ACCE ACEW Program Review: Health Technology Country/Region Results Since the ACEWs, March 2010
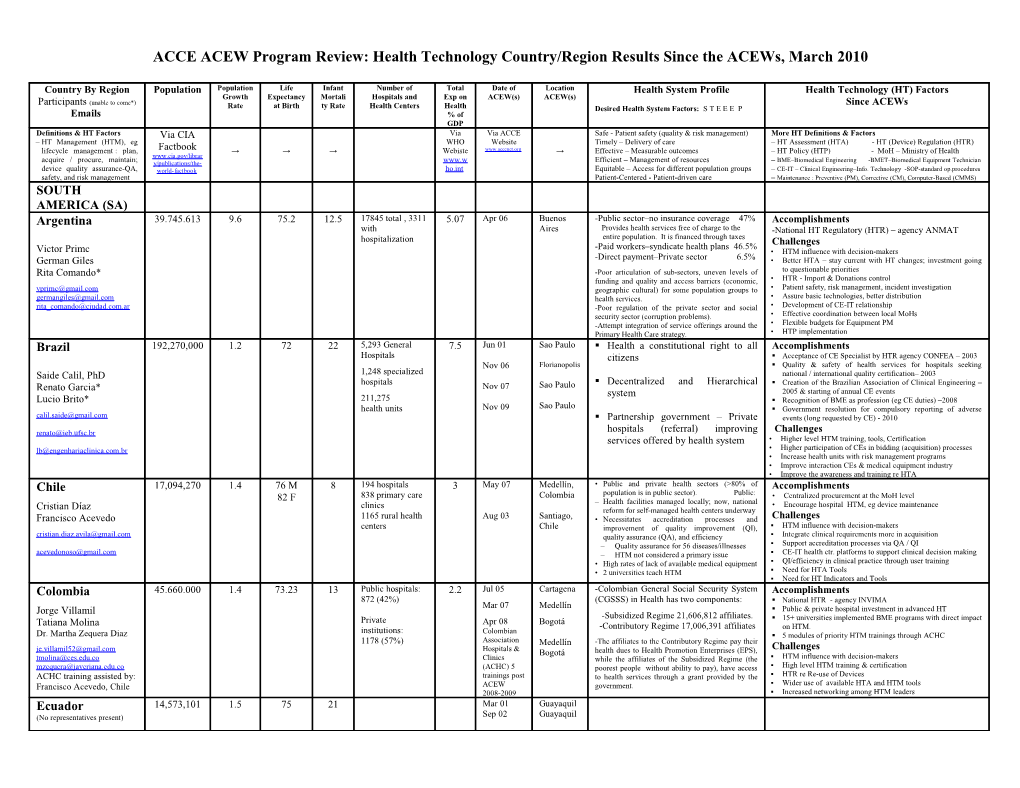
Country By Region Population Population Life Infant Number of Total Date of Location Health System Profile Health Technology (HT) Factors Growth Expectancy Mortali Hospitals and Exp on ACEW(s) ACEW(s) Participants (unable to come*) Since ACEWs Rate at Birth ty Rate Health Centers Health Desired Health System Factors: S T E E E P Emails % of GDP Definitions & HT Factors Via CIA Via Via ACCE Safe - Patient safety (quality & risk management) More HT Definitions & Factors – HT Management (HTM), eg WHO Website Timely – Delivery of care – HT Assessment (HTA) - HT (Device) Regulation (HTR) lifecycle management : plan, Factbook → → → Webiste www.accenet.org → Effective – Measurable outcomes – HT Policy (HTP) - MoH – Ministry of Health www.cia.gov/librar acquire / procure, maintain; y/publications/the- www.w Efficient – Management of resources – BME–Biomedical Engineering -BMET–Biomedical Equipment Technician device quality assurance-QA, world-factbook ho.int Equitable – Access for different population groups – CE-IT – Clinical Engineering–Info. Technology -SOP-standard op.procedures safety, and risk management Patient-Centered - Patient-driven care – Maintenance : Preventive (PM), Corrective (CM), Computer-Based (CMMS) SOUTH AMERICA (SA) Argentina 39.745.613 9.6 75.2 12.5 17845 total , 3311 5.07 Apr 06 Buenos -Public sector–no insurance coverage 47% Accomplishments with Aires Provides health services free of charge to the -National HT Regulatory (HTR) – agency ANMAT hospitalization entire population. It is financed through taxes -Paid workers–syndicate health plans 46.5% Challenges Victor Primc • HTM influence with decision-makers German Giles -Direct payment–Private sector 6.5% • Better HTA – stay current with HT changes; investment going Rita Comando* -Poor articulation of sub-sectors, uneven levels of to questionable priorities funding and quality and access barriers (economic, • HTR - Import & Donations control [email protected] geographic cultural) for some population groups to • Patient safety, risk management, incident investigation [email protected] health services. • Assure basic technologies, better distribution [email protected] -Poor regulation of the private sector and social • Development of CE-IT relationship security sector (corruption problems). • Effective coordination between local MoHs -Attempt integration of service offerings around the • Flexible budgets for Equipment PM Primary Health Care strategy. • HTP implementation Brazil 192,270,000 1.2 72 22 5,293 General 7.5 Jun 01 Sao Paulo . Health a constitutional right to all Accomplishments Hospitals citizens . Acceptance of CE Specialist by HTR agency CONFEA – 2003 Nov 06 Florianopolis . Quality & safety of health services for hospitals seeking Saide Calil, PhD 1,248 specialized national / international quality certification– 2003 hospitals . Decentralized and Hierarchical . Creation of the Brazilian Association of Clinical Engineering – Renato Garcia* Nov 07 Sao Paulo system 2005 & starting of annual CE events Lucio Brito* 211,275 . Recognition of BME as profession (eg CE duties) –2008 health units Nov 09 Sao Paulo . Government resolution for compulsory reporting of adverse [email protected] . Partnership government – Private events (long requested by CE) - 2010 [email protected] hospitals (referral) improving Challenges services offered by health system • Higher level HTM training, tools, Certification [email protected] • Higher participation of CEs in bidding (acquisition) processes • Increase health units with risk management programs • Improve interaction CEs & medical equipment industry • Improve the awareness and training re HTA Chile 17,094,270 1.4 76 M 8 194 hospitals 3 May 07 Medellín, • Public and private health sectors (>80% of Accomplishments 82 F 838 primary care Colombia population is in public sector). Public: • Centralized procurement at the MoH level clinics – Health facilities managed locally; now, national • Encourage hospital HTM, eg device maintenance Cristian Díaz reform for self-managed health centers underway Francisco Acevedo 1165 rural health Aug 03 Santiago, • Necessitates accreditation processes and Challenges centers Chile improvement of quality improvement (QI), . HTM influence with decision-makers [email protected] quality assurance (QA), and efficiency . Integrate clinical requirements more in acquisition – Quality assurance for 56 diseases/illnesses . Support accreditation processes via QA / QI [email protected] – HTM not considered a primary issue . CE-IT health ctr. platforms to support clinical decision making • High rates of lack of available medical equipment . QI/efficiency in clinical practice through user training • 2 universities teach HTM . Need for HTA Tools . Need for HT Indicators and Tools Colombia 45.660.000 1.4 73.23 13 Public hospitals: 2.2 Jul 05 Cartagena -Colombian General Social Security System Accomplishments 872 (42%) (CGSSS) in Health has two components: . National HTR - agency INVIMA Mar 07 Medellín . Public & private hospital investment in advanced HT Jorge Villamil -Subsidized Regime 21,606,812 affiliates. Private Apr 08 Bogotá . 