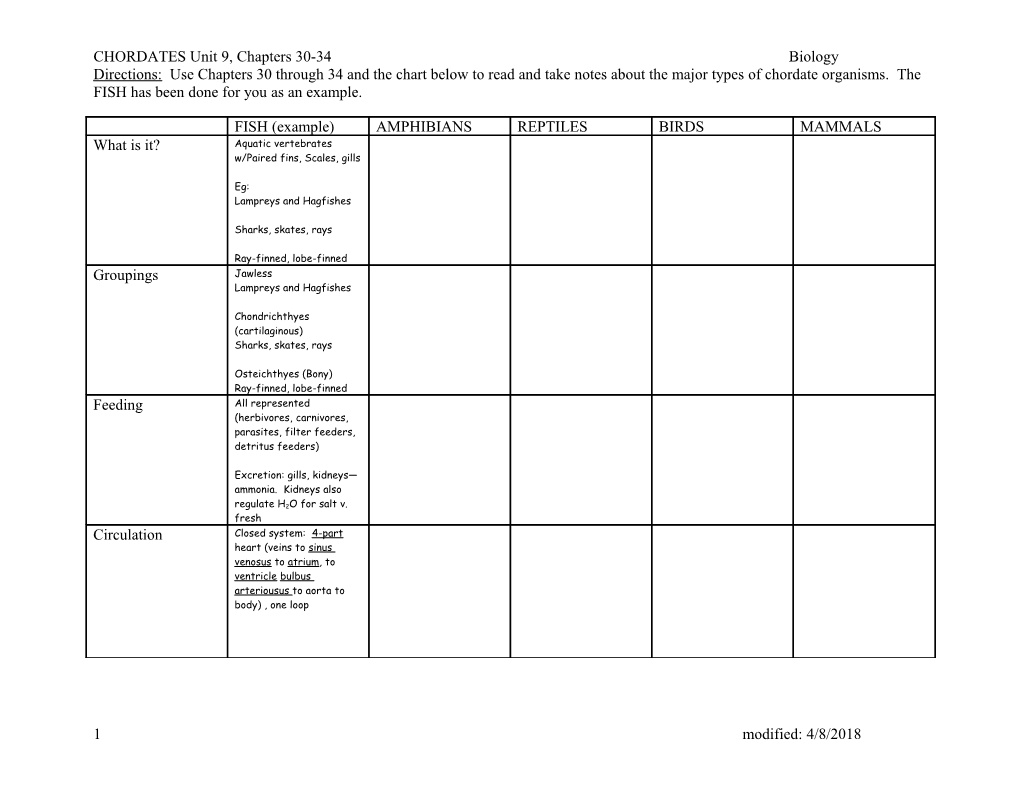
CHORDATES Unit 9, Chapters 30-34 Biology Directions: Use Chapters 30 through 34 and the chart below to read and take notes about the major types of chordate organisms. The FISH has been done for you as an example.
FISH (example) AMPHIBIANS REPTILES BIRDS MAMMALS What is it? Aquatic vertebrates w/Paired fins, Scales, gills
Eg: Lampreys and Hagfishes
Sharks, skates, rays
Ray-finned, lobe-finned Groupings Jawless Lampreys and Hagfishes
Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous) Sharks, skates, rays
Osteichthyes (Bony) Ray-finned, lobe-finned Feeding All represented (herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders, detritus feeders)
Excretion: gills, kidneys— ammonia. Kidneys also
regulate H2O for salt v. fresh Circulation Closed system: 4-part heart (veins to sinus venosus to atrium, to ventricle bulbus arteriousus to aorta to body) , one loop
1 modified: 4/8/2018 CHORDATES Unit 9, Chapters 30-34 Biology Directions: Use Chapters 30 through 34 and the chart below to read and take notes about the major types of chordate organisms. The FISH has been done for you as an example.
