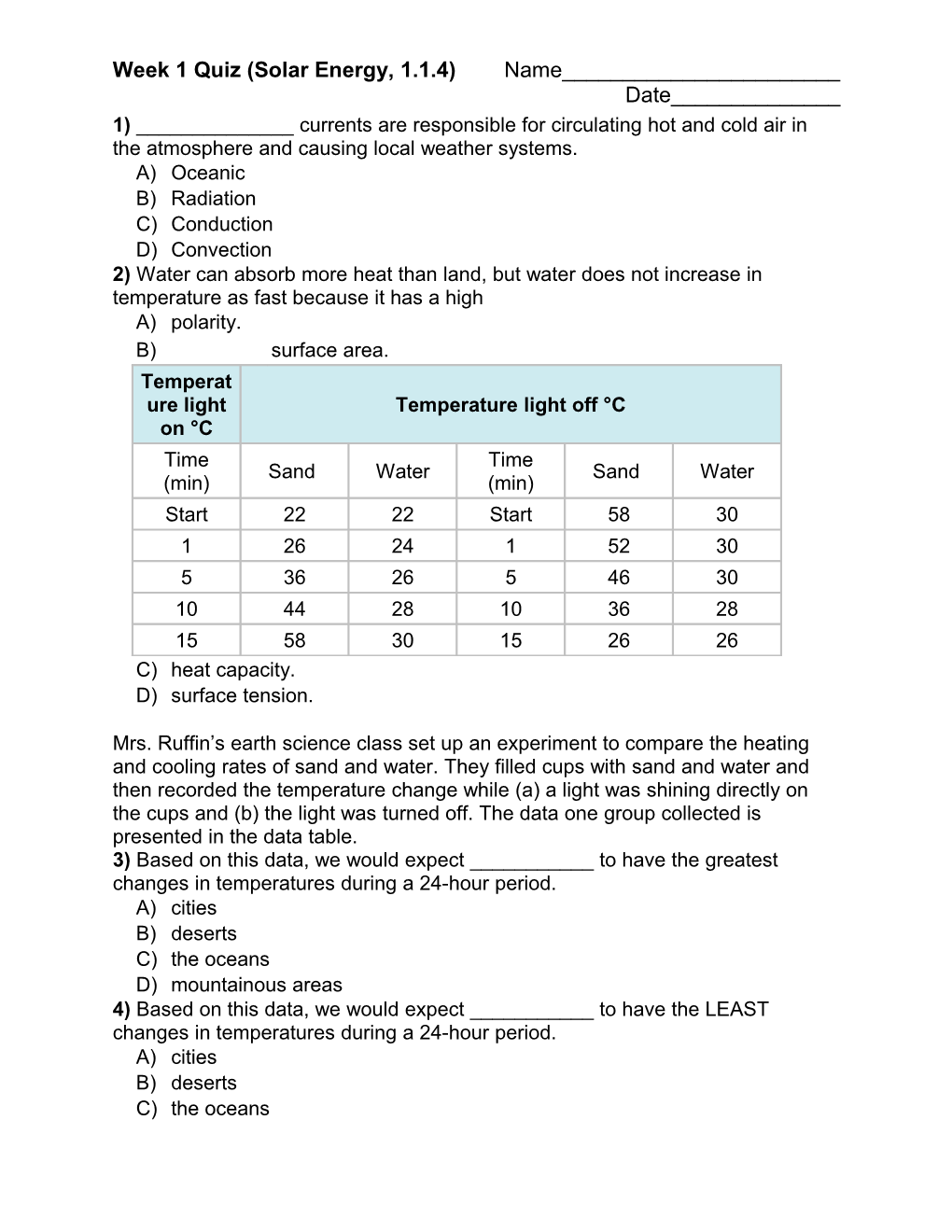
Week 1 Quiz (Solar Energy, 1.1.4) Name______Date______1) ______currents are responsible for circulating hot and cold air in the atmosphere and causing local weather systems. A) Oceanic B) Radiation C) Conduction D) Convection 2) Water can absorb more heat than land, but water does not increase in temperature as fast because it has a high A) polarity. B) surface area. Temperat ure light Temperature light off °C on °C Time Time Sand Water Sand Water (min) (min) Start 22 22 Start 58 30 1 26 24 1 52 30 5 36 26 5 46 30 10 44 28 10 36 28 15 58 30 15 26 26 C) heat capacity. D) surface tension.
