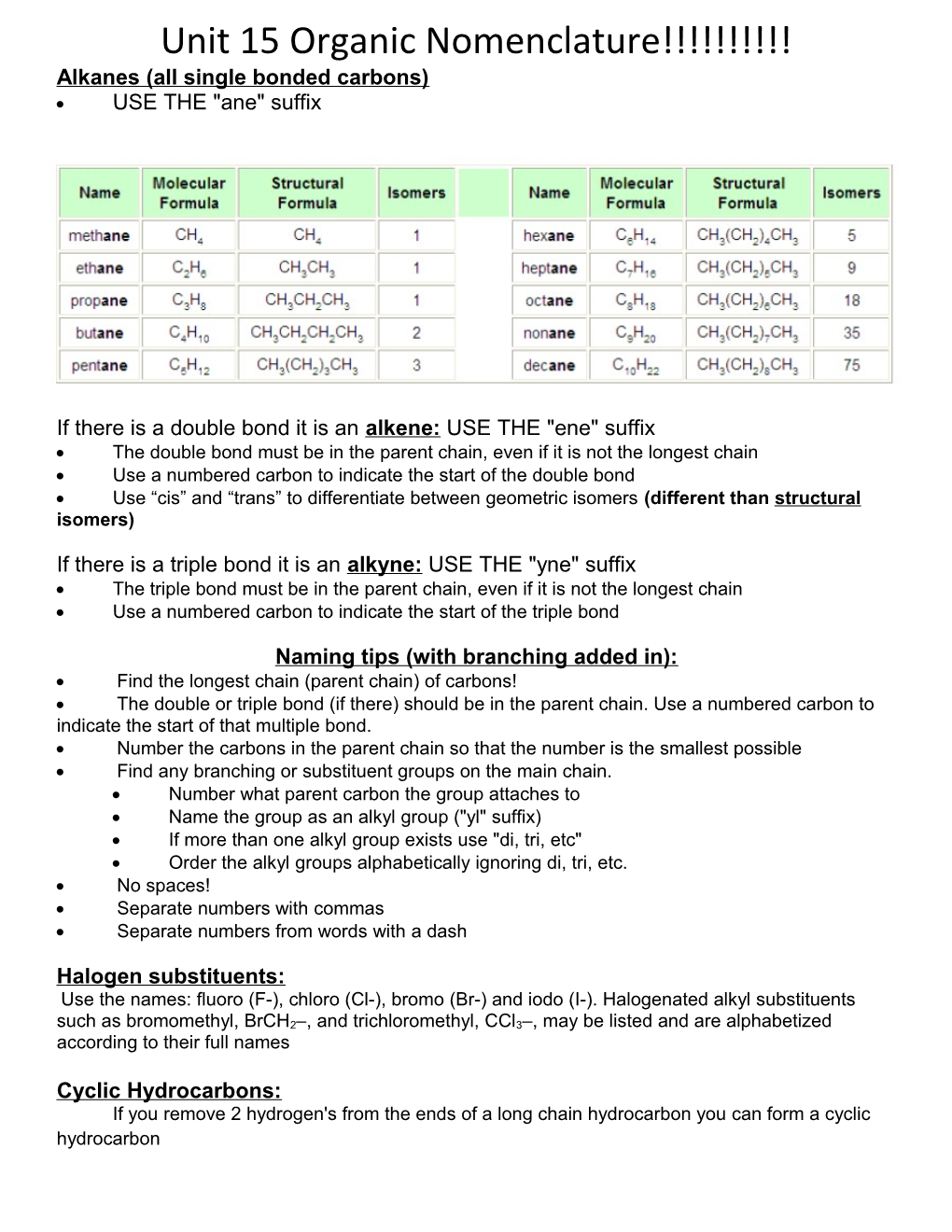
Unit 15 Organic Nomenclature!!!!!!!!!! Alkanes (all single bonded carbons) USE THE "ane" suffix
If there is a double bond it is an alkene: USE THE "ene" suffix The double bond must be in the parent chain, even if it is not the longest chain Use a numbered carbon to indicate the start of the double bond Use “cis” and “trans” to differentiate between geometric isomers (different than structural isomers)
If there is a triple bond it is an alkyne: USE THE "yne" suffix The triple bond must be in the parent chain, even if it is not the longest chain Use a numbered carbon to indicate the start of the triple bond
Naming tips (with branching added in): Find the longest chain (parent chain) of carbons! The double or triple bond (if there) should be in the parent chain. Use a numbered carbon to indicate the start of that multiple bond. Number the carbons in the parent chain so that the number is the smallest possible Find any branching or substituent groups on the main chain. Number what parent carbon the group attaches to Name the group as an alkyl group ("yl" suffix) If more than one alkyl group exists use "di, tri, etc" Order the alkyl groups alphabetically ignoring di, tri, etc. No spaces! Separate numbers with commas Separate numbers from words with a dash
Halogen substituents: Use the names: fluoro (F-), chloro (Cl-), bromo (Br-) and iodo (I-). Halogenated alkyl substituents such as bromomethyl, BrCH2–, and trichloromethyl, CCl3–, may be listed and are alphabetized according to their full names
Cyclic Hydrocarbons: If you remove 2 hydrogen's from the ends of a long chain hydrocarbon you can form a cyclic hydrocarbon Unit 15 Organic Nomenclature!!!!!!!!!!