FISH (example) AMPHIBIANS REPTILES BIRDS MAMMALS Gills for gas exchange: Gills w/ filaments w/ capillaries w/ large Respiration surface area to exchange
O2 and CO2, some have multiple openings (lampreys and sharks), most only 1, behind operculum. Lungfishes: specialized
tube to air for more O2 Reproduction Oviparous: eggs hatch outside body,Eg: Salmon
Ovoviviparous: eggs stay in body after internal fertilization, embryo develops in egg, egg hatches inside, and young born live. Eg: guppy
Viviparous: embryos stay in mom’s body after internal fert. Get nutrients from mom, not yolk. Born live.
Movement Alternating paired sets of muscles along backbone. S-shaped movements w/ backwards force to move forward. Fins: stabilizers, flaps, and rudders. Increase SA of tail for propulsion. Streamlined, to reduce drag. Swim Bladder for buoyancy.
2 modified: 4/8/2018 CHORDATES Unit 9, Chapters 30-34 Biology Directions: Use Chapters 30 through 34 and the chart below to read and take notes about the major types of chordate organisms. The FISH has been done for you as an example.
FISH (example) AMPHIBIANS REPTILES BIRDS MAMMALS Body Temperature Ectothermic: outside H2O temp = inside body temp.
Ecology FreshH2O, SaltH2O, some both w/ specialized ability
to control H2O balance.
Anadramous (salt to fresh), eg: salmon
Catadromous (fresh to salt), eg: European eels
herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders, detritus feeders
3 modified: 4/8/2018 CHORDATES Unit 9, Chapters 30-34 Biology Directions: Use Chapters 30 through 34 and the chart below to read and take notes about the major types of chordate organisms. The FISH has been done for you as an example.
What Groupings Feeding Respiration Circulation Reproduction Movement Body Ecology Is it Temp Control
Aquatic Jawless All represented Gills for gas Closed system: Oviparous: eggs Alternating Ectothermic: FreshH2O, Fishes vertebrates Lampreys and (herbivores, exchange: Gills 4-part heart hatch outside paired sets of outside H2O SaltH2O, some w/Paired Hagfishes carnivores, w/ filaments w/ (veins to sinus body,Eg: Salmon muscles along temp = inside both w/ (Ch 30) fins, Scales, parasites, filter capillaries w/ venosus to backbone. S- body temp. specialized gills Chondrichthyes feeders, detritus large surface atrium, to Ovoviviparous: eggs shaped ability to
Evolution: first (cartilaginous) feeders) area to ventricle bulbus stay in body after movements w/ control H2O vertebrates, common invert Eg: Sharks, skates, exchange O2 and arteriousus to internal backwards balance. ancestor. Jaws and paired Lampreys rays Excretion: gills, CO2, some have aorta to body) , fertilization, force to move appendages arose w/in and kidneys— multiple one loop embryo develops in forward. Fins: Anadramous fishes and lungfishes (tube Hagfishes Osteichthyes ammonia. Kidneys openings egg, egg hatches stabilizers, (salt to fresh), for air). Early fishes: (Bony) also regulate H2O (lampreys and inside, and young flaps, and eg: salmon plates, no jaws. Adaptive Sharks, Ray-finned, for salt v. fresh sharks), most born live. Eg: rudders. radiation 505-410mya: some skates, rays lobe-finned only 1, behind guppy Increase SA Catadromous lost armor, some maintained operculum. of tail for (fresh to salt), but went extinct, some had Ray-finned, Lungfishes: Viviparous: propulsion. eg: European jaws can be used to eat a lobe-finned specialized tube embryos stay in Streamlined, eels variety of animals/plants to air for more mom’s body after to reduce and for defense. This O2 internal fert. Get drag. Swim herbivores, occurred at same time as nutrients from Bladder for carnivores, paired fins attached to mom, not yolk. buoyancy. parasites, girdles (pectoral and pelvic) Born live. filter feeders, which allows for variety of detritus mvmt, allows branching out feeders (lobe-fins, ray fins, etc) increased speed, accuracy. Cartilage and bone present.
