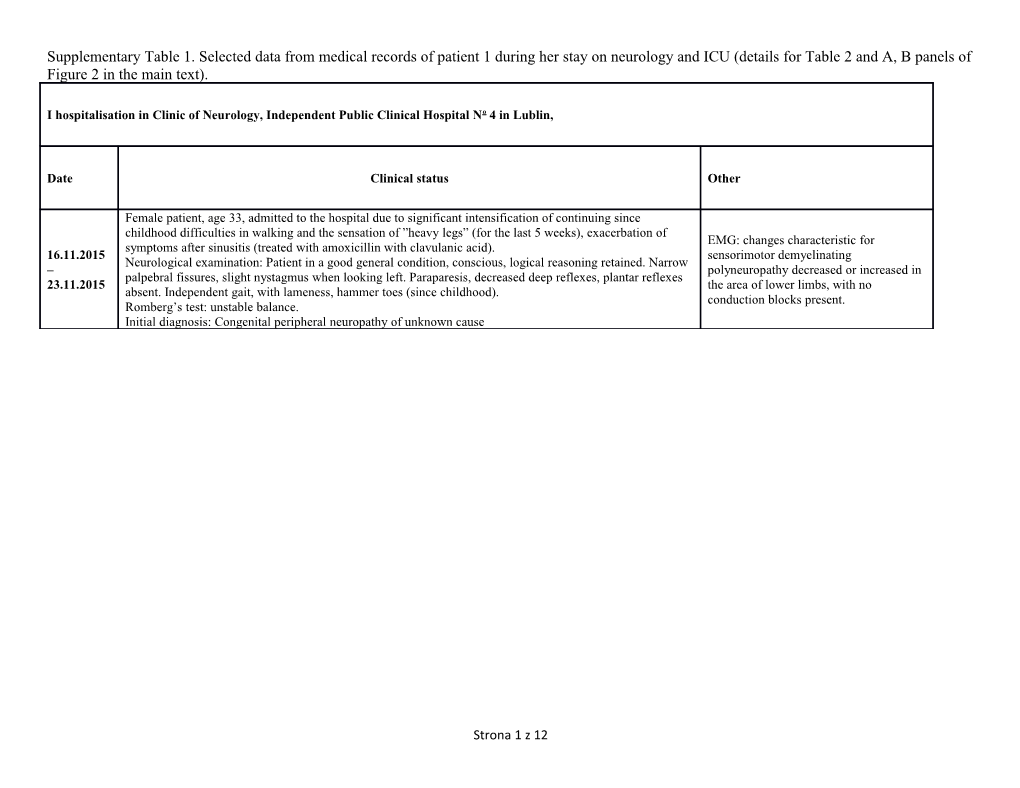
Supplementary Table 1. Selected data from medical records of patient 1 during her stay on neurology and ICU (details for Table 2 and A, B panels of Figure 2 in the main text).
I hospitalisation in Clinic of Neurology, Independent Public Clinical Hospital No 4 in Lublin,
Date Clinical status Other
Female patient, age 33, admitted to the hospital due to significant intensification of continuing since childhood difficulties in walking and the sensation of ”heavy legs” (for the last 5 weeks), exacerbation of EMG: changes characteristic for symptoms after sinusitis (treated with amoxicillin with clavulanic acid). 16.11.2015 sensorimotor demyelinating Neurological examination: Patient in a good general condition, conscious, logical reasoning retained. Narrow – polyneuropathy decreased or increased in palpebral fissures, slight nystagmus when looking left. Paraparesis, decreased deep reflexes, plantar reflexes 23.11.2015 the area of lower limbs, with no absent. Independent gait, with lameness, hammer toes (since childhood). conduction blocks present. Romberg’s test: unstable balance. Initial diagnosis: Congenital peripheral neuropathy of unknown cause
Strona 1 z 12 II hospitalization in Clinic of Neurology, Independent Public Clinical Hospital No 4 in Lublin, 06.12.2015–16.12.2015
Type of acid-base Day of profile; hospitalization; interpretation Acid-base data Clinical status Other results, treatment time of blood (see point number sampling on Figure 1A/B) Female patient admitted to the hospital due to an attack of dyspnoea, weakness, ptosis, continued since the 1 day day before (06.12.2015) admission. Directed to the Clinic of Neurology in Lublin with the diagnosis of the myasthenic syndrome. Temperature up to troponin I: 0.024 ng/ml 37.4°C, this day pH = 7.59 EMG (7.12.2015): incorrect result of the 1. only. pCO = 11.2 mmHg electrical stimulation muscle weakness test, acute > chronic 2. day 2 Spontaneously HCO = 10.4 mmol/L pO = 148.4 mmHg disorders of the postsynaptic nature. Slight respiratory (7.12.2015) 3 2 breathing patient BE (ecf) = 11.3 mmol/L degree of deviations did not, however, alkalosis) with oxygen explain existing breathing disturbances and therapy (FiO = 2 the general clinical condition of the patient. 0.35). 3 day (08.12.2015) Supratentorial, leukocytosis: 19.59 K/uL weakly isolated, symmetric areas of Brain MR (8.12.2015): inconclusive image, elevated signals on changes in pons and medulla oblongata T2-weighted might suggest: Leigh syndrome, ADEM images located (Acute Demyelinating Encephalomyelitis), entrally and in the inflammatory. posterior of the midbrain, in the peripheral part of the pons and centrally and slightly more peripherally in
