCSS Standards Formative Explanations and Examples/Activities Resources Assessments 4.MD.3 Students developed understanding of area and Apply the area and perimeter Visual Display of perimeter in 3rd grade by using visual models. formulas for rectangles in real world Information Topic 14: Lessons and mathematical problems. For 1-3 example, find the width of a Accountable Talk While students are expected to use formulas to calculate Lessons 6-8 rectangular room given the area of area and perimeter of rectangles, they need to the flooring and the length, by Place Value Line-Up understand and be able to communicate their Study Jams: understanding of why the formulas work. viewing the area formula as a Perimeter multiplication equation with an Hand Signals unknown factor Video: Exploring The formula for area is I x w and the answer will always Area Mathematical Practices be in square units. MP.2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Area and Perimeter Unit MP.4. Model with mathematics. The formula for perimeter can be 2 l + 2 w or 2 (l + w) Inside, Outside, MP.5. Use appropriate tools strategically. and the answer will be in linear units. and All Around (Lessons 1 & 2) MP.6. Attend to precision.
MP.7. Look for and make use of structure.
Aizona Department of Education: Standards and Assessment Division o Explanation and Examples Update 5/20/11
6