4 modified: 4/8/2018 CHORDATES Unit 9, Chapters 30-34 Biology Directions: Use Chapters 30 through 34 and the chart below to read and take notes about the major types of chordate organisms. The FISH has been done for you as an example.
Amphibians WHAT GROUP FEED RESPIRE CIRC REPRO MVMT TEMP ECO 0 (Ch 30) Vertebrate Salamanders: Larval: filter Through skin Double loop: 1 external Larval stage— Ectotherms In water and that lives in Urodela long feeders or and lungs (some one loop carries fertilization, some swim (wiggling, land.
H2O as larva bodies and tails, herbivores eating thru mouth). oxygen poor salamanders, using tail for Nictitating Evolution: about 360mya. and land as 4 legs, algae. Intestines Some blood (from internal. Eggs must propulsion). membranes to Similar to lobe-finned adult (some carnivores, in generally filled salamanders heart to lungs stay moist. Male Adult: walking, keep eyes open fishes, but with legs (lobe- exceptions), moist woods w/food, adults don’t have lungs and skin), one climbs on female but in S- in water. Keen fin fleshy). Need to has moist where they meat-eaters, at all, all thru oxygen rich frog to squeeze, shaped curves, eyesight to breathe air so lungs skin w/ tunnel under changed digestive skin (from lungs and eggs released, male or jumping, catch bugs. necessary (tie to lungfishes mucous rocks and logs. tract (shorter skin to body). fertilizes. Eggs some have Carnivores as again). Eggs need to not glands, no Also newts intestines). Larval: skin and encased in sticky discs for adults. Larval dry out, so stay in H O. 2 scales, no (land) and mud Caecilians just gills. 3-chambered jelly attaching to suction. stage generally Bones in girdles, stronger. claws. puppies, (w/ snap jaws heart: RA, LA underwater plants filter-feeders Sternum for shield to external gills in open/closed, Ventricle: body for protection, and algae protect lungs. Eg: H2O) frogs and to RA (O2 poor), abandoned by eaters. Salamanders, salamanders have simultaneously parent, generally. All must be Frogs and Frogs and long-sticky with lungs to LA Yolks nourish near water for Early amphibians huge: up Toads, Toads: Anura tongue. (O2 rich). Both embryo until hatch reproduction, to 5 meters. Carboniferous Caecilians jump (frogs, to ventricle into tadpoles. Go but toads drier period, amphibians were long, toads All have mouth to (some mixing) through areas, stay dominant. Gave rise to short) no tails stomach to pumped out metamorphosis. inactive to modern amphibians and as adults. Frogs intestine to back to body conserve H2O. reptiles. Climate changes closer to H2O cloaca (all wastes, and lungs. Some care for eggs Usually caused extinction. Very than toads sperm, and eggs or young (in mouth, tropical.Bright few left. leave from) on back, connected coloration, Caecilians: to legs) camouflage, or Apoda no legs, poisonous skin
in H2O, eat for protection. small inverts. Fishlike scales Global decline in populations, not understood.
5 modified: 4/8/2018 CHORDATES Unit 9, Chapters 30-34 Biology Directions: Use Chapters 30 through 34 and the chart below to read and take notes about the major types of chordate organisms. The FISH has been done for you as an example.
