Diploma Programme subject outline—Group 5: mathematics and computer science
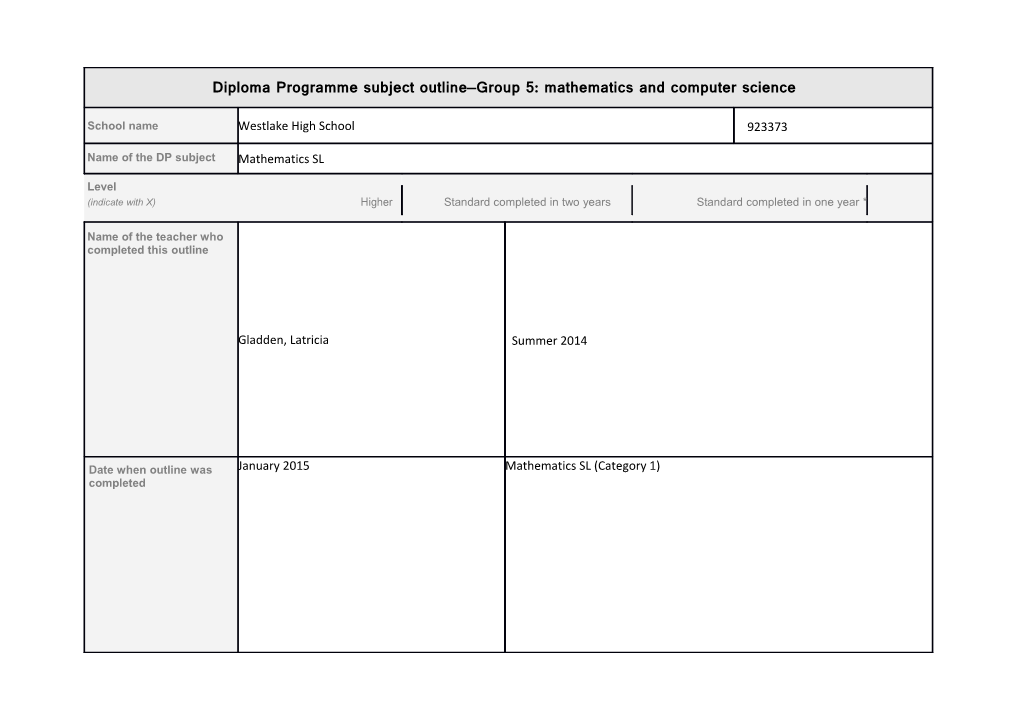
School name Westlake High School 923373
Name of the DP subject Mathematics SL
Level (indicate with X) Higher Standard completed in two years Standard completed in one year *
Name of the teacher who completed this outline
Gladden, Latricia Summer 2014
Date when outline was January 2015 Mathematics SL (Category 1) completed * All Diploma Programme courses are designed as two-year learning experiences. However, up to two standard level subjects, excluding languages ab initio and pilot subjects, can be completed in one year, according to conditions established in the Handbook of procedures for the Diploma Programme.
1. Course outline – Use the following table to organize the topics to be taught in the course. If you need to include topics that cover other requirements you have to teach (for example, national syllabus), make sure that you do so in an integrated way, but also differentiate them using italics. Add as many rows as you need.
– This document should not be a day-by-day accounting of each unit. It is an outline showing how you will distribute the topics and the time to ensure that students are prepared to comply with the requirements of the subject.
– This outline should show how you will develop the teaching of the subject. It should reflect the individual nature of the course in your classroom and should not just be a “copy and paste” from the subject guide.