15+ universities implemented BME programs with direct impact Tatiana Molina -Contributory Regime 17,006,391 affiliates on HTM. institutions: Colombian Dr. Martha Zequera Diaz . 5 modules of priority HTM trainings through ACHC 1178 (57%) Association -The affiliates to the Contributory Regime pay their Medellín Challenges [email protected] Hospitals & Bogotá health dues to Health Promotion Enterprises (EPS), [email protected] Clinics while the affiliates of the Subsidized Regime (the . HTM influence with decision-makers [email protected] (ACHC) 5 poorest people without ability to pay), have access . High level HTM training & certification ACHC training assisted by: trainings post to health services through a grant provided by the . HTR re Re-use of Devices Francisco Acevedo, Chile ACEW government. . Wider use of available HTA and HTM tools 2008-2009 . Increased networking among HTM leaders Ecuador 14,573,101 1.5 75 21 Mar 01 Guayaquil (No representatives present) Sep 02 Guayaquil Paraguay 6,200,000 2.3 70 22 1207 1.5 Nov 00 Panama . Public hospitals underutilized Accomplishments Public sector 62.2% City, . Inadequate equipment user training . HTM staffing (CE-BMET Education implemented) State hospitals 60.1% Panama . 48.9% equipment out or malfunctioning . PM/CM Program (Training, Manuals implemented) Social Security 8.5% Pedro Galvan . Low efficiency in allocation of resources . Donation Guideline Development (HTR for donation and used Private hospitals 24.5% for equity and access to health services or refurbished devices implemented) [email protected] . Procurement Policy Development (HTM/HTR) . Low technical/financial capacity of . Quality Management (HTR-importers /sellers/ users) leaders Challenges . Absence of HTA . CMMS-computer maintenance management system inventories . University-based HTM program . HTM influence with decision-makers; HTA Tools . MoH licensed HTM health professionals . Safety, risk management, & incident investigation tools Peru 29,132,013 1.3 76 18 2,551 hospitals; 4.2 Mar 02 Lima . Universal Health Insurance System (public & Accomplishments 8600 primary private) soon implemented . Creation of CENGETS-PUCP with MoH recognition: eg, . Governance of MoH is transferring to Regions several projects to model HTM, HTA, & HTR, to address health centers Aug 07 Lima under decentralization. Luis Vilcahuaman mother-child issues, telemedicine, etc. . MoH current national investment program, . Key national hospitals, eg INMP, HNCH, HNDM, changing Rossana Rivas mainly device acquisitions, building of hospitals, organizational structure with HTM/CE units without plan to improve practices, is risky. . CE/BMEs opportunity for professional development; MoH: [email protected] . Health organisations have difficulties hospital internships now supported by law. [email protected] understanding the value of CE, HTM, HTA . HTR: health sector better understands safety and techno- multi-disciplinary, consensus, team-based surveillance relevance to the welfare of society. solutions. . HTR: health begins to include international standards in . Creation of national HT center CENGETS- technical processes related to medical devices PUCP, 2005, that is university-based; with focus on solutions under innovation model and Challenges sustainable market for the Peruvian health . Include CE/HTM in MoH’s strategic agenda sector; 35 members & collaborators and a Further develop HTM, HTP, HTA, & HTR nationally network with more than 20 local and . international research, governmental, academic . HT staffing: recognition of CE / BME as health profession, and private organizations. provide HTM hospital internships, and other training capabilities, eg long-distance Internet-based training 3,494,382 0.47 76 11 Mar 91 Washington, Uruguay DC Gonzalo Ambrosi* [email protected] Venezuela 28,833,845 16.4 74 21 655 hospitals: 5.1 Mar 91 Washington, • National Public Health System, controlled by Accomplishments 282 public, DC MoH, based on principles of free service, • Within the MoH a Vice Ministry of Health Resources was universality, integrity, equity, social integration created. This Vice Ministry is responsible for HTM, (182 MoH), Mar 02 Coro and solidarity. including: facilities, drugs, and devices. Ricardo Silva, PhD • Financial support for the MoH responsibility of Luis Lara-Estrella, PhD* 344 private & • Graduate CE studies at Simon Bolivar University; engineers the state, and everyone has right to Social from MoH & Institute for Social Services are being trained. [email protected] 29 non-profit Security as a public non-lucrative service. [email protected] * • Public Health Services are divided amongst Challenges several providers, mainly the MoH, the • Far from implementing CE as a common practice for medical Venezuelan Institute for Social Services and facilities; even though MoH has recognized the need for HTM, “Barrio Adentro” Mission. such a practice has not been implemented at medical institutions. PAHO: Latin America ACEW Statistics ACEW Outcomes Sustainability & Caribbean (LA&C) . 