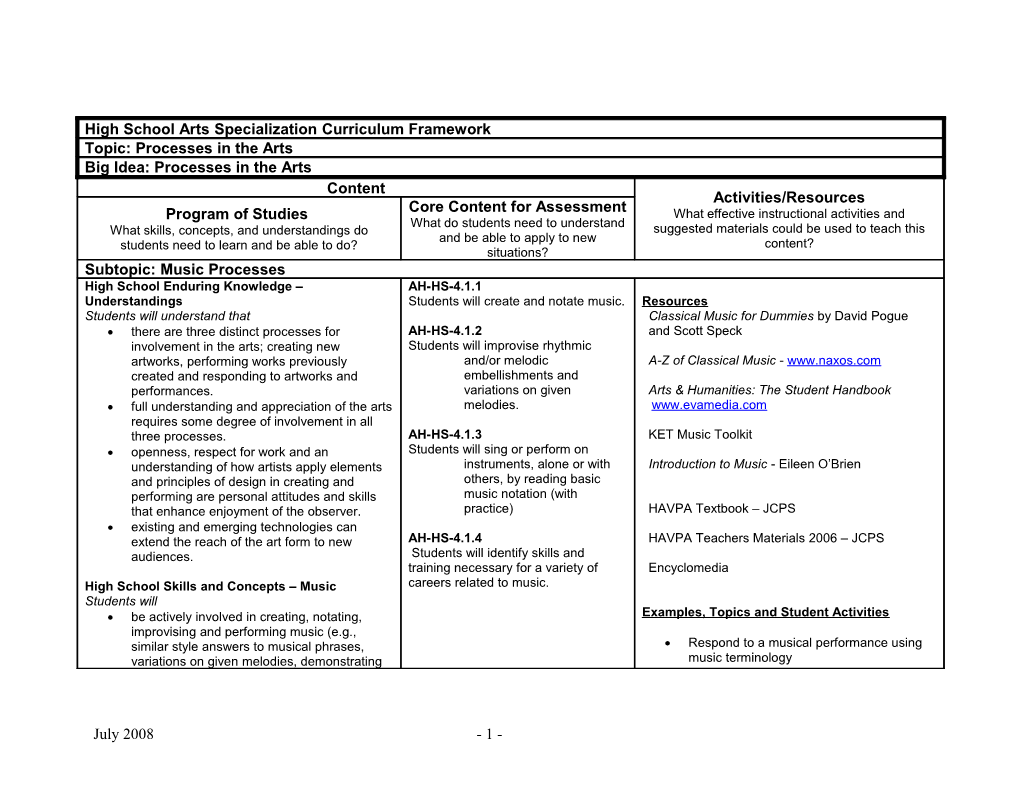
High School Arts Specialization Curriculum Framework Topic: Processes in the Arts Big Idea: Processes in the Arts Content Activities/Resources Core Content for Assessment Program of Studies What effective instructional activities and What do students need to understand What skills, concepts, and understandings do suggested materials could be used to teach this and be able to apply to new students need to learn and be able to do? content? situations? Subtopic: Music Processes High School Enduring Knowledge – AH-HS-4.1.1 Understandings Students will create and notate music. Resources Students will understand that Classical Music for Dummies by David Pogue there are three distinct processes for AH-HS-4.1.2 and Scott Speck involvement in the arts; creating new Students will improvise rhythmic artworks, performing works previously and/or melodic A-Z of Classical Music - www.naxos.com created and responding to artworks and embellishments and performances. variations on given Arts & Humanities: The Student Handbook full understanding and appreciation of the arts melodies. www.evamedia.com requires some degree of involvement in all three processes. AH-HS-4.1.3 KET Music Toolkit openness, respect for work and an Students will sing or perform on understanding of how artists apply elements instruments, alone or with Introduction to Music - Eileen O’Brien and principles of design in creating and others, by reading basic performing are personal attitudes and skills music notation (with that enhance enjoyment of the observer. practice) HAVPA Textbook – JCPS existing and emerging technologies can extend the reach of the art form to new AH-HS-4.1.4 HAVPA Teachers Materials 2006 – JCPS audiences. Students will identify skills and training necessary for a variety of Encyclomedia High School Skills and Concepts – Music careers related to music. Students will be actively involved in creating, notating, Examples, Topics and Student Activities improvising and performing music (e.g., similar style answers to musical phrases, Respond to a musical performance using variations on given melodies, demonstrating music terminology
July 2008 - 1 - High School Arts Specialization Curriculum Framework Topic: Processes in the Arts unity/variety, tension/release, and balance) Itunes U - Select a university and go to the alone and with others music site for recordings and lectures. use knowledge of musical elements to create Create music using Finale Notepad and perform music in an expressive manner Critique students compositions using music sing or perform on instruments, alone or with terminology others, reading basic music notation (with Research careers in music related careers practice) use knowledge of the elements of music and music terminology to describe and critique their own performances and the performances of others identify and apply criteria for evaluating music (e.g., skill of performers, originality, emotional impact, variety, interest, technical accuracy) demonstrate behavior appropriate for observing the particular context and style of music being performed; discuss opinions with peers in a supportive and constructive way explore skills and training necessary for a variety of careers related to music Vocabulary: Elements of Music: rhythm, tempo, melody, harmony, form, timbre, dynamics What terms could students use to clarify communication about this content? Assessment: Students will How will students be assessed to find out what they be actively involved in creating, notating, improvising and performing music (e.g., already know and what they’ve learned? similar style answers to musical phrases, variations on given melodies, demonstrating unity/variety, tension/release, and balance) alone and with others use knowledge of musical elements to create and perform music in an expressive manner sing or perform on instruments, alone or with others, reading basic music notation (with practice) use knowledge of the elements of music and music terminology to describe and critique their own performances and the performances of others
July 2008 - 2 - High School Arts Specialization Curriculum Framework Topic: Processes in the Arts identify and apply criteria for evaluating music (e.g., skill of performers, originality, emotional impact, variety, interest, technical accuracy) demonstrate behavior appropriate for observing the particular context and style of music being performed; discuss opinions with peers in a supportive and constructive way explore skills and training necessary for a variety of careers related to music
