Name ______Per. _____ Chapter 9 Review – Nuclear Changes 1. What is the mass number of potassium-41? a. 19 c. 22 b. 41 d. 39.1
2. Which of the following statements is true about the isotope nickel-64? a. It has 36 protons, 28 neutrons, and 36 electrons b. It has 28 protons, 36 neutrons, and 36 electrons c. It has 28 protons, 31 neutrons, and 28 electrons d. It has 28 protons, 36 neutrons, and 28 electrons
3. What is the name of an isotope with 19 electrons and 22 neutrons? a. Titanium-19 c. Potassium-41 b. Niobium-41 d. Potassium-39
4. Which of the following statements is false because of the underlined word or phrase? a. Gamma radiation, released from atoms like high-energy nickel, are the most dangerous type of electromagnetic radiation. b. Alpha particles are very similar to the nucleus of a helium. c. Beta particles are so small their mass is given as zero, but they can be blocked by just a sheet of aluminum foil. d. Alpha waves have the most mass of any radioactive wave.
5. Examine the following radioactive decay. What type of decay is this, and what is the missing atom? a. Beta decay; xenon-137 c. Beta decay; barium-137 b. Gamma decay; barium-137 d. Gamma decay; xenon-137
6. Examine the following radioactive decay. What type of decay is this? a. Gamma b. Beta c. Alpha
7. Which type of radiation would best be described as “looking like a simple redistribution of energy in the nucleus of an atom, but which releases high-energy radiation that can only be blocked by thick barriers of very dense material”? a. Beta radiation c. Alpha radiation b. Electromagnetic radiation d. Gamma radiation
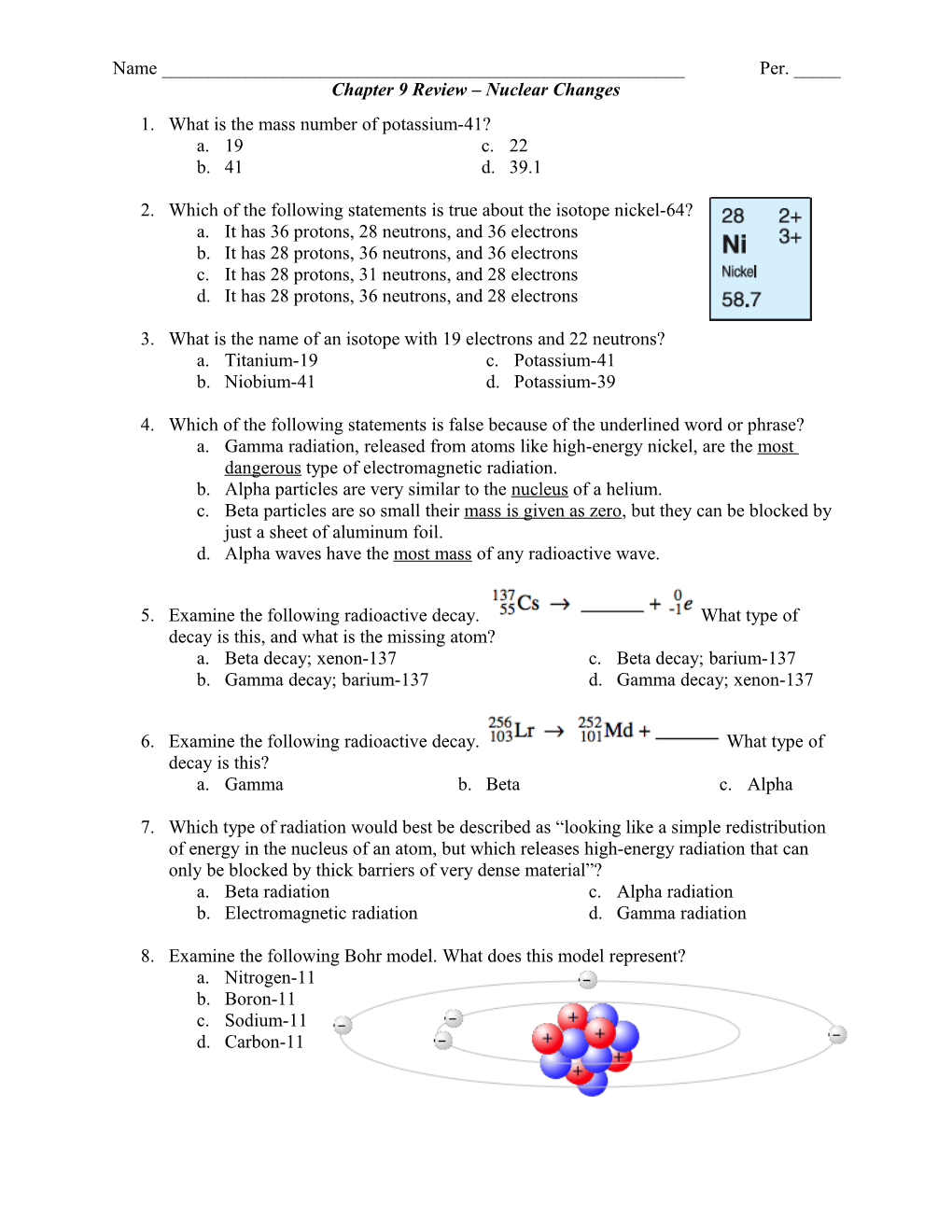
8. Examine the following Bohr model. What does this model represent? a. Nitrogen-11 b. Boron-11 c. Sodium-11 d. Carbon-11 Name ______Per. _____ Chapter 9 Review – Nuclear Changes 9. A 200 g sample of lawrencium is left in a container from 8:00 AM until 2:00 PM the next afternoon. If the mass of the sample of lawrencium was 25 g, what is the half-life of lawrencium? a. 10 hours c. 30 hours b. 5 hours d. 1 day
10. The following decay curve shows the isotope carbon-14. If it was determined that a fossil contained a little over 3% of the original amount of carbon-14 it once was composed of, what would be an approximate age for the fossil? a. 22,000 years old b. 17,000 years old c. 29,000 years old d. 35,000 years old
11. The following decay curve shows the isotope iodine-131, which is used in the treatment of thyroid cancer. It is important that the radioactive iodine does not remain in the body at high levels.