1991-present . National HTP created . National Strategic Alliances (Public-Private) . 45 ACEWs . HTM Incorporated in National Health Plans . Coordination with Academic Sector Challenges . 28 Countries . Organizing HTR programs . Interaction with Scientific and Professional Societies • HT-dependent Countries hosted ACEWs . Organizing National HT Centers (eg, CENETEC) . Designation of WHO/PAHO Collaborating Centers • Lack of HTP; HTR programs -15 from LA&C . Promoting HTA Agencies . Institutional Capacity Building on HTM • Limited Evidence-Based . 63 Countries . HT on WHO/PAHO agenda (Res. WHA60.29) . Networks of: Experts; Institutions; Schools of Engineering Info for Decision-Making have participated, . HTM and HTA are “Institutional Priority” . Links to Global Initiatives • Average 50% of Equipment 32 from LA&C . Hospital directors, administrators in HTM o International Standards for HT (OMS/ISO/IEC/ITU) Out of Service or Not in Use . 4,030 Attendees, . Universities Organizing CE Programs o Health Technology Assessment International (HTAi) • Obsolete Buildings and 3,350 LA&C . Distance Learning (VU; CES-U; Catholic U) o Medical Devices Regulation (GHTF/PAHO) Highly Deteriorated (50%) . 72 ACCE Faculty . CE Departments in Hospitals Global Alliance for Patient Safety (WHO) • Shortage of HTM Staff o including 20 . Clinical Engineering (CE) Widely Promoted o e-Health/Telemedicine (PAHO/WHO) • Few Universities/Schools former ACEW . Academia & Engineering Societies Leadership o Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise (IHE) - Patient Care with Programs on BME/CE . Attendees WHO/PAHO Collaborating Centers on HT Domain (HIMSS/ACCE) • Lack of Physical . 1,810 Hours of . Active Role of CE on: WHO 23 May 2007 Resolution WHA60.R29 on HT Infrastructure Planning Lecture o Medical Device Regulation • Deficient PM/CM Programs . Exchange information on HT and Medical Devices . 2 Certification o Risk Management & after sale support service . Strategies and Plans for Heath Technology Management Boards for CE o Telemedicine – e-Health • Low budget for Maintenance . Regulatory & GMP (Good Device Manufacturing Processes) (Brazil, Mexico) Incident Investigations (Forensic CE) • Lack of CMMS Systems o . Establish National and Regional Institutions for HT • Continuous HT Acquisition o HTA . Information on Medical Devices based on Health Priorities . Request to WHO Director General South America Group Combined SA How the Region Summary Decision Strategy . Periodic Publications: successes; guidelines; response to failures Recommendations ACEW and its Countries of makers not . Empowerment: WHO Collaborative Groups . Collaborative Websites: social networking, projects; follow-up attending will address the Challenges aware of and Taskforces locally recognized. . Training: local trainers, educators/practitioners; internships and exchanges WHO CE Initiative countries’ Initiative to reach the added . Education: Webinars, Online Information, Best Practices, Success and Failure Stories WHO CE Initiative: communicate via (2) Brochures: Increase the availability and population Stated Goals. value . Key Players: Centers of excellence within the . General (high level): Description of Initiative, Statistics / accessibility of healthcare provided country or the region Advances, Goals, Tasks while reducing operation 291,597,611 by HTM Tools . Country: Situation Analysis (WHO), Local and Regional costs. . Brochures: Why, What and How of CE-IT Resources (to address the Situation) AFRICA Dr Jean-Bosco Ndihokubwayo* [email protected] Cameroon 18,879,301 2.2 54 63 -University hosp. 4 4 Nov 99 CapeTown, Health system is based on referrals from District Accomplishments -Central hospitals 3 South Africa Hospitals. Since 2008, government has launched . Implementation of technology unit in health districts Vincent Ngaleu Toko -Regional hosp. 9 Nov 06 CapeTown program to install in all Regions (10): medical . Training of staff -Dist hospitals 150 imaging and hemodialysis centers. 