July 2008 - 3 - Subtopic: Dance Processes High School Enduring Knowledge – AH-HS-4.2.1 Resources Understandings Students will create an individual or a KET Dance Toolkit Students will understand that group dance using dance there are three distinct processes for elements (space, time and Arts & Humanities: The Student Handbook involvement in the arts; creating new force) that communicates www.evamedia.com artworks, performing works previously thoughts, ideas and/or feelings. created and responding to artworks and HAVPA Textbook - JCPS performances. AH-HS-4.2.2 full understanding and appreciation of the arts Students will demonstrate appropriate HAVPA Teachers Materials 2006 – JCPS requires some degree of involvement in all alignment, strength, and three processes. flexibility while performing Encyclomedia openness, respect for work and an dance movement. understanding of how artists apply elements Examples, Topics and Student Activities: and principles of design in creating and AH-HS-4.2.3 Charades, then “make a dance out of it” performing are personal attitudes and skills Students will perform dances utilizing Chair Dances (from 2006 HAVPA that enhance enjoyment of the observer. various forms. (Choreographic Teachers Materials) – perform different existing and emerging technologies can forms: theme and variation, forms of dance (AB, ABA, Rondo, Theme extend the reach of the art form to new rondo, narrative) & Variation) while seated or standing in audiences. one place AH-HS-4.2.4 Verbs & Adverbs activity (act them out High School Skills and Concepts – Dance Students will perform social, through movement) recreational, and artistic dances Students will Develop chart of dance styles listing from various historical periods be actively involved (individually and in groups) in characteristics of each – What type of and cultures. creating and performing dance (using the movements would you see/use? How are elements of dance: space, time and force) in a the elements of dance used? AH-HS-4.2.5 variety of choreographic forms (theme and Attend and critique dance Students will identify skills and variation, rondo, narrative) performances/events in the community demonstrate appropriate alignment, strength and training for a variety of careers related to dance. Create your own dance flexibility while performing dance movement Critique student performances (group or apply knowledge of dance elements and dance individual) using dance terminology (KET terminology to: Toolkit – Responding to Dance) expressively create and perform dance to Perform a variety of dances communicate thoughts, ideas and/or feelings Create brochure on careers in dance describe and critique their own performances (portfolio piece)
July 2008 - 4 - and the performances of others identify and apply criteria for evaluating dance (e.g., skill of performers, originality, emotional impact, variety, interest) demonstrate behavior appropriate for observing the particular context and style of dance being performed; discuss opinions with peers in a supportive and constructive way explore skills and training necessary for a variety of careers related to dance Vocabulary: Elements of Dance: space, time, force What terms could students use to clarify communication about this content? Assessment: Students will How will students be assessed to find out what they be actively involved (individually and in groups) in creating and performing dance (using already know and what they’ve learned? the elements of dance: space, time and force) in a variety of choreographic forms (theme and variation, rondo, narrative) demonstrate appropriate alignment, strength and flexibility while performing dance movement apply knowledge of dance elements and dance terminology to: expressively create and perform dance to communicate thoughts, ideas and/or feelings describe and critique their own performances and the performances of others identify and apply criteria for evaluating dance (e.g., skill of performers, originality, emotional impact, variety, interest) demonstrate behavior appropriate for observing the particular context and style of dance being performed; discuss opinions with peers in a supportive and constructive way explore skills and training necessary for a variety of careers related to dance
July 2008 - 5 - Subtopic: Drama/Theatre Processes High School Enduring Knowledge – AH-HS-4.3.1 Resources Understandings Students will create and perform KET Drama Toolkit Students will understand that using elements of drama. there are three distinct processes for (Literary-script writing, Arts & Humanities: The Student Handbook involvement in the arts; creating new Technical- designing and www.evamedia.com artworks, performing works previously directing, Production- created and responding to artworks and acting) HAVPA Textbook - JCPS performances. full understanding and appreciation of the arts AH-HS-4.3.2 HAVPA Teachers Materials 2006 – JCPS requires some degree of involvement in all Students will identify skills and three processes. training necessary for a The Stage and the School, published by openness, respect for work and an variety of careers related to Glencoe McGraw-Hill understanding of how artists apply elements drama. and principles of design in creating and Theatre: Art in Action, published by Glencoe performing are personal attitudes and skills McGraw-Hill that enhance enjoyment of the observer. existing and emerging technologies can Theater, A Crash Course by Rob Graham extend the reach of the art form to new audiences. History of Theater by Neil Grant
