Test 3 - Sections 11, 12, 13 & 14 - MC Questions for Web Site
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
____ 1. In the short run, for a perfectly competitive firm, the portion of the MC curve at or above the shut-down price is also its: a. individual short-run supply curve. b. ATC curve. c. AVC curve. d. individual demand curve. e. profit curve. ____ 2. Suppose a monopoly is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output. At that level of output: a. marginal revenue equals marginal cost. b. marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost. c. marginal revenue is less than marginal cost. d. price is less than marginal cost. e. price is equal to marginal revenue.
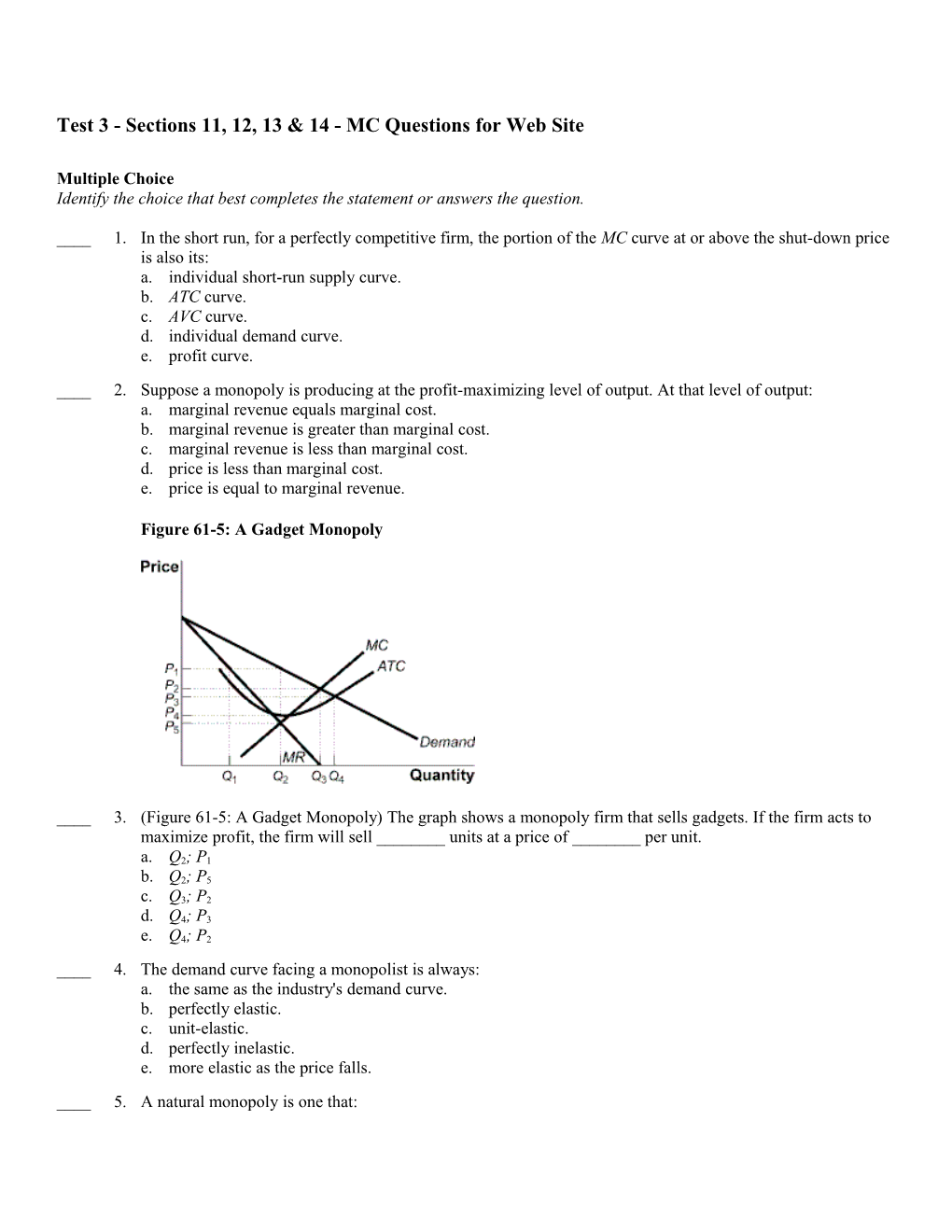
Figure 61-5: A Gadget Monopoly
____ 3. (Figure 61-5: A Gadget Monopoly) The graph shows a monopoly firm that sells gadgets. If the firm acts to maximize profit, the firm will sell ______units at a price of ______per unit.
a. Q2; P1 b. Q2; P5 c. Q3; P2 d. Q4; P3 e. Q4; P2 ____ 4. The demand curve facing a monopolist is always: a. the same as the industry's demand curve. b. perfectly elastic. c. unit-elastic. d. perfectly inelastic. e. more elastic as the price falls. ____ 5. A natural monopoly is one that: a. monopolizes a natural resource such as a mineral spring. b. is based on control of something occurring in nature (such as diamonds). c. has increasing returns to scale over the entire relevant range of output. d. typically has low fixed costs, making it easy and “natural” for it to shut out competitors. e. is created by a patent or copyright. ____ 6. An industry with two firms producing is generally called: a. a monopoly. b. monopolistic competition. c. a duopoly. d. perfect competition. e. monopsony.