Strona 2 z 12 medulla oblongata. After administration of the gadolinium- based contrast, discreet post- contrast enhancement in areas of increased signal intensity in medulla oblongata. 4 day (09.12.2015) lactic acid = 2.0 mmol/L Shallow breath. Until now mobile (walked poorly), 5 day 10.12.2015 have used the leukocytosis: 21.53 K/uL wheelchair. Talked, reported dyspnoea. 2. Time: 17:13 pH = 7.35 2. pCO2 = 25.2 mmHg Significant HCO = 13.6 mmol/L deterioration in the 3. 3 pO2 = 83 mmHg patient’s condition. BE (ecf) = 12 mmol/L Increased dyspnoea. troponin I: 0.462 ng/ml (compensation: 6 day 11.12.2015 Spontaneously Time 17:04 increased HCO , 3 3. Time: 23:12 breathing patient troponin I: 2.53 ng/ml decreased pH = 7.33 with oxygen hyperventilation, pCO = 38.3 mmHg therapy (FiO 0.35 no metabolic 2 2 HCO = 19.7 mmol/L to 0.45). acidosis) 3 pO2 = 148.4 mmHg BE(ecf) = 11.3 mmol/L
Strona 3 z 12 From 12 noon to 4 p.m. temperature up to 38.9°C. Unconscious,
tachycardia, SpO2 87–94%. CT: pulmonary embolism excluded. Increased left atrium and left heart ventricle. 4. Time: 09:25 Pulmonary pH = 7.45 oedema/alveolar pCO = 39.6 mmHg 2 haemorrhage. HCO = 27 mmol/L 4. 3 Massive left lung troponin I: 5.168 ng/ml pO = 61.1 mmHg 5. 2 parenchymal troponin I: 3.6 ng/ml BE(ecf) = 3 mmol/L (compensation densities of NT-proBNP: 11550 pg/ml 7 day 12.12.2015 continued, inflammatory CRP: 43.385 mg/l metabolic nature, ground glass WBC: 40 K/uL 4. Time: 19:44 adaptation) opacities, procalcitonin: 0.38 ng/ml pH = 7.49 supradiaphragmatic pCO = 37 mmHg 2 and in the right lung HCO = 27.8 mmol/L 3 apex. pO = 210.4 mmHg 2 Time 14:10: BE(ecf) = 4.5 mmol/L INTUBATED, mechanical ventilation applied. DIAGNOSIS: PNEUMONIA CIRCULATORY FAILURE PULMONARY OEDEMA
Intubated, WBC: 22.04 K/uL mechanical 8 day 13.12.2015 D-dimer: 1662 ng/ml ventilation CRP: 23.905 mg/l applied. pH = 7.54 WBC: 12.06 K/uL pCO = 37.5 mmHg 2 Intubated, D-dimer: 1398 ng/ml HCO = 31.3 mmol/L 3 mechanical CK: 278 U/L >> 209 U/L 6. 9 day 14.12.2015 pO = 228.1 mmHg 2 ventilation CK-MB: 20.1 U/L >> 15.9 U/L BE(ecf)= 8.7 mmol/L applied. troponin I: 0.487 ng/ml lactic acid: 2.2 mmol/L (19.8 mg/dl) Metabolic alkalosis Strona 4 z 12 Lab tests: CK: 141 U/L pH = 7.50 troponin I: 0.206 ng/ml pCO = 39 mmHg 2 NT- proBNP: 334.6 pg/ml HCO = 29.9 mmol/L 3 Intubated, EEG: 10 day 15.12.2015 pO = 158.5 mmHg 2 mechanical In the frontal-parietal-temporal lobe area, 7. (metabolic BE(ecf) = 6.8 mmol/L ventilation individual, series or groups of slow waves alkalosis) applied. (delta–theta: 1.5–2,4 Hz, amplitude: 60– 90–120 uV) standing out against the systolic activity. Echocardiography: within normal range. Intubated, pH = 7.52 11 day 16.12.2015 mechanical pCO = 37.6 mmHg (metabolic 2 ventilation WBC: 17.1 K/uL 8. HCO = 30.6 mmol/L alkalosis) 3 applied. lactic acid: 1.5 mmol/L (13.5 mg/dl) pO = 103.7 mmHg 2 Squeezes hand on BE(ecf) = 7.9 mmol/L request.