High School Skills and Concepts – Drama/Theatre Encyclomedia Students will be actively involved in creating, improvising and The Drama Game File (CD) by Jonas Basom performing dramatic works alone and with others, using elements of drama (Literary, Technical, Helpful Websites for locating scenes and Production) monologues: use knowledge of elements of drama to: http://www.theaterwords.com/scenes.html create and perform dramatic works in an http://drama.eserver.org/ expressive manner http://www.kmrscripts.com/scenes/index.htm describe and critique their own performances http://www.iisd1.org/hs_theatre/monologues.htm and the performances of others http://www.monologuearchive.com/ use a variety of resources (e.g., research, Examples, Topics and Student Activities: peers, technology) to: Puppet shows o write, refine, and record dialogue,
July 2008 - 6 - monologues, and action Dramatic readings (find scenes from o explore jobs/careers (e.g., playwright, auditions, drama books or see drama director, actor) and skills associated with toolkit) dramatic arts (theater, dramatic media) Using a Ten Minute Play or short scene o identify and apply criteria for evaluating have the students analyze for the dramatic works (e.g., skill of performers, presence of Aristotle’s six elements of originality, emotional impact, variety, drama or the elements of plot structure interest, technical requirements: lighting, Convert a chapter or episode from a novel sound, scenery, costumes, make-up) into a play (scriptwriting); include stage o demonstrate behavior appropriate for directions observing the particular context and style Take a scene from a play; divide class into of dramatic works being performed; groups giving each a technical element; discuss opinions with peers in a have groups make design proposals as to supportive and constructive way how their technical element would be o explore skills and training necessary for a implemented in the play variety of careers related to dramatic arts Monologues/Soliloquies Duo improv Critique of a play School performances Write a script based on a myth with elements of Greek theatre Create brochure on careers in drama (portfolio piece)
Vocabulary: Elements of Drama: What terms could students use to clarify Literary elements - Plot structures (rising action, turning point, falling action), Suspense, communication about this content? Theme, Language, Style, Monologue, Dialogue Technical elements - Scenery, Sound, Lights, Make-up, Props Performance elements - Acting (e.g. character motivation and analysis, empathy) Speaking (e.g., breath control, projection, vocal expression and inflection, diction), Nonverbal expression - (e.g., gestures, body alignment, facial expression, character blocking and movement) Assessment: Students will
July 2008 - 7 - How will students be assessed to find out what they be actively involved in creating, improvising and performing dramatic works alone and with already know and what they’ve learned? others, using elements of drama (Literary, Technical, Production) use knowledge of elements of drama to: create and perform dramatic works in an expressive manner describe and critique their own performances and the performances of others use a variety of resources (e.g., research, peers, technology) to: o write, refine, and record dialogue, monologues, and action o explore jobs/careers (e.g., playwright, director, actor) and skills associated with dramatic arts (theater, dramatic media) o identify and apply criteria for evaluating dramatic works (e.g., skill of performers, originality, emotional impact, variety, interest, technical requirements: lighting, sound, scenery, costumes, make-up) o demonstrate behavior appropriate for observing the particular context and style of dramatic works being performed; discuss opinions with peers in a supportive and constructive way explore skills and training necessary for a variety of careers related to dramatic arts
July 2008 - 8 - Subtopic: Visual Art Processes High School Enduring Knowledge – Resources: Understandings AH-HS-4.4.1 KET Visual Art Toolkit Students will understand that Students will incorporate the elements there are three distinct processes for of art and principles of Arts & Humanities: The Student Handbook involvement in the arts; creating new design to generate several www.evamedia.com artworks, performing works previously solutions to a variety of created and responding to artworks and visual art problems. HAVPA Textbook – JCPS performances. full understanding and appreciation of the arts AH-HS-4.4.2 HAVPA Teachers Materials 2006 – JCPS requires some degree of involvement in all Students will use media and three processes. processes, subject matter, Encyclomedia openness, respect for work and an symbols, ideas, and themes understanding of how