Mrs. Ruffin’s earth science class set up an experiment to compare the heating and cooling rates of sand and water. They filled cups with sand and water and then recorded the temperature change while (a) a light was shining directly on the cups and (b) the light was turned off. The data one group collected is presented in the data table. 3) Based on this data, we would expect ______to have the greatest changes in temperatures during a 24-hour period. A) cities B) deserts C) the oceans D) mountainous areas 4) Based on this data, we would expect ______to have the LEAST changes in temperatures during a 24-hour period. A) cities B) deserts C) the oceans D) mountainous areas 5) If left in the sun, which would increase in temperature FIRST? A) a red object B) a black object C) a brown object D) a white object 6) What is primarily responsible for the creation of seasons on the earth? A) the tilt of the sun B) the distance from the sun C) the axial tilt of the earth D) the reflection of the sun's rays from the earth 7) Plants perform ______to process ______from the atmosphere and produce carbohydrates (sugars). A) Photosynthesis; Oxygen B) Photosynthesis; Carbon dioxide C) Respiration; Oxygen D) Respiration; Carbon dioxide 8) If Earth's atmosphere did NOT contain any water vapor, the temperature of the earth's surface would A) be about the same. B) be unable to fluctuate. C) be significantly lower. D) be significantly hotter. 9) Los Angeles is a city on the west coast of the United States that is very close to the Pacific Ocean. Land temperatures in Los Angeles remain relatively constant because of winds blowing from the ocean to the land at night and from the land to the ocean during the day. These winds are a result of: A) Conjunction B) Convection C) Nondisjunction D) Subduction 10) The temperature on land around the equator stays about the same throughout the year. This is because this area A) has a greater tilt than other parts of the Earth. B) receives less direct sunlight throughout the year. C) receives similar amounts of sunlight throughout the year. D) receives more direct sunlight than other parts of the Earth. 11) Polaris, the North Star, is almost always visible in the same location because A) it is the brightest star in the sky. B) it is gravitationally attracted to our sun. C) it is the closest star to the earth, besides our sun. D) the axis of the earth passes directly through the North Star. 12) The temperature in a desert can fluctuate from being over 100° F during the day to below 40° F at night. Why can the desert experience such a daily temperature change? A) The high amount of vegetation helps to shade the area. B) Being far away from the equator allows for the cooler temperatures. C) The high humidity of the desert allows for the air to cool down quickly. With no clouds and low humidity, much of the days heat is reflected back D) into the atmosphere. 13) Usually, it is observed that climates in coastal regions are moderate as compared to climates in the interiors of continents. Why is this so? Regions along the coast receive rain throughout the year; regions inland A) do not. A cool breeze constantly blows from the ocean across the land at all times B) of the year. Conditions over the oceans change rapidly because water loses or gains C) heat faster than land. Conditions over the oceans change slowly because water takes more time D) than land to gain or lose heat. 14) Day and night are the result of the earth's rotation on its own axis and its location from the sun. As the earth spins on its axis, parts of the planet are in the sun while others are in the dark. In other words, the sun appears to rise and set. The parts of the world that are in daylight get warmer while the parts that are dark gradually lose the heat they absorbed during the day. What causes day and night on Earth? A) The Earth orbits the Sun. B) The Sun goes around the Earth. C) The moon rises causing night time. D) The Earth rotates or spins on its axis every 24 hours.
Hand Washing Test Treatment Bacterial cultures (#/plate) Warm water 24 Hand sanitizer 28 Soap A 12 Soap B 13 15) Mr. Gomez's science class was studying bacteria. They learned that some bacteria are helpful but other species are harmful. With this in mind, the students conducted a test to see which hand washing method would be most effective in killing bacteria on the students' hands. The class data is found in the data table above. What is the independent variable in the experiment? A) Number of Harmful Bacteria. B) Number of Bacteria. C) Warm water. D) Hand Washing Method.
Root Word Matching
_____ 16) Anthro- a) crop
_____ 17) Agri- b) human
_____ 18) Aqu- c) height or distance
_____ 19) Alt- d) water
_____ 20) A- e) without
Week 1 Quiz (Solar Energy, 1.1.4) Name______Answer Sheet Date______
1. 5. 11. 15.
2. 6. 12. 16. 3. 7. 13. 17.
4. 8. 14. 18.
9. 19.
10. 20.
Week 1 Quiz (Solar Energy, 1.1.4) Name______Answer Sheet Date______
1. 5. 11. 15.
2. 6. 12. 16.
3. 7. 13. 17.
4. 8. 14. 18.
9. 19.
10. 20.
Week 1 Quiz (Solar Energy, 1.1.4) KEY
1. D 5. B 11. D 15. D
2. C 6. C 12. D 16. B
3. B 7. B 13. D 17. A 4. C 8. C 14. D 18. D
9. B 19. C
10. C 20. E
Week 1 Quiz (Solar Energy, 1.1.4) KEY
1. D 5. B 11. D 15. D
2. C 6. C 12. D 16. B
3. B 7. B 13. D 17. A
4. C 8. C 14. D 18. D
9. B 19. C
10. C 20. E