Strona 5 z 12 ICU, Independent Public Clinical Hospital No 4 in Lublin, 16.12.2015–16.02.2016
No Date Clinical status Other
Intubated, mechanical ventilation applied. On admittance, the patient conscious, basic verbal contact maintained.
Respiratory failure, intubated, mechanical ventilation applied, FiO2 = 0.35, PEEP = 5. No own respiratory drive??? 11 day, 16.12.2015 oxygen = 35% (metabolic alkalosis) Repeatable low grade fever, own diuresis efficient. Enteral nutrition. 1. Patient hemodynamically stable. (slightly too low Pupils equal and reactive to light. Ptosis. CO = 2–3 mmHg) 2 Quadriparesis especially pronounced in the area of lower limbs. SAPS II: 34; 15,3% APACHE II: 18; 29,1% SOFA: 4; <10% 12 day, 17.12.2015 (metabolic alkalosis) 1. Intubated, mechanical ventilation applied. (slightly too low CO2 = 2–3 mmHg)
13 day, 18.12.2015, 19:46 Intubated, mechanical ventilation applied. 2. Tracheotomy. Following the procedure patient ventilated in SIMV 35% (metabolic alkalosis) oxygen.
Patient critical but stable. Sedated but easy to wake. Contact possible to Dexdor (dexmedetomidine) 14 day, 19.12.2015, 15:19 establish. On request squeezes both hands, left hand weaker. Moves toes 2% Propofol (Diprivan) 3. of both lower limbs. Significant weakening of muscle strength visible. no amines Tracheostomy. Artificial lung ventilation in SIMV mode, no own (metabolic alkalosis) no antibiotics breathing. FiO2 = 0.5. Cardiovascular system stable.
Strona 6 z 12 15 day, 20.12.2015, 21:55 Patient sedated but contact possible to establish. Cardiovascularly stable. (respiratory alkalosis) Decrease respirator, weak 4. Ventilation mode changed into proportional assist ventilation (PAV), muscles??? with good tolerance. reducing ventilator support
Following reduction in sedation the patient conscious, but unwilling to establish contact. Auscultatory examination detects correct vesicular 16 day, 21.12.2015, 07:28 murmur. Patient ventilated in CPAP mode with PS and 35% oxygen in 5. ( respiratory acidosis - reducing respiratory mixture. Attempt at PAV unsuccessful, significant tachypnea ventilator support) and retention of CO2. Enteral nutrition, industrial diet. Temperature up to 38°C.
16 day, 21.12.2015, 15:16 6 (acute respiratory alkalosis) increasing ventilatory support
16 day, 21.12.2015, 22:42 (acute respiratory alkalosis) 7 – increased ventilatory support
Patient sedated, but contact possible to establish. Cardiovascularly stable. 17 day, 22.12.2015, 14:20 creatinine = 0.4 mg/dL 7. Patient ventilated in CPAP mode with PS and 35% oxygen in respiratory (acute respiratory alkalosis) urea = 32.4 mg/dl mixture, temperature: 38.2°C.
Patient sedated, but contact possible to establish. Tracheostomy. Patient 18 day, 23.12.2015, 15:18 7. ventilated in CPAP mode with PS and 35% oxygen in respiratory mixture. (acute respiratory alkalosis) Cardiovascularly stable. Abdomen soft, painless.
The patient’s condition seems to improve. Muscle strength improves. 19 day, 24.12.2015, 22:20 Today the patient respired in the automatic tube compensation (ATC) 7. (acute respiratory alkalosis) mode, with no retention of carbon dioxide. Conscious, limited sedation, reducing ventilator support enteral nutrition, industrial diet. Fever absent.