Reptiles WHAT GROUP FEED RESPIRE CIRC REPRO MVMT TEMP ECO (Ch 31) Vertebrate Lizards and Herbivores w/ Spongy lungs, Double-loop, 1 Internal Larger, Ectotherms, Endangered w/ well snakes: Squamata long digestive more area than loop to/from fertilization , male stronger limbs rely on due to habitat developed Lizards: legs, tracts. amphibians. lungs. 1 loop deposits sperm into compared to behavior to destruction Evolution: First clawed toes, skull, Carnivores, jaws, Lungs only, not to/from body. female w/ penislike amphibians. help control and hunting. vertebrates to have external ears, backbone w/ swallow whole. skin. Muscles 2 atria, 1 or 2 organ to cloaca., Walk, run, T. Bask in (food, pets, Amniotic Egg, leathery movable eyelids. tail, 2 Some venomous. Insectivores, around ribs help ventricles. female covers burrow, swim, sun to warm skins). Sea shell, 2-looped circulation, girdles, 4 Snakes: legless, sticky tongues. expand and Partial septum embryo climb. Often (or stay turtle recovery jaws, girdles to support limbs some venomous. contract chest in single w/membranes and rotated under underwater), programs weight. O Crocodilians: for inhalation ventricle 1 . leathery shell. body allowing move to underway. Vertebrate Crocodilia and exhalation. Alligators/Crocs Some lay eggs, them to carry shade, swim, First known reptile fossils alligators w/dry scaly Some Crocodiles most developed some in nests, some more weight. or take Herbivores, 350mya. Cooler, drier time, (America), crocs skin, lungs, have flaps of hearts (4 not, some guard Flippers in shelter to carnivores, amphibians dying, adaptive (s. Hemi), caimans, terrestrial and gavials: long skin to separate chambers)—like and care aquatic cool down. insectivores. radiation of reptiles. eggs w/ broad snout, squat mouth from birds and (alligators), some reptiles. Live on land, in Mammal like reptiles in membranes. appearance nasal passages mammals. ovoviviparous. Backbone fresh and Permian 245 mya. carnivores. Guard to breathe thru allows for marine waters, Dry skin eggs and young. nostrils while Amniotic Egg: mvmt. and deserts. Dinosaurs in Triassic and Tropics. must be mouth open. 2 amnion, yolk sac, Jurassic, large aquatic Turtles/Tortoises: shed, not lungs, except chorion, and reptiles, small to enormous Testudines turtles grow w/ in H2O tortoises some snakes only allantois land dinosaurs. 2 legged organism, land 1O. Shell built 1 lung. running, or 4, small family but keeps into skeleton. groups w/ nests, or not. water in. Carapace (dorsal) Some w/ feathers. All were and plastron either Ornithischia (bird- (ventral). Eg: lizard, hipped) or Saurishia (lizard- Protection, no alligator, hipped). teeth but strong turtle, jaws w/horny tuatara ridges, strong 65mya mass extinction of limbs to carry dinosaurs. shell Tuataras: Sphenodonta only members left, look like lizards, but no external ears and 3rd eye (see sun)
6 modified: 4/8/2018 CHORDATES Unit 9, Chapters 30-34 Biology Directions: Use Chapters 30 through 34 and the chart below to read and take notes about the major types of chordate organisms. The FISH has been done for you as an example.