artists apply elements to communicate cultural and Incredible Art Department and principles of design in creating and aesthetic values. www.princetonol.com/groups/iad/ performing are personal attitudes and skills that enhance enjoyment of the observer. AH-HS-4.4.3 existing and emerging technologies can Students will identify skills and Examples, Topics and Student Activities: extend the reach of the art form to new training necessary for a variety of Use media and processes to create audiences. careers in visual arts. artwork imitating the style of an artist “In the manner of…” High School Skills and Concepts – Visual Arts Cubism project with portraits Students will Create CD covers or covers for the New be actively involved in selecting media, techniques, Yorker subject matter and processes for creating artworks for Printmaking, Monoprints specific purposes, applying the elements of art and Create original works of art in a variety of principles of design media use knowledge of the elements and principles of art Make a poster about an artist’s work, life & and art terminology to: context create expressive artworks Make a poster about a time period describe and critique their own work including characteristics of the time, and creations and the creations of others using the elements & principles of design (e.g., how the communication of ideas in their creation. relates to media, techniques, or Make a poster of the purposes of art processes used) Brochure on careers in the arts (portfolio
July 2008 - 9 - identify and apply criteria for evaluating piece) for incoming freshmen visual arts (e.g., skill of artist, originality, Betty Edwards’ “Drawing on the Right Side emotional impact, variety, interest, of the Brain” technical quality) Design an art gallery demonstrate behavior appropriate for Create a Powerpoint presentation observing the particular context and style Sketching works of famous artists of the artwork being viewed; discuss Role play an artist at a “reception” opinions with peers in a supportive and Field trip to museums, galleries, etc. constructive way Attending local arts events describe personal responses to artwork; Critique of an artwork explain why there might be different (4 steps of critique process: description, responses to specific works of art (e.g., analysis, judgment, evaluation) personal experience, interest, medium School exhibits used, effectiveness of message) Guest speakers (artists, gallery owners, explore skills and training necessary for a museum directors, architects, graphic variety of careers in visual arts designers, etc.)
Vocabulary: Elements of art: What terms could students use to clarify Line, Shape, Form, Texture, Space (perspective: aerial or atmospheric, 2 point linear communication about this content? perspective), Value (lightness and darkness, tints and shades), Color (color theory - primary, secondary, intermediate hues, intensity - brightness and dullness, color schemes/groups - triadic, complementary, analogous) Principles of Design: Repetition, Pattern, Rhythm, Movement, Contrast, Proportion, Balance (symmetrical, asymmetrical, radial), Emphasis (focal point), Variety, Unity
Media (plural)/ Medium (singular): Two-dimensional: paint (watercolor, tempera, oil, and acrylic), fabric, yarn, paper, ink, pastel (oil and chalk), fiber, photography, and computer design Three-dimensional: clay, wood, glass, metal, stone, and plaster Art processes: Two-dimensional: drawing, painting, fiber art (e.g. fabric printing, stamping, batik, tie dye), photography Three-dimensional: textiles, fiber art (e.g. constructing with fiber, weaving, rugs, crocheting, knitting, quilting), ceramics, sculpture, architecture
July 2008 - 10 - Subject matter: representational (e.g. landscape, portrait, still life) nonrepresentational (e.g. abstract, non-objective) Assessment: Students will How will students be assessed to find out what they be actively involved in selecting media, techniques, subject matter and processes for already know and what they’ve learned? creating artworks for specific purposes, applying the elements of art and principles of design use knowledge of the elements and principles of art and art terminology to: create expressive artworks describe and critique their own work creations and the creations of others (e.g., how the communication of ideas relates to media, techniques, or processes used) identify and apply criteria for evaluating visual arts (e.g., skill of artist, originality, emotional impact, variety, interest, technical quality) demonstrate behavior appropriate for observing the particular context and style of the artwork being viewed; discuss opinions with peers in a supportive and constructive way describe personal responses to artwork; explain why there might be different responses to specific works of art (e.g., personal experience, interest, medium used, effectiveness of message) explore skills and training necessary for a variety of careers in visual arts
July 2008 - 11 -