Strona 7 z 12 20 day, 25.12.2015, 14:52 Fever absent. In the morning patient weaned from respirator and 7. Acute respiratory alkalosis - maintained on passive oxygen therapy with a nasal cannula. spontaneously breathing patient
Conscious, limited sedation. Before noon infusion of sedatives terminated. 21 day, 26.12.2015 The patient breathes on her own via the tracheostomy with passive Normalization of blood gases - oxygen therapy. Moves her hands and legs, however muscle strength 8. spontaneously breathing patient weakening still noticeable. Abdomen soft, painless, peristalsis present. Efficient diuresis. Enteral nutrition, industrial diet. Temperature up to 38.1°C. No sedation, basic contact possible to maintain, pupils equal and reactive to light. The patient breathes on her own via the tracheostomy with passive 22 day, 27.12.2015, 07:37 oxygen therapy. Numerous rales above the lungs, considerable amounts of 3. (mild metabolic alkalosis= thin mucous secretion sucked off the bronchial tree. Cardiovascularly stable. Temporary tachycardia at a rate of 130 BPM. Betaloc (Metoprololi succinas) administered. Muscle strength weakening still noticeable.
22 day, 27.12.2015, 15:35 3. (metabolic alkalosis
No sedation, basic contact possible to maintain, pupils equal and reactive 23 day, 28.12.2015, 07:36 to light. Muscle strength weakening. The patient breathes on her own via (respiratory acidosis) the tracheostomy with passive oxygen therapy. Numerous rales above the 4. lungs, considerable amounts of thin mucous secretion sucked off the hypodynamic respiratory bronchial tree. Aflegan (Ambroxoli hydrochloridum) stopped. insufficiency Cardiovascularly stable. Temporary tachycardia at a rate of 130 BPM.
25 day, 30.12.2015, 07:54 29.12.2015 No sedation, the patient sleepy, breathes via the tracheostomy, Respiratory acidosis - CRP: 4.3 mg/l 9. cardiovascularly stable. Considerable amounts of mucous secretion sucked hypodynamic respiratory procalcitonin < 0.1 ng/ml off the bronchial tree. insufficiency Reduction of diuresis.
26 day, 31.12.2015, 07:56 Respiratory acidosis - Patient still sleepy, in the morning respiration again supported in the Reduction of diuresis: 9. hypodynamic respiratory bilevel positive airway pressure (BPAP) mode, considerable amounts of Furosemid (furosemidum). insufficiency mucous secretion sucked off the bronchial tree. Continuous tendency for CI: 2.9–2.7 (slightly too low hypotension.
CO2 = 5 mmHg)
Strona 8 z 12 26 day, 31.12.2015, 19:14 Mixed respiratory and metabolic 10. alkalosis – the use of mechanical ventilation 27 day, 01.01.2016, 07:45 Patient conscious, temporarily sleepy, establishes basic contact easily. (mixed respiratory/metabolic Mechanical respiration in the bilevel positive airway pressure (BPAP) Reduction of diuresis: 11. alkalosis) mode maintained, mucous secretion sucked off the bronchial tree. Patient Furosemid (furosemidum). Normalization of blood gases - cardiovascularly stable. the use of mechanical ventilation
27 day, 01.01.2016, 13:52 3. (as above)
27 day, 01.01.2016, 21:23 (as 2. above)
Patient conscious, remains in basic contact. Mechanical ventilation in the bilevel positive airway pressure (BPAP) mode continued, 28 day, 02.01.2016, 4:16 Reduction of diuresis: 2. PEEP = 10/3, FiO = 0.3. Individual rales hearable from the areas above (metabolic alkalosis) 2 Furosemid (furosemidum). the lungs. Considerable amounts of mucous secretion still sucked off the air passages.
Patient conscious, attempts to answer questions moving her head, still 2. 29 day, 03.01.2016, 07:55 muscle strength very weak. Weakly squeezes both hands on request and (metabolic alkalosis) moves both feet.
12. 29 day, 03.01.2016, 21:41
30 day, 04.01.2016, 07:22 (metabolic alkalosis) Patient conscious, remains in basic contact. Muscle strength still very 12. Interpretation: ↑pCO2 caused by weak. Spontaneous respiration of very low volume, not ensuring decrease in ventilator support; elimination of carbon dioxide. CPAP with PS maintained.
delay in urinary HCO3 excretion
Strona 9 z 12 30 day, 04.01.2016, 15:08 3. (as above)
31 day, 05.01.2016, 14:30 (metabolic alkalosis) Patient conscious, remains in basic contact. CPAP mode ventilation with 3. Interpretation: ↑pCO2 caused by PS, FiO2 = 0.3. ↓ventilator support
32 day, 06.01.2016, 14:10 (metabolic alkalosis) Patient conscious, it seems that right hand mobility has improved greatly. Interpretation: delay in urinary Also head movements cover wider range. Cardiovascularly stable, fever 3. HCO3 excretion absent, mechanical ventilation in the CPAP mode with PS, 30% oxygen. (disproportionally low pCO2 of Short apnoea temporarily during sleep. 1–2 mmHg)
33 day, 07.01.2016, 07:42 2. (metabolic alkalosis)
34 day, 08.01.2016, 21:31 Respiratory acidosis caused by Patient conscious, remains in basic contact, muscle strength still very
5. reducing ventilator support weak. Assisted PAV respiration, FiO2 = 0.3. Patient cardiovascularly (slightly too low stable.