– If you will teach both higher and standard level, make sure that this is clearly identified in your outline. Topic Allocated time (as identified in One minutes. 90 Assessment Resources the IB subject class is guide) instruments to be used List the main resources to be Contents In one State the topics in used, including information week the order you are technology if applicable. there are 2/3 classes. planning to teach them. Topic 2: Functions 2.4 Quadratic Functions 5 class periods Students will be assessed Safari Montage, Ti-84 Plus GDC’s, Year 1 and Equations Solve(2.7) using formative assessments, Promethean Board and Active Topic 1: Algebra weekly topic quizzes, monthly Graph (2.2) expressions, All-in-Learning Student cumulative assessments, response remotes and data analysis. Characteristics performance assessments, the Fathom software, Calculus in motion o Domain/Range internal assessment Sketchpad to visually display o Relative extrema concepts. Test generator software, o Intercepts USA Test prep where applicable, Text book TBD o Axis of symmetry transformations(2.3) 3 class periods Applications(2.8) 1.2 Elementary treatment of exponents and logarithms. Laws of exponents Laws of logarithms Change of base 3 class periods Solving equations(2.7) 2.6 Exponential functions Solve(2.7) Graph (2.2) Characteristics o Domain/Range o asymptotes o Intercepts 1 class periods o increasing/decreasing transformations(2.3) Applications(2.8) 3 class periods 2.1 Inverse function Establish the relationship between exponents and logarithms as inverses algebraically and graphically. 2.6 Logarithmic functions Solve(2.7) Topic Allocated time Resources (as identified in One 90 minutes. Assessment the IB subject Contents class is List the main resources to be guide) instruments to be used used, including information In one State the topics in 2/3 classes. technology if applicable. week the order you are there are Graph (2.2) Characteristics o Domain/Range o asymptotes o Intercepts o increasing/decreasing transformations(2.3) Applications(2.8)
Topic 1: Algebra 1.1 Arithmetic sequences and series 3 class periods Students will be assessed Safari Montage, Ti-84 Plus GDC’s, Year 1 using formative assessments, Promethean Board and Active Sum of a finite series using sigma weekly topic quizzes, monthly expressions, All-in-Learning Student notation cumulative assessments, response remotes and data analysis. Geometric sequences and series performance assessments, the Fathom software, Calculus in motion Sum of a finite and infinite series using internal assessment Sketchpad to visually display sigma notation concepts. Test generator software, Applications USA Test prep where applicable, Text 2 class periods book TBD 1.2 The binomial theorem Expansion of (a+b)n Calculation of binomial coefficients using Pascal’s triangle and Topic Allocated time Resources (as identified in One 90 minutes. Assessment the IB subject Contents class is List the main resources to be guide) instruments to be used used, including information In one State the topics in 2/3 classes. technology if applicable. week the order you are there are Topic 2: Functions 2.5 The reciprocal functions 3 class periods and Equations Solve(2.7) Graph (2.2) Self-inverse nature(2.1) Characteristics o Domain/Range o asymptotes o Intercepts o increasing/decreasing Transformations(2.3) 1 class periods Applications(2.8)
2.1 Composite Functions Topic Allocated time Resources (as identified in One 90 minutes. Assessment the IB subject Contents class is List the main resources to be guide) instruments to be used used, including information In one State the topics in 2/3 classes. technology if applicable. week the order you are there are Topic 3: Circular 3.1 The circle: Students will be assessed Safari Montage, Ti-84 Plus GDC’s, Year 1 2 class periods functions and Degrees to radian measure of angles using formative assessments, Promethean Board and Active trigonometry weekly topic quizzes, monthly expressions, All-in-Learning Student Length of an arc cumulative assessments, response remotes and data analysis. Area of a sector. performance assessments, the Fathom software, Calculus in motion internal assessment Sketchpad to visually display class periods 3.2 Definition of cosθ and sinθ in terms of the unit 3 concepts. Test generator software, circle USA Test prep where applicable, Text Definition of tanθ as sin θ /cos θ . book TBD Exact values of trigonometric ratios of π/ 6, π/4,π/3, π/2,0 and their multiples. 3 class periods 3.4 The circular functions sin x , cos x and tan x : Solve(2.7) Graph (2.2) Characteristics o Domain/Range o Asymptotes o amplitude o periodic nature o Intercepts Transformations(2.3) Applications(2.8) 3 class periods
3.3 Trigonometric Identities Pythagorean identity Double angle identity (sine and cosine) 3 class periods Relationship between trigonometric ratios
3.5 Solving trigonometric equations on a finite interval including quadratic equations in sine cosine or tangent. Analytically 4 class periods Graphically
