Note-taking Guide: Basic Internet for Teachers
At the beginning of the workshop, use the Pre column and mark the skills you have right now. At the end of the workshop, use the Post column to mark skills that you have learned.
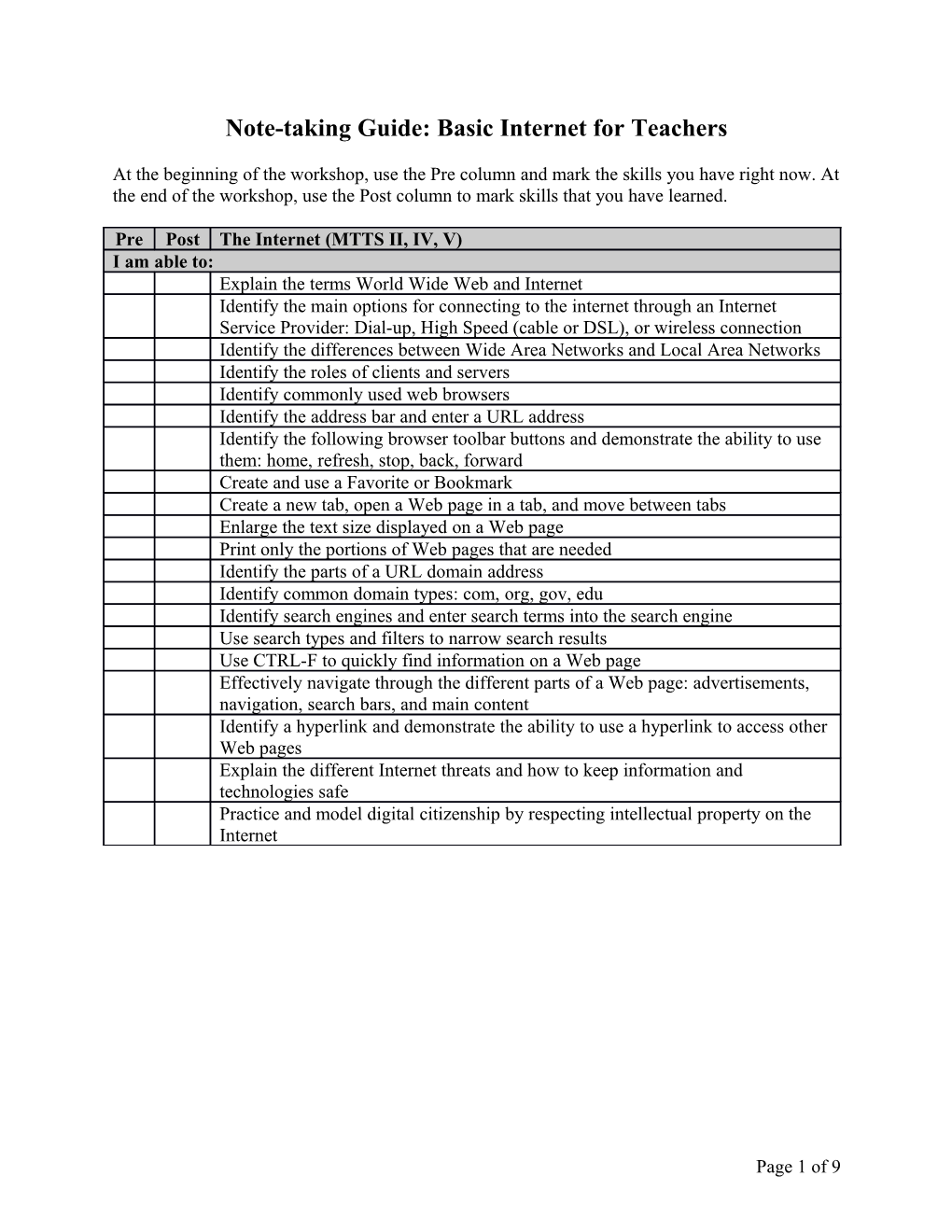
Pre Post The Internet (MTTS II, IV, V) I am able to: Explain the terms World Wide Web and Internet Identify the main options for connecting to the internet through an Internet Service Provider: Dial-up, High Speed (cable or DSL), or wireless connection Identify the differences between Wide Area Networks and Local Area Networks Identify the roles of clients and servers Identify commonly used web browsers Identify the address bar and enter a URL address Identify the following browser toolbar buttons and demonstrate the ability to use them: home, refresh, stop, back, forward Create and use a Favorite or Bookmark Create a new tab, open a Web page in a tab, and move between tabs Enlarge the text size displayed on a Web page Print only the portions of Web pages that are needed Identify the parts of a URL domain address Identify common domain types: com, org, gov, edu Identify search engines and enter search terms into the search engine Use search types and filters to narrow search results Use CTRL-F to quickly find information on a Web page Effectively navigate through the different parts of a Web page: advertisements, navigation, search bars, and main content Identify a hyperlink and demonstrate the ability to use a hyperlink to access other Web pages Explain the different Internet threats and how to keep information and technologies safe Practice and model digital citizenship by respecting intellectual property on the Internet
Page 1 of 9 Page 2 of 9 Computer Networks
two or more connected computers sharing certain resources in a typically consisting of two or more local networks, these relatively small geographic location, often in the same building connected computers are farther apart and are linked by telephone Example: Your school computer, printer, and server lines, dedicated telephone lines, or radio waves Example: the BCPS district intranet that includes email and website servers
You need the Internet to access the World Wide Web: The ______is like the highway system transporting information, (not people) between places. The ______is like the many locations in a city, all part of a larger community, but each with a different purpose and address.
Page 3 of 9 Web Browsers
Mozilla Google Microsoft Apple
Browser Toolbar
1 6
2 7
3 8
4 9
5
Page 4 of 9 Page 5 of 9 Anatomy of a URL http://blog.teacher.com/~jweaver/March.htm
Protocol Sub-domain Domain Top-level Domain Directory File or Webpage
Common Top-level domains are: .com .org .gov .edu
Search Engines
Search Types
Search Filters
Page 6 of 9 Anatomy of a Webpage
Use ______to quickly find something on a web page.
Open a hyperlink in a new tab by using ______.
Zoom in and out of the web page by pressing ______.
Page 7 of 9 Internet Safety
Passwords should…
Common Computer Threat Explanation
Keep your computer safe while browsing the Internet by:
Page 8 of 9 Internet Citizenship
Explain Fair Use:
Web sites for finding public domain and creative commons works:
Page 9 of 9