CO2 = 1–2 mmHg) 35 day, 09.01.2016, 07:27 (slightly too low Patient’s general and neurological condition with no greater alterations.
5. CO2 = 1–2 mmHg) Patient conscious, remains in basic contact. Assisted PAV respiration, Respiratory acidosis caused by FiO2 = 0.3. reducing ventilator support 36 day, 10.01.2016, 07:52 Patient in general critical but stable condition. Patient conscious, reacts to Respiratory acidosis caused by commands, sleeps for most of the on-call time. Muscle strength 5. reducing ventilator support considerable weakened. No spontaneous activity. Assisted PS (slightly too low respiration, with temporal apnoea periods. Change to SIMV.
CO2 = 2–3 mmHg) FiO2 = 0.35. CO2 = 40–50 mmHg.
37 day, 11.01.2016, 03:36 Metabolic alkalosis caused by 1. increasedventilatory support
Strona 10 z 12 37 day, 11.01.2016, 22:24 Patient’s general and neurological condition with no greater alterations. 12. Metabolic alkalosis caused by Patient conscious, remains in basic contact. Assisted CPAP respiration, Reduction of diuresis.
increased ventilatory support FiO2 = 0.35. Patient cardiovascularly stable.
38 day, 12.01.2016, 07:59 ormalization of blood gases - the 3. use of appropriate mechanical ventilation
Patient conscious, reacts to commands, sleeps for most of the on-call time. 38 day, 12.01.2016, 20:46 Muscle strength considerable weakened. No spontaneous activity. 4. Respiratory acidosis caused by Assisted PS respiration, FiO2 = 0.35. CO2 = 40–50 mmHg. Before noon reducing ventilator support change to TC. CO2 levels stable. 39 day, 13.01.2016, 13:52 Respiratory acidosis caused by reducing ventilator support 5. (slightly too low CO2 = 2–3 mmHg)
39 day, 13.01.2016, 21:13 Patient conscious, remains in basic contact. Assisted TC respiration, Respiratory acidosis - rise the Chronic respiratory 5. FiO = 0.3, later the patient breathes on her own, with passive oxygen carbon dioxide caused by 2 acidosis. therapy. Patient cardiovascularly stable. spontaneously breathing patient
40 day, 14.01.2016, 21:26 Patient conscious, reacts to commands, sleeps for most of the on-call time. Mixed respiratory acidosis and Muscle strength considerable weakened. No spontaneous activity. The Chronic respiratory 13. metabolic alkalosis patient has been breathing on her own for a day, with no visible respiratory acidosis.
effort. CO2 = 55–65 mmHg.
41 day, 15.01.2016, 14:48 (metabolic alkalosis) 13. Patient conscious, sleepy. Spontaneous respiration. (slightly too low
CO2 = 1–2 mmHg)
42 day, 16.01.2016, 14:37 Spontaneous respiration via the tracheostomy with no with passive oxygen 13. (metabolic alkalosis) therapy.
Strona 11 z 12 43 day, 17.01.2016, 15:57 Spontaneous respiration via the tracheostomy with no with passive oxygen 13. (metabolic alkalosis) therapy. Cardiovascularly stable.
44 day, 18.01.2016, 13:39 13. (mixed respiratory acidosis/metabolic alkalosis)
Patient conscious, reacts to commands. Has been breathing on her own for 45 day, 19.01.2016, 08:06 the following day, with no visible respiratory effort, parameters of Chronic respiratory 14. (respiratory acidosis) respiratory gas exchange within normal range. Patient cardiovascularly acidosis. stable.
At present patient conscious, contact with patient difficult. Spontaneous 46 day, 20.01.2016, 07:45 respiration via the tracheostomy tube, patient cardiovascularly stable, 1. (metabolic alkalosis, slow blood gastroenteric tube feeding, industrial diet. Fever absent. Patient transferred gases normalization)s to the Clinic of Neurology.
Strona 12 z 12