4 now operating. . Standard list of medical equipment Yunkap Kwankam, PhD* -Medical Health Ctrs In 2010, 2 more centers built/ equipped. Also, small . Created and validated the national HTP [email protected] (MD present) 141 health centers are built through many cooperation Challenges [email protected] -Health centers 1638 projects. The goal-1000 health centers by 2015. . Implement HTP 85,237,338 3.2 55 81 Public health 85% 5.9 Jan 06 Addis • 9 regionally-based states (ethnicity) & 2 city Accomplishments Ethiopia (143 hospitals, 690 administrations: Adis Abeba (Addis Ababa); Mulugeta Mideksa Ababa . Developed HTP, eg guidelines for HTA/HTM, and an extensive health centres and Afar, Amara (Amhara); Binshangul Gumuz; . Developed EBLEEA, national BME/CE professional society Senait Semtime 9914 health posts). Dire Dawa; Gambela Hizboch (Gambela Gebru Ayehubzu* Private 15% (397 Peoples); Hareri Hizb (Harari People); Oromiya Challenges Jennifer Barragan* private not-for-profit (Oromia), Sumale (Somali); Tigray; and • Most equipment out-dated and came via donation. [email protected] clinics, 1756 private Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples • Limited spare parts, documentation, and maintenance budget [email protected] • HTM staffing limited (100 in country, 60 in EBLEEA; of which [email protected] clinics for profit). • 85% of people in rural areas [email protected] 10 ACCE) Ghana 18,912,079 2.7 58 50 3011 in 10 regions: 5.1 Mar 09 Accra . Health system managed by MoH, service Accomplishments 2 teaching hospitals, delivery agencies, statutory & regulatory bodies . Clear understanding HT issues among healthcare managers and 9 regional hospitals, Jun 09 Accra . Service delivery agencies are Ghana Health awareness of BME/CE as profession in health sector Nicholas Adjabu, MD 93 district Hospitals, Service-GHS; 2 teaching hospitals and CHAG . Donation policy implementation improvement 10 polyclinics, 1059 . HTR Statutory & regulatory bodies are FDB, . Train/deploy HTM software (WHO ‘TEMP’ CMMS software) John Zienaa health centres and GMDC, GRNMC, Pharm. Council, Traditional . Began national BME association 285 community Medicine health compounds . Health delivery function managed by GHS Challenges [email protected] decentralised to 10 regions & 170 districts • Develop HTR and HTP at national level [email protected] . Active private participation in health delivery • Finances for maintenance & training programs, HTM . MoH funds capital; local facilities fund their • Inadequate HTM staffing and curricula for training own facility operations and maintenance (O&M) • HTM: spare-parts, information & support from manufacturers 39,002,772 2.7 58 55 1 national referral 4.3 Aug 06 Nairobi / MoH: Ministry of Public Health and Sanitation Accomplishments Kenya hospital, 7 regional . Level I - Community Health (Unable to attend) Mombasa . 6 regional HTM workshops: staff does 20% CE 80%f hospitals, and 70 . Level II – Community Dispensary acilities; current staff ~350, established in 1988 with the support district hospitals . Level III – Health Center of GTZ Martin Owino* Ministry of Medical Services . BME/CE training:Mombasa Poly., Kenya Medical Trg. Philip Anyango* Government versus . District Hospitals College Private facilities: 52- . Provincial Referral Hospitals . AMEK - Association of Medical Engineering of Kenya [email protected] 48% . Teaching and Referral Hospitals [email protected] Challenges . Also the BME & Facilities Services Division . Influence with decision-makers re HTM; need for HTP . HTM: spare parts; funds for maintenance; district staff, technical information, test equipment, and work environment 49,052,489 0.28 49 44 381 hospitals in 9 7 Nov 99 Cape Town • Each province follows its own HT system Accomplishments South Africa • HTM: in-house & out-sourced maintenance Baset Khalaf provinces . Provided a lot of HTM training for other Sub-Saharan May 06 Cape Town • Shortage of skilled HTM staffing countries Mladen Poluta* • Lack of proper maintenance facilities Rob Dickinson* . Developed HTP; conducted nation-wide HTM inventory taking [email protected] Excellent HTM training provided through [email protected] • University of Cape Town & Tshwane University Challenges [email protected] . Needs country-wide HTM/HTA system; finalized HTR system . Needs action plan to address HTM staffing/skills development 41,048,532 2.9 52 69 Referral hospitals 8 4.3 Aug 06 Nairobi / . United Republic of Tanzania (URT) composed Accomplishments Tanzania Regional hospitals 21 of Tanzania Mainland and the state of Zanzibar. District hospitals 95 Mombasa . HTM: central acquisition; operator training; PM/CM; Health Centres 331 . 