If less than 2 g of iodine-131 should remain in the body after 24 days, what is the largest mass of iodine-131 that should be used for treatment? a. 24 g c. 32 g b. 16 g d. 8 g Name ______Per. _____ Chapter 9 Review – Nuclear Changes 12. The following decay curve shows the isotope mercury-203.
If the initial amount of mercury-203 was 120 g on January 1, approximately how much would be left on June 30, six months later? a. 7.5 g c. 60 g b. 30 g d. 15 g
13. The following decay curve shows the isotope californium-252.
What is the half life of californium-252? a. 133 days c. 5 years b. 2.6 years d. 2.5 days Name ______Per. _____ Chapter 9 Review – Nuclear Changes 14. Use the following chart to answer this question.
Which isotope would be best to examine if an archeologist claimed to have found an artifact from the early bronze age in Egypt, around the year 3000 BC? a. Potassium-40 b. Uranium-235 c. All three isotopes would be equally effective for dating the artifact d. Carbon-14
15. Protactinium-231 is a radioactive isotope with a half life of 32,760 years. Protactinium- 231 decays into the daughter isotope actinium-227. What type of decay does Protactinium-231 undergo? a. Gamma decay b. Beta decay c. Alpha decay d. There is not enough information to determine the type of decay.
16. Examine the following equation. Which of the following statements best describes the equation? a. Alpha decay c. Fusion reaction b. Neutron emission d. Fission reaction
17. In nuclear fission, a chain reaction occurs when a neutron given off by the initial fission reaction cause another nearby nucleus to split as well. What method is used in nuclear reactors to stop this chain reaction from occurring uncontrolled, releasing dangerous amounts of energy in a very short time? a. Nuclear material is removed from the reaction chamber every few. b. The original nuclear material used is a lower quality, and neutrons will not always be released. c. Half of the nuclear material in the reactor gives off beta radiation, so less neutrons are released from the alpha decay. d. Materials like cadmium, built into the rods and placed into the nuclear material, absorb many released neutrons to slow the chain reaction. Name ______Per. _____ Chapter 9 Review – Nuclear Changes 18. In order, from left to right, what are these three subatomic particles involved in nuclear
reactions? a. A neutron, a gamma particle, and a beta particle b. An electron, an alpha particle, and a beta particle c. A neutron, an alpha particle, and a beta particle d. A neutron, a beta particle, and an alpha particle
19. Which of the following is not a characteristic of fusion? a. Not used commercially in reactors b. Often do not produce products that are radioactive c. Heavy unstable nuclei split apart d. Lightweight nuclei join together
20. Consider these particles taken together: What is the most likely missing particle in this reaction? a. Uranium-235 c. Neptunium-238 b. Americium-241 d. Plutonium-240
21. Consider these particles taken together: What is the most likely missing particle in this reaction? a. Neptunium-238 c. Americium-241 b. Uranium-235 d. Plutonium-240
22. Why have scientists been working for more than 50 years to try to create nuclear fusion power plants? a. There is excess hydrogen in our atmosphere that fusion reactions would use up. b. If the sun ever burns out, scientists would have the same form of energy here on Earth to keep life on this planet alive. c. Nuclear fusion produces huge amounts of energy with little or no hazardous wastes. d. Nuclear fusion reactions are much easier to create in a chemistry lab than nuclear fission reactions.
Directions: Write the letter answer for each question below.
23. ____ List the three main types of nuclear radiation, in order of increasing penetrating power.
24. ____ What is the mass of an alpha particle?
25. ____ What is the mass of a beta particle?
26. ____ What is the mass of a gamma ray?
27. ____ Which type of radioactivity is stopped by a piece of paper? Name ______Per. _____ Chapter 9 Review – Nuclear Changes
28. ____ Which type of radioactivity needs lead or concrete to stop it?
29. ____ What happens to the atomic number and the atomic mass during alpha decay?
30. ____ What happens to the atomic number and the atomic mass during beta decay?
Answer Choices a. Alpha b. 4 amu c. Alpha, Beta, Gamma d. Gamma e. Mass decreases by 4, atomic number decreases by 2. f. Gamma, Beta, Alpha g. Mass unchanged, atomic number increases by 1. h. Zero i. Approx 1/2000th amu