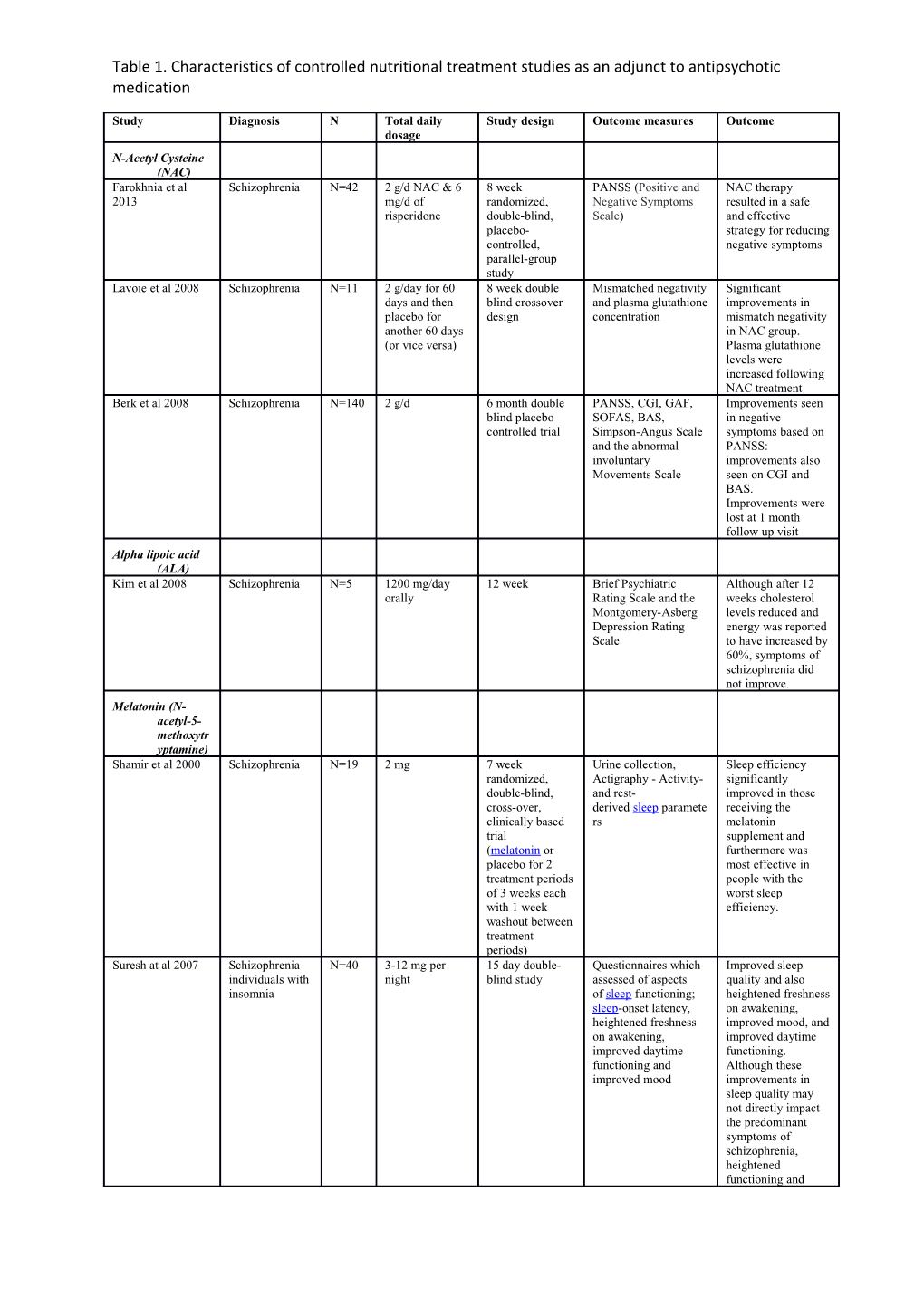
Table 1. Characteristics of controlled nutritional treatment studies as an adjunct to antipsychotic medication
Study Diagnosis N Total daily Study design Outcome measures Outcome dosage N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) Farokhnia et al Schizophrenia N=42 2 g/d NAC & 6 8 week PANSS (Positive and NAC therapy 2013 mg/d of randomized, Negative Symptoms resulted in a safe risperidone double-blind, Scale) and effective placebo- strategy for reducing controlled, negative symptoms parallel-group study Lavoie et al 2008 Schizophrenia N=11 2 g/day for 60 8 week double Mismatched negativity Significant days and then blind crossover and plasma glutathione improvements in placebo for design concentration mismatch negativity another 60 days in NAC group. (or vice versa) Plasma glutathione levels were increased following NAC treatment Berk et al 2008 Schizophrenia N=140 2 g/d 6 month double PANSS, CGI, GAF, Improvements seen blind placebo SOFAS, BAS, in negative controlled trial Simpson-Angus Scale symptoms based on and the abnormal PANSS: involuntary improvements also Movements Scale seen on CGI and BAS. Improvements were lost at 1 month follow up visit Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) Kim et al 2008 Schizophrenia N=5 1200 mg/day 12 week Brief Psychiatric Although after 12 orally Rating Scale and the weeks cholesterol Montgomery-Asberg levels reduced and Depression Rating energy was reported Scale to have increased by 60%, symptoms of schizophrenia did not improve. Melatonin (N- acetyl-5- methoxytr yptamine) Shamir et al 2000 Schizophrenia N=19 2 mg 7 week Urine collection, Sleep efficiency randomized, Actigraphy - Activity- significantly double-blind, and rest- improved in those cross-over, derived sleep paramete receiving the clinically based rs melatonin trial supplement and (melatonin or furthermore was placebo for 2 most effective in treatment periods people with the of 3 weeks each worst sleep with 1 week efficiency. washout between treatment periods) Suresh at al 2007 Schizophrenia N=40 3-12 mg per 15 day double- Questionnaires which Improved sleep individuals with night blind study assessed of aspects quality and also insomnia of sleep functioning; heightened freshness sleep-onset latency, on awakening, heightened freshness improved mood, and on awakening, improved daytime improved daytime functioning. functioning and Although these improved mood improvements in sleep quality may not directly impact the predominant symptoms of schizophrenia, heightened functioning and Table 1. Characteristics of controlled nutritional treatment studies as an adjunct to antipsychotic medication