2 independent Ministry Health & Social Welfare CMMS Yohana Mkwizu* Dispensaries 3038 . Tanzania Mainland, health services with 21 . HTM staffing: developed integrated program, with for both Regions, 113 districts, 133 local authorities managerial and technical skills. Foreign aid/development: Richard Masanja . Zanzibar, 2 health zones and 10 districts manpower/skills, internal training, CMMS, equip. replacement . In recent years 40% MOH budget financed . TAME - Tanzania Association of Medical Engineering [email protected] through bilateral agencies: Swiss Development Cooperation, DANIDA, The Netherlands, Irish Aid, GTZ, Challenges [email protected] KfW, CIDA Canada, JICA, USAID, and EU, and . Influence with decision-makers re HTM selection & purchasing multilateral: African Development Bank, The World . Lack of HTP for all levels of care Bank, UNICEF, and UNFPA. . Lack of HTM infrastructure Uganda 32,369,558 2.7 53 65 Hospitals 129 8 Aug 06 Nairobi / . Levels of Health Care: MoH, national Accomplishments Health centres 4265 Mombasa referral & regional referral hospitals, district . Completed HTP in ‘09 for all care levels; 8 regional Sam Wanda health services, general hospitals, Health Centres workshops Government versus (HC) level IV, III, II . National BME/CE association – UNAMHE - affiliated to IFHE Sitra Mulepo* Private facilities: . Provision of Ultrasonography at HC IV level spearheading public private partnership in HTM Sam Byamukama* 50% each . Built and equipped facilities in East Uganda . Initiated BMET training at Kyambogo University, Kampala [email protected] with Japanese donor JICA support . Introduction of HTM maintenance aspect in the Challenges [email protected] . Local HTM capacity to maintain medical equipment [email protected] Dutch / Uganda Governments’ funded country- wide Diagnostic Imaging project . Funding HTM operation & maintenance (O&M), especially for HCs; need inventories as basis for planning HTM O&M costs . Health planners not appreciated linkage between HT & quality
Africa Group 284,502,069 • Information Platform: Country • Training: Medical decision-makers; Equipment Users; comparison; Advocacy of HTM; Technical Technical training and test tools Recommendations information/discussion; Common nomenclature Focal point for HTM • Equipment Management: Donation; • Collect technical information Procurement; Disposal • Share technical information ASIA-EUROPE Albania 3,639,453 0.55 78 19 Oct 04 Pristina, Ilir Kullolli, CE USA, Observer Kosovo [email protected] 156,050,883 1.29 60 59 Mar 07 Dhaka, Bangladesh Bangladesh Georgia (Denmark) 4,615,807 -0.33 77 16 278 inpatient 8.2 May 93 Boston, • No HTR prior to ‘91, implemented FDA advice Accomplishments health facilities, USA • High hospital bed capacity, low utilization rate • After ACEW lasted few years but do not exist now (MoH Irakli, Jaliashvilli, PhD, 14 regions and 63 • Privatization of hospitals; high private costs Medical Device Department, CE certification, HTR) Radiometer, Inc. in Denmark • Underdeveloped primary health sector and low • University school of BME; 2 BME professional associations [email protected] districts; 90% utilization of outpatient services Challenges - Currently no real HTM/HTR; MoH – reinitiating private • Trend toward Deregulation • Education – need external assistance, eg regional CE training Germany 82,239,758 -0.05 79 4 2087 hospitals 10.4 Lutz with Philippines • Health system undergoing transition due to Accomplishments - HTM an integral part of the health care system GTZ in Malawi reunification of East/West/changing requirements • HTM mixture of in-house plus private providers and OEMs Lutz Kempe, consultant Africa Kenya, since 1988 • Number of hospitals has considerably decreased • Training of HTM professionals conducted on various levels Joachim Nagel, PhD* • Health care funded by a health insurance system Challenges [email protected] Senegal, El • Almost 99 % of population has a full coverage • Reduce costs while more HT is being introduced and utilized Salvador, [email protected]* • Increasing life expectancy and utilization of • Has strong private sector of medium sized HT manufacturers Jordan, → modern HT goes with increased health costs • Strong co-operation of HT industry and health care providers Greece Observer 10,737,428 0.13 80 5 George Panagiotopoulos, CE in USA [email protected] 1,156,897,766 Oct 09 Thiruvanan India Bhat Observer 1.4 66 51 Niranjan Khambete PhD* thapuram, Abhijeet Bhat, CE in USA India [email protected] [email protected] Iran PhD student, Canada 66,429,284 0.88 71 36 Sharareh Taghipour [email protected] Kosovo 1,804,838 ? ? ? Oct 04 Pristina, Agron Boshnjaku,* Shpresa Kosovo Ramiqi,* Kushtrim Hashani* [email protected] [email protected] Kyrgyzstan 5,431,747 1.4 69 24 72 FMC - Primary 3.1 Jul 00 Chicago, • State HC system, national HC reform programs Accomplishments - Implement HTP: MoH national Maintenance 146 Hospitals – USA • Establishment of family medicine institute Center (2009), Maintenance Fund (08), and High Technology Fund Kazbek Agibetov, PhD Secondary and • Introduced mandatory health insurance system • Develop national database for physical assets, and equipment [email protected] tertiary healthcare • Single payer system and separation of health standards of equipment for primary HC clinics (HC) sector into providers (called HI) and purchasers • Pilot WHO software-based tool – iHTP