3.6 Solutions if triangles Law of Sines (including the ambiguous case) Topic Allocated time Resources (as identified in One 90 minutes. Assessment the IB subject Contents class is List the main resources to be guide) instruments to be used used, including information In one State the topics in 2/3 classes. technology if applicable. week the order you are there are Law of Cosines Area of a triangle Applications(2.8) Topic Allocated time Resources (as identified in One 90 minutes. Assessment the IB subject Contents class is List the main resources to be guide) instruments to be used used, including information In one State the topics in 2/3 classes. technology if applicable. week the order you are there are Topic 6: Calculus 6.1 Informal ideas of limit and convergence 5 class periods Students will be assessed Safari Montage, Ti-84 Plus GDC’s, Year 1 Investigate limits graphically, numerically using formative assessments, Promethean Board and Active and algebraically weekly topic quizzes, monthly expressions, All-in-Learning Student cumulative assessments, response remotes and data analysis. Definition of the derivative performance assessments, the Fathom software, Calculus in motion o f’(x)= internal assessment Sketchpad to visually display o f’(x)= concepts. Test generator software, Interpret the derivative as a rate of change USA Test prep where applicable, Text book TBD Interpret the derivative as the slope function Find and use the equation of tangent lines to approximate values of functions Find equations of normal lines 3 class periods 6.2 Use of Derivatives rules on polynomials, trigonometric functions, ex, lnx, (include ax, rational functions, radical functions, and inverse functions) Sum and difference Product rule Quotient rule Chain rule for composite functions Second derivatives Higher order derivatives Implicit differentiation 10 class periods
6.3 Applications of Derivatives Curve Analysis Find local and global extrema using derivative tests Find points of inflection using the second derivative test for concavity Relate the behavior of the graphs of f f’ and f” Solve optimization problems Solve Related rates problems using implicit differentiation Solve motion problems determining when an object is at rest, moving in a Topic Allocated time Resources (as identified in One 90 minutes. Assessment the IB subject Contents class is List the main resources to be guide) instruments to be used used, including information In one State the topics in 2/3 classes. technology if applicable. week the order you are there are Topic 6: Calculus 6.4 Indefinite integration 3 class periods Students will be assessed Safari Montage, Ti-84 Plus GDC’s, Year 1 Polynomials using formative assessments, Promethean Board and Active weekly topic quizzes, monthly expressions, All-in-Learning Student Trigonometric functions cumulative assessments, response remotes and data analysis. ex and performance assessments, the Fathom software, Calculus in motion Composite functions with a linear function internal assessment Sketchpad to visually display concepts. Test generator software, Integration using U substitution for USA Test prep where applicable, Text book TBD 6.5 Definite integration with applications 10 class periods Analytically, graphically and using technology Differential equations Slopefields Find area under a curve Find area between two curves Find volumes of revolution , about horizontal and vertical axis Find volumes using cross sections of different shapes using bases with different shapes. i.e. squares, circles, triangles, and 3 class periods rectangles.
6.6 Integration problems n involving displacement, total distance traveled, velocity and acceleration. Topic 4: Vectors 4.1 Vectors as displacements in a plane and in three Students will be assessed Safari Montage, Ti-84 Plus GDC’s, Year 2 5 class periods dimensions using formative assessments, Promethean Board and Active Components of a vector and column weekly topic quizzes, monthly expressions, All-in-Learning Student representation cumulative assessments, response remotes and data analysis. performance assessments, the Fathom software, Calculus in motion Algebraic and geometric approaches to internal assessment Sketchpad to visually display o Sum and difference of two concepts. Test generator software, vectors, USA Test prep where applicable, Text o The zero vector, book TBD o The negative vector o Multiplication by a scalar o Magnitude of a vector and Unit vectors i,j and k o 5 class periods o Position vectors Topic Allocated time Resources (as identified in One 90 minutes. Assessment the IB subject Contents class is List the main resources to be guide) instruments to be used used, including information In one State the topics in 2/3 classes. technology if applicable. week the order you are there are 4.2 Scalar product of two vectors, Perpendicular vectors Parallel vectors angles between two vectors
Topic 4: Vectors 4.3 Representation of a line as r=a+tb and the angle 5 class periods Students will be assessed Safari Montage, Ti-84 Plus GDC’s, Year 2 between two lines; using formative assessments, Promethean Board and Active weekly topic quizzes, monthly expressions, All-in-Learning Student 4.4 Distinguish between coincident and parallel lines 5 class periods cumulative assessments, response remotes and data analysis. Determine if lines intersect locate the point performance assessments, the Fathom software, Calculus in motion of intersection of two lines as the solution to internal assessment Sketchpad to visually display a system concepts. Test generator software, USA Test prep where applicable, Text Topic: 5 Statistics and 5.1 Comparison of concepts 5 class periods book TBD Probability Population Sample Random sample Discrete data Continuous data Graphical Representations of data Frequency table Frequency histograms Box-and-whisker plots o Use of upper and lower boundaries o Interval widths 5 class periods o Mid-interval values