improved mood Roma-Nava et al Schizophrenia N=44 5mg per day 8 week weight, blood pressure, Improvements in 2014 with second N=24 randomized, lipid, glucose, body diastolic blood generation anti- composition, and pressure and psychotic anthropometric attenuated weight treatment double‐blind, measures gain, although individuals with bipolar disorder observed the strong beneficial metabolic parallel‐group, effects of melatonin on fat mass.
placebo‐
controlled clinical trial
Vitamins C and E Dakhale et al 2005 Schizophrenia N=40 500 mg/day 8 week Increased serum High levels of serum (on atypical prospective, Malondialdehyde MDA and low antipsychotics double-blind, (MDA), plasma plasma ascorbic acid medication) placebo- ascorbic acid levels were found in the controlled, and brief psychiatric sample as a whole noncrossover rating scale (BPRS) but at follow-up score. normalisation of these markers were observed only in the group receiving vitamin C group as an adjunct to anti- psychotic treatment. Schizophrenic symptomatology also improved significantly in the experimental group compared to those receiving a placebo. Adler et al 1993 Schizophrenia N=28 Vitamin E 8-22 week The Abnormal Significant with tardive (27 of (maximal dose double-blind, Involuntary Movement improvement was dyskinesia which 1,600 IU/day) parallel-group Scale scores found in the have comparison study Abnormal schizop Involuntary hrenia) Movement Scale scores for those treated with Vitamin E Lohr et al 1996 Schizophrenia N=35 Vitamin E 8 week double- Several measures to Treatment of with tardive (800 IU b.i.d) blind placebo- assess abnormal vitamin E resulted in dyskinesia controlled study involuntary movement, reduced levels of parkinsonism and severity of tardive psychopathology and dyskinesia. measures of tardive Involuntary dyskinesia movement scale score was reduced and positive symptoms for those with schizophrenia were reduced. Lohr et al 1988 Schizophrenia N=15 Vitamin E Randomized Abnormal Involuntary Reduction in AIMS with tardive crossover design Movements Scale score. Decrease in dyskinesia (AIMS) / Brief BPRS. No change Psychiatric Rating in SAS Scale (BRRS)/ Simpson-Angus Scale (SAS) for Extrapyramidal Side Effects Essential polyunsat urated Table 1. Characteristics of controlled nutritional treatment studies as an adjunct to antipsychotic medication
fatty acids (PUFAs) Amminger et al Prodromal N=81 840 mg EPA 12 week Transition to Lowered the risk of 2010 adolescents and 700 mg Randomized, psychiatric disorder / symptoms DHA double-blind, symptomatic and developing into a /d placebo- functional changes psychotic disorder, controlled trial – as compared to followed by 40 placebo week monitoring Arvindakshan M et Schizophrenia N=28 Mixture 4 months – pre Control (=45), PANSS Significant al 2003 (on medication) EPA/DHA treatment, post improvements on (180:120 mg) & treatment and 4 most of the clinical vitamins E/C month post measures, sustained (400iu:500mg) treatment for additional 4 months of supplement free period