www.ihtp.info (national Mandatory Health Insurance Fund- Challenges - Institutionalization of HTM (current lack of training) MHIF) • Development of SOPs; standardize HT resources and costs • Laboratory QA system; Insufficient HTM financing Malaysia 25,715,819 1.7 73 16 130 (government) 4.7 Mar 07 Dhaka, • Comply Healthcare Facilities/Services Act (1998) Accomplishments - Privatize 5 hospital support services since ‘97 209 (private); Bangladesh • Seek JCI (Joint Commission International) • Result of privatization, BME/CE popular at many universities Azman Hamid Implement integrated accreditation for government hospitals • Harmonization of standards [email protected] hospitals-traditional • Establish 50 clinics initially for urban poor Challenges - CE certification, Medical Device Act (HTR) Secretary, Commission for the & complementary • Capitalize on health tourism with appropriate HT . Role of CE within HT acquisition at hospital level Advancement of HTM in Asia . Implement digital hospital concepts; address CE-IT needs Oct 04 Pristina, Macedonia Observer 2,066,718 0.26 75 9 Kosovo Clay Buttemere,lives Skopje [email protected] 28,563,377 1.28 65 47 Hospitals: 11 5.3 Apr 01 Katmandu, • Health Sector Reform includes HTM Accomplishments – Develop HTM Policy & validation in 2004 Nepal • Priorities: preventive and primary health care • Strengthening regional HTM workshop at Nepalganj David Porter PhD, consultant zonal, 62 district Nepal 193 health centres along with key interventions such as Emergency • HR development with establishing a 2-year training course Nepal, India, etc. from Scotland Obstetrical, safe motherhood, & secondary care Challenges - Scarce resources limit all activities e.g. HTM [email protected] 701 health posts • Human resource development needed • Political instability hindering HT Policy implementation Peoples Rep. China 1,338,612,968 0.66 73 20 Nov 95 Beijing
Sep 99 Moscow, R Russia [email protected] 140,041,247 -0.47 66 11 Oleg Shereshevsky PhD Sep 00 Vilnius, Lit Sri Lanka 21,324791 0.9 75 19 Jul 00 Chicago, Muditha Jayatilaka* USA [email protected] ASIA-Europe 3,044,171,884 Problem: OEM = Solution: 1. Obtain certification from OEM that local vendor 4. Establish guidelines and management capacity for alternative Without India, Local vendors original is authorized (guarantee of service continuity) service modalities (in-house, outsource (OEM, third party)) Group China, Russia, equipment 2. Obtain technical service manual as part of sale 5. Demand in-service training as part of sale; defined by contract disappear after - WHO advocacy re size of problem 6. Withdrawal of payment until all requirements have been & Bangladesh manufacturer Recommendations sale of medical 3. Make procurement guideline more specific to satisfied, eg work with lending institutions 252,569,020 devices address device issues 7. Direct registration of customers with manufacturers (OEMs) CENTRAL AMERICA and the CARIBBEAN Health services provided CCSS strategic plan is further investment in (CR) 4,253,877 1.36 78 9 Mar 02 San Jose Challenges, continued Costa Rica by CCSS, CR Social medical equipment Gabriela Mur. Jenkins Security Bureau covers Mar 04 San Jose Promote forums for: new ACEW in Costa Rica as a “kick There also is growing demand for clinical [email protected] 95% of the population; off” activity; create a web portal web with chats, e-learning, & 29 hospitals, 103 clinics engineers Mónica Ingiana Mora* data bases; promote CE society and 1100 Primary Health Challenges Integration of CE with IT and facilities (eg electronic medical [email protected] Service units Create a HTP linked with the strategic plan. records-EMRs, digital imaging). Address issue of CE-IT. Create our first HTA Centre to aim new Training Program of new CEs must be re-oriented to HTM investments and act like an advisor. (instead of maintenance only). Caribbean Islands Oct 08 Bridgetown, Dominica Accomplishments - Anguilla Barbados . An increase in knowledge base across the board Clavis Carter-Gumbs* . Drafting of first equipment procurement policy 14,436 2.27 78 3.5 Dominica . Recent purchase of equipment management software (CMMS) [email protected] • Main hospital of 200 Beds for secondary care - Antigua 85,632 1.3 75 16 • Supported by 52 primary health care centres, Dominica Challenges Keithroy Joseph* which focuses on prevention through education. • Implementation of procurement policy and HTR [email protected] • Introduced hyperbaric facility to be utilized for • Lack of necessary autonomy for CE/BME - Barbados 284,589 0.38 74 12 dive-related illnesses and Clinical medicine. • Manufacturers and distributors taking advantage of this adhoc Brandon McDonald* • Improvement of physical structure and facilities procurement approach; avoiding CE/BME at all cost [email protected] Island wide; includes ICU at main hospital • Absence of succession