Aves WHAT GROUP FEED RESPIRE CIRC REPRO MVMT TEMP ECO (Ch 31) Reptile-like; Pelicans and High energy need Unique; highly Highly efficient Sexual Many fly; some Endotherms.; Many pollinate constant their relatives; based on need for efficient four - reproduction; only generate flowers; Evolution: May have come body Parrots; Birds controlled body system. chambered reproductive tracts walk/run/swim body heat dispersal of from extinct reptiles based temperature; of Prey; temperature and heart; two for both sexes with a high fruit seeds by on the following evidence— feathers Perching Birds; flight; Inhale = air separate open into the Feather- metabolic some birds; 0 amniotic eggs; nitrogenous- cover; two Cavity-Nesting enters large air circulatory cloaca. Sex organs covered wings. rate; 41 C control of rich body wastes called uric scaled Birds; Herons Different bills sacks, then loops. Complete change size based Two feather common body insects acid; similar skeletal covered legs, and their adapted to travels to lungs, separation of on the season; types—contour temperature. populations, features/hollow bones. used walking, relatives; different types through oxygen-rich and increase in size (flight); down such as Archaeopteryx—possible perching. Ostriches and of food. breathing tubes oxygen-poor during mating (warmth). Rigid mosquitoes; transition species between their relatives = one-way flow blood. season. Internal but light- indicators of reptiles and birds. Eg: Emerald No teeth but crop of oxygen-rich fert. (press weight environmental Another theory—reptiles Toucan; (wet food); two- air. High heart rate cloacas together) skeleton oven health. and birds evolved from an Barbet; part stomach; (150-1000 with a large earlier common ancestor. Macaws; some a gizzard beats/min.) to Amniotic eggs with keel. Large Owls; (food grinding). keep blood hard shells. Usually chest muscles Boobies. moving rapidly. incubated by (up to 30% of Herbivores; parents. body mass). omnivores; carnivores. EXCRET Some migrate long distances (e.g., 1000s Nitrogenous RESPONSE miles open waste converted ocean), using to uric acid; Well-developed the Earth’s water sense organs. Good magnetic field, reabsorbed in —eyes (see color); celestial the cloaca. hearing. Bad-taste bodies, land White pasty and smell. forms as excretion Relatively large guides. brain to body size; well developed cerebrum and cerebellum
7 modified: 4/8/2018 CHORDATES Unit 9, Chapters 30-34 Biology Directions: Use Chapters 30 through 34 and the chart below to read and take notes about the major types of chordate organisms. The FISH has been done for you as an example.
Mammals WHAT GROUPS FEED RESPIRE CIRC REPRO MVMT TEMP ECO Two notable Monotremes: (Ch 32) High metabolic Lungs to Two completely By internal A wide variety Endotherms. Endothermic features: Lay eggs. Have rate = eat 10X breathe. separate loops— fertilization of egg of limbs and Have hair, nature and hair and physiological Evolution: Fossils identified reptile same size. Breathing one from the by sperm. digits adapted subcutaneous efficient mammary similarities to on the basis of the lower Herbivores; controlled by lungs; one to to different fat layer to kidneys = glands. Also reptiles. E.g., jaw, complex teeth replaced omnivores; two sets of the rest of the Young need care, needs and conserve homeostasis breathe air, platypus, spiny 1X/lifetime; distinct limbs carnivores; filter muscles; one is body; four usually from habitats (e.g., body heat; can be have a four- anteaters, and backbones. Appeared in feeders. the powerful chambered mother but also climbers; sweat glands maintained in a chambered echidnas. the Triassic Period 220 diaphragm. heart: right the father, when runners; to cool the wide variety of heart; are million years ago. Small; Different jaw Muscles cause side—receives they are born and diggers; body. habitats. endotherms. Marsupials: nocturnal; insect-feeders. features and the chest cavity O2-poor blood for a long time flyers; Example of Bear live young Demonstrate examples of specialized teeth, to expand or from the body afterward. swimmers). homeostasis. Highly but at a very convergent evolution. E.g., based on food contract. and sends to developed young stage of armadillo and pangolin; giant source. lungs; left side immune system development; anteater and aardvark. —O2-rich blood allows them to complete Carnivores— is received, fight diseases. development in RESPONSE canine teeth; EXCRE pumped to body. an external ridged Roles to play in pouch. Highly developed molars/premolars; Highly developed ecosystem, E.g., kangaroos, brain; three main short digestive kidneys that based on koalas, and parts—cerebrum tract. conserve salts, feeding wombats. (outer layer called nature/position sugars, water cerebral cortex), Herbivores— and release in food web. Placental cerebellum, and broad flat molars urea. Mammals: medulla oblongata. and premolars; Homeostasis Nutrients, O2, Highly developed long digestive CO2, and senses. tract; specialized wastes are stomach (rumen). exchanged efficiently between the embryo and the mother through a placenta.
8 modified: 4/8/2018