L-Theanine Ritsner et al 2011 Schizophrenia N=40 400mg/d of L- 8-week, Reduction of or (20 did theanine added randomized, anxiety, positive and schizoaffective not to ongoing double-blind, general disorder comple antipsychotic placebo- psychopathology. te the treatment controlled, 2- However, negative study) center study symptomatology, objective neuro- cognitive functioning, general functioning, quality of life and side effect prevalence did not differ in the groups. Miodownik et al Schizophrenia N=40 400 mg/d 8-week, double- Brain-derived Observed clinical 2011 or blind, neurotrophic factor improvements in schizoaffective randomized, (BDNF), schizophrenia disorder placebo- dehydroepiandrosteron symptoms, although controlled trial e (DHEA), its sulfate the exact reason for (DHEAS), cortisol, this relationship is cholesterol, and insulin unclear Folate and B vitamin suppleme ntation Godfrey et al 1990 Acute N=41 15mg 6 month double Patients sig. schizophrenics methylfolate blind, placebo improved clinical with borderline daily for 6 controlled trial and social recovery, folate deficiency months + greater with time psychotropic meds. Roffman, Lamberti, Schizophrenia N=440 folic acid (2 mg) 16 week Improvement in Achtyes et al 2013 and vitamin B12 randomised, negative symptoms (400 mcg) placebo but only when controlled trial genotypes that were previously associated with negative symptom severity were taken into account. Levine et al 2006 Chronic N=42 2mg folic acid + 6 month PANSS & AIMS Sig. difference in schizophrenia 25mg randomised, baseline, 3 months and reduced PANSS at 3 patients pyridoxine + double-blind, 6 months. Plasma Hcy months. inpatients with 400μB12 per placebo- taken monthly >15μmol/l day or placebo controlled, as add-on crossover design Exclusion diets as an adjunct to anti- psychotic medicatio n Vlissides, Venulet Psychotic N=24 Gluten-free v 14 week double- Psychotic In-Patient Beneficial changes Table 1. Characteristics of controlled nutritional treatment studies as an adjunct to antipsychotic medication
& Jenner, 1986 disorders, gluten- blind, placebo profile (PIP) found between pre- particularly containing diet control trial trial and gluten-free schizophrenia time in 5 aspects of PIP. Potkin et al 1981 Young N=8 30 g of gluten 13 week double- BPRS / Serum alpha 1 No reduction in individuals with for 5 weeks and blind, placebo acid glycoprotein BPRS. No chronic a placebo control trial measurement inflammatory schizophrenia challenge for 8 response (Serum). weeks Sensitivity to dietary gluten not found. Storms, Clopton & Schizophrenia N=26 gluten-free 10 day double- Profile on Mood States No improvement Wright, 1982 peanut-flour blind, placebo found in supplementary control trial experimental group. cookies In fact the gluten- added group showed greater improvement in tension-anxiety and anger-hostility