plans for staff; insufficient staffing - Belize 307,899 2.16 68 23 Carlos Perea* [email protected] Jamaica Accomplishments 13.3 Jul 03 Roseau, - Dominica 71,546 0.21 73 10 • Utilisation of info from ACEW for structured approach to Robin Williams Dominica facility development and project planning [email protected] Jamaica • Utilisation of US Department of the Army(April1998)Operating - Grenada 90,739 0.47 66 13 • The public health system is comprised of the Guide for Maintenance to develop SOP for Maintenance Rawle Ross* Ministry of Health and Environment, its agencies • A draft copy of T&T contract document is being utilized to [email protected] and departments, a network of 23 public enhance our service contracts. - Jamaica 2,682,120 0.5 74 21 hospitals, 322 Primary Health Centres. • Currently implementing SOP for the acceptance of technology / Keith Richards Apr 05 Kingston, • Hospital services in the public sector are provided refurbished devices (gifts) [email protected] Jamaica through general and specialist facilities 5,097 0.39 73 16 Jamaica Challenges - Montserrat • These are administered through the boards of the • Culture; Limited Funding; Procurement Process Schon Daway* [email protected] four (4) Regional Health Authorities. 40,131 0.85 73 14 • Shortage of Skilled Maintenance Personnel. - Nevis & St Kitts • Hospitals are classified A, B or C and Heath • Shortage of specialized diagnostic tools for Bio–Medical team. Shelisa Martin-Clarke* Centres ; Types I- IV according to the level of • Lack of redundant capacity to facilitate proper repairs [email protected] service and the size of the population served. Collin Mulley* • More physical and exercises related to the theory being taught. [email protected] • Under the National Health Service Act, 1997 - • What can PAHO/ACCE do to assist our Regional BME to - St. Lucia 160,267 0.42 76 13 Establishment of four Regional Health become Certified Clinical Engineers ?- there is a need in the Angus Jn Baptiste* Authorities to administer the national health Caribbean is to empower this profession to realize the full [email protected] services and facilities. potential of their capabilities. - Trinidad & Tobago 1,229,953 -0.10 68 30 • MoH re-oriented from that of a central care • Online resources created by Dr. Sloan - Faraz Rahamut* provider of health care services, to one of a ( http:// www70.homepage.villanova.edu/elliot.sloane/PAHO- ECC/ ) [email protected] 4,972,409 steering/monitoring role. Dominican Republic 9,650,054 1.49 74 26 Mar 00 Santa Diogenes Hernandez* Domingo [email protected] El Salvador 6,875,000 1.8 74 26 883 Public hospitals 7.9 Mar 91 Washington, • Primarily curative rather than preventive (44 Accomplishments 83 Private hospitals DC public hospitals and 39 private hospitals. • HTM Maintenance/Service Management-SM; outsourcing SM Salvador Juarez Total of 966 Jul 10 San Salvador Important new project: Maternity Hospital) • Micro HTA [email protected] • Country's epidemiological profile in transition, where still mainly ID respiratory and GI, Challenges however, in the last decade are diseases such as • HTM HR; Prof. Registration, Certification HTN, psychosomatic and chronic gastritis. • HTR: Safety, RM, QA • Injuries as a result of violence, high transmission • Macro HTA, HTP as dengue, pneumonia, TB and HIV / AIDS. • Safety, Risk Management and Quality Assurance Nicaragua 5,891,199 1.78 72 25 Mar 04 Managua Jose Delabarra, CE in USA [email protected] Mexico 111,211,789 1.13 76 18 Segmented Health Mar 91 Washington DC Accomplishments Challenges • Many results in HTM but mainly • CENETEC working to: Maria Luisa González Rétiz, Services: concentrated on the metropolitan area of Mexico • Improve HTM, HTA and application General Director, CENETEC- . 49% Soc. Sec. Jun 97 Washington DC City • Coordinate national efforts for HT homogenous processes National Center HT Excellence . 25% MoH & 32 • Involvement with country health authorities; • Provide guidelines, platforms and models [email protected] states Mexico City/ Nov 98 CENETEC HT advisors, coordinate national efforts • Provide information, technical opinions and Laura Patricia Lopez* . 14% Popular Mazatlan • HTM & other HT activities are part of recommendations for HT Decision Makers, eg Cabinet level [email protected] Insurance (very Monterrey National Health Program, eg creation of BME/CE weekly meetings Luis Martinez* poor) Nov 02 units • Legal support [email protected] . 6% Security staff Cancun • 4 specific national Action Plans, see • Modification of CENETEC’s legal attributions: more Fernando Prieto, MD PhD* of govern-ment Sep 03 www.cenetec.salud.gob.mx: medical equipment influence [email protected] . 