Price ($ per stake) Quantity $14 30 13 35 12 40 11 45 10 50 9 55 8 60 7 65 Table 64-2: Demand for Wooden Stakes
____ 7. (Table 64-2: Demand for Wooden Stakes) The table shows the demand for wooden stakes in the town of Sunnyvale. Suppose the marginal cost of producing stakes is zero. The only two firms producing wooden stakes, Spike Inc. and Buffy Co., agree to produce only 50 stakes, with each firm producing only 25. What is Buffy's price effect if she cheats on the agreement and produces 30 stakes? a. $10 b. –$25 c. $20 d. $1 e. -$45
Figure 67-7: Firms in Monopolistic Competition
____ 8. (Figure 67-7: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) In panel C, the profit-maximizing quantity of output is generated by the intersection at point: a. U. b. V. c. W. d. X. e. T. ____ 9. (Figure 67-7: Firms in Monopolistic Competition) Zero economic profit is earned if the profit-maximizing price is price ______in panel ______. a. F; A b. G; A c. H; B d. I; C e. T; B ____ 10. The demand curve for a firm under monopolistic competition is best described as which of the following? a. U-shaped b. upward-sloping c. vertical d. horizontal e. downward-sloping
Figure 67-11: Comparing Long-Run Equilibriums
____ 11. (Figure 67-11: Comparing Long-Run Equilibriums) In the figure, which of the following statements is false? a. Firms in the market structure shown in panel (a) cannot have excess profits in the long run, but those in panel (b) can have excess profits in the long run. b. Panel (a) and panel (b) show markets in which firms are earning normal profits. c. Firms in the market shown in panel (a) produce identical products, whereas firms in the market shown in panel (b) produce similar products. d. Panel (a) and panel (b) show markets that have many firms. e. Panel (a) and panel (b) show markets that have no barriers to entry. ____ 12. The firm's value of marginal product curve slopes downward: a. only if the firm is a perfect competitor in the product market. b. because of diminishing returns. c. only if the firm is a perfect competitor in the labor market. d. only if the firm is a perfect competitor in both the labor and product market. e. only if the supply of labor is upward sloping. ____ 13. The best example of a private good is: a. the coast guard. b. public education. c. national defense. d. law enforcement. e. an automobile. ____ 14. The best example of a common resource is: a. public education. b. a municipal library. c. clean water. d. cable television broadcasting. e. a textbook. ____ 15. Volunteer fire departments are good examples of ______provision of ______. a. private; private goods b. public; common resources c. private; public goods d. public; artificially scarce goods e. public; private goods ____ 16. The best example of a good whose consumption is exclusive is: a. a park. b. an ocean. c. street lights. d. national defense. e. a bicycle.
Figure 76-4: Correcting for Market Failure
____ 17. (Figure 76-4: Correcting for Market Failure) Assume that there is an external cost involved in the market illustrated in the figure provided. If the government sector forces the private sector firms to face the external cost, then:
a. the supply curve shifts to the right from S2 to S1. b. the supply curve shifts to the left from S1 to S2. c. the supply curve is unaffected. d. price per unit decreases. e. the point of equilibrium will move from T to V. ____ 18. A software program is similar to an apple in that it is ______, but it is also similar to public safety in that it is ______. a. rival in consumption; nonexcludable b. nonrival in consumption; excludable c. excludable; nonrival in consumption d. nonexcludable; rival in consumption e. nonexcludable; nonrival in consumption ____ 19. Redistribution programs are means-tested. To qualify for such a program, a person must demonstrate that: a. his or her family size is larger than the average family size for the country as a whole. b. his or her average family income has fallen (or not gone up) during the past three years. c. he or she is making serious efforts to get a job, even though he or she is currently unemployed. d. his or her income is below a certain specified level. e. his or her age is above the average age in that demographic group. ____ 20. A sudden loss of income or a significant increase in costly medical expenses are examples of: a. economic insecurity. b. economic inequality. c. poverty thresholds. d. the Great Compression. e. discrimination. Test 3 - Sections 11, 12, 13 & 14 - MC Questions for Web Site Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 59/23 MSC: Critical Thinking 2. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: E REF: Module 61/25 MSC: Concept-Based 3. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: E REF: Module 61/25 MSC: Analytical Thinking 4. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 61/25 MSC: Concept-Based 5. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 62/26 MSC: Definitional 6. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: E REF: Module 62/48 MSC: Definitional 7. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: D REF: Module 62/48 MSC: Analytical Thinking 8. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 67/31 MSC: Critical Thinking 9. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 67/31 MSC: Critical Thinking 10. ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 67/31 MSC: Concept-Based 11. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 67/31 MSC: Critical Thinking 12. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 69/33 MSC: Analytical Thinking 13. ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 76/40 MSC: Concept-Based 14. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 76/40 MSC: Concept-Based 15. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 76/40 MSC: Critical Thinking 16. ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: E REF: Module 76/40 MSC: Concept-Based 17. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: D REF: Module 76/40 MSC: Concept-Based 18. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 76/40 MSC: Critical Thinking 19. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 78/42 MSC: Fact-Based 20. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 78/42 MSC: Critical Thinking