6% private, others management; Telehealth; HTA; CPGs-clinical • CENETEC will continue Training Claudia Cardenas* . CENETEC practice guidelines • Telemedicine workshops [email protected] reports to Vice- • Heterogenous conditions in HTM in the rest • Sandra Rocha Nava MoH Introductory course to HTA of country, lack of specialized personnel & • [email protected] Workshop of CE re PM and CM planned each year. budget leads to over-utilization, excessive CM, increased costs, poor control, inequity of care, limited replacement funds, added risks 3,360,474 1.5 77 13 Nov 00 Panama City, Panama Panama Kathia Guerra* [email protected] 3,966,213 0.3 78 8 Nov 00 Panama City, Puerto Rico Panama Oscar Misla [email protected] CENTRAL AMERICA & 150,181,015 Documents Tools (aligned with WHO, led by ACCE or others) Networking Opportunities (hosted by an international organization) CARIBBEAN GROUP • Produced in the • United Nations official languages • Social networking sites (facebook) language of UN • Cheap telecommunications tools • Use of virtual space to be comunicated RECOMMENDATIONS • Share what is already • Generic procedures • Using mass email by subscription done. • Public website / Information repository • Chat rooms • Hosted by WHO • Standard templates • Collaborative platform information repository • Translation tools (voice to text) Advocacy Strategies • Aligned with WHO, • Sharing experiences (positive and negative) • Evidence of HTM & Following WHO resolutions and guidelines … by … and standardized Education (with international & regional speakers; • Collecting evidence on HTM to show the impact to decision • Accessible by the participation of experts of the host country or region) makers/authorities in an understandable way for them general public. • Webinars and other modalities (e-learning) • Participating with WHO to build guidelines and recommendations • Focus on local • Low cost – subsidies • Including in the authorities agenda conditions and needs. • Exchange programmes / internships • Promoting at national level first and international level later • Coaching & Mentoring FACULTY CASTAÑEDA Mario [email protected] CLARK Tobey [email protected] DAVID Yadin, PhD Overview International CE IFMBE CED Chairman • CE/BME training brightest univ. students today. 1. IFMBE federation of > 60 BME societies from ~ 55 countries. [email protected] • Need to articulate a consistent brand. 2. Clinical Engineering Division (CED) of IFMBE re-organized in Join at: • Hospitals/Industry needs to understand what they September 2009 along Working Groups. http://health.groups.yahoo.com/group/ are passing up by not hiring BMEs with B.S. deg. 3. Group #1 Professional Practice & Education CEDGlobal/ • Our challenge is to clarify the CE/BME brand Group #2 Standards and Guidelines Group #3 Strategic development & communications EASTY Tony, PhD [email protected] GENTLES Bill PhD INFRATECH Leader [email protected] ISSAKOV Andrei MD, PhD, MPH* [email protected] HEIMANN Peter* [email protected] HERNANDEZ Antonio [email protected] JACKSON Jennifer [email protected] JUDD Thomas [email protected] PAINTER Frank [email protected] SCHMITT Roger [email protected] SLOANE, Elliot PhD [email protected] Student Chapters EWH Summer Institute Summer, cont. Kit builds: Ghana Training 2009 (Med. Equip.Training-MET) Philippines MET Training TENINTY Billy, EWH • 22 student Over 200 Working units: [email protected] • 179 students have participated • 145 students have participated; 74 technicians graduated chapters, univ. • Engineering students student ESU power • 91 Technicians have graduated • 4 colleges now offer BMET training using MET curriculum engineering in learn new language, participants; meter; ECG • 16 African countries are benefiting EWH Study re Training Retention Rate EWH-Engineering World Health the U.S., Canada, train in equip. repair training, Pat.Simulator; IA CE training prior to ACEW Kosovo 2002-03 • In 2005, 2006 and 2008 EWH conducted On-site evaluations of MET (before Billy was with International Mexico, assistance Defib Tester . All lectures/materials translated into Albanian programs in Ghana, Honduras, Indonesia and the Philippines. 80% of MET Aid-IA) has provided HTM training in Denmark & U.K. provided to over Design: O2 • Work in hospitals in . Training facility set up and equipped at UCCK, main graduates remain at hospitals within the country of training 5 years after Honduras, Indonesia, Kosovo, • Activities: 25 hospitals analyzer; tertiary hospital in capital city graduation! Philippines, Ghana 2009 & Rwanda equipment repair; Nicaragua, Honduras, Development or Tanzania; nearly . 45 students participated, 43 graduated • EWH Rwanda - In March 2010 EWH will begin a 3-year MET program 2010 design; kit builds; timer; Exposure . 6 hospitals received BMET shops & equipment Adopt a Hospital $4,000,000 worth of Timer for 45 technicians in Rwanda & Francophone Africa. non-functioning equipment repaired between 2003-2009 WANG Binseng ScD [email protected] WEAR James PhD [email protected] VELAZQUEZ Adriana [email protected]