5.2 Calculations of Statistical measures and make interpretations of data using the results. Mean, median, mode, Range, interquartile range, quartiles, percentiles, variance and standard deviation Topic Allocated time Resources (as identified in One 90 minutes. Assessment the IB subject Contents class is List the main resources to be guide) instruments to be used used, including information In one State the topics in 2/3 classes. technology if applicable. week the order you are there are 5 class periods 5.3 Find median, quartiles and percentiles from cumulative frequencies and their graphs 5 class periods 5.8 Binomial distribution Binomial probabilities Mean and Variance of the binomial distribution 5 class periods Determine when random variables are best described using binomial distributions
5.9 Normal distribution and the “Bell” curve Standardization of normal variables Z-values and z-scores Characteristics of a normal distribution Year 2 Various Math Exploration Activities 10 class periods Topic: 5 Statistics and 5.4 Linear correlation of bivariate data 5 class periods Safari Montage, Ti-84 Plus GDC’s, Probability Pearson’s product-moment correlation Promethean Board and Active coefficient r expressions, All-in-Learning Student response remotes and data analysis. Scatter plots and linear regression equations Fathom software, Calculus in motion Use regressions lines to make predictions Sketchpad to visually display Use mathematical findings to make concepts. Test generator software, interpretations in the context of the USA Test prep where applicable, Text problem. book TBD 5 class periods 5.5 Probability Concepts trials, outcomes, equally likely outcomes, sample space and event probability of an event and its complement Use of Venn diagrams, tree diagrams and tables to solve problems 5 class periods
5.6 Find probabilities Combined events Mutually exclusive events Conditional probability definition Independent events definition Probabilities with and without replacement 5 class periods Topic Allocated time Resources (as identified in One 90 minutes. Assessment the IB subject Contents class is List the main resources to be guide) instruments to be used used, including information In one State the topics in 2/3 classes. technology if applicable. week the order you are there are 5.7 Concept of discrete random variables and their probability distributions Find expected value for discrete data Investigate real world uses of probability distribution and expected value
IB Exam Review 15 class periods 2. IB internal assessment requirement to be completed during the course
Briefly explain how and when you will work on it. Include the date when you will first introduce the internal assessment requirement to your students, the different stages and when the internal assessment requirement will be due.
The internal assessment (IA) will involve investigations and problem solving assignments. Students will be assessed on their ability to read, interpret and solve a given problem using appropriate mathematical terms, organize and present information and data in tabular, graphical and/or diagrammatic forms, using appropriate notation and terminology, formulate a mathematical argument and communicate it clearly, select and use appropriate mathematical strategies and techniques, demonstrate an understanding of both the significance and the reasonableness of results, recognize patterns and structures, make generalizations, recognize and demonstrate an understanding of the practical applications of mathematics, use appropriate technological devices as mathematical tools and demonstrate an understanding of and the appropriate use of mathematical modeling. The topic will be introduced and students will begin working on the IA when Calculus is introduced. The IA will be due at the beginning of the second semester of the second year.
3. Links to TOK
You are expected to explore links between the topics of your subject and TOK. As an example of how you would do this, choose one topic from your course outline that would allow your students to make links with TOK. Describe how you would plan the lesson.
Topic Link with TOK (including description of lesson plan)
1.1 Arithmetic sequences and Students in pairs would be challenged to find the sum of the first 100 integers without the use of a calculator. After they work on the task for a few minutes I’ll let them series: Sum of a finite know that an 8 year old was able to find the sum in his head. After pairs arrive at their conclusions we will discuss their methods and any patterns they observed. Students series using sigma notation will be prompted to find an equation that describes their pattern or process and verify that it works for any number of integers. We will then discuss the idea of mathematical intuition and the basis for formal proof.
4. International mindedness
Every IB course should contribute to the development of international mindedness in students. As an example of how you would do this, choose one topic from your outline that would allow your students to analyze it from different cultural perspectives. Briefly explain the reason for your choice and what resources you will use to achieve this goal.
Topic Contribution to the development of international mindedness (including resources you will use)
3.1 Circular functions and Students will investigate the origins of the metric system and countries willingness to adopt the metric system for their units of measure for distance, weight and capacity. trigonometry Students will then investigate the answer the question. Why haven’t circular functions been converted to the metric system? Students will research the Babylonian origins of the 360 degree circle and its influences on the world. 5. Development of the IB learner profile
Through the course it is also expected that students will develop the attributes of the IB learner profile. As an example of how you would do this, choose one topic from your course outline and explain how the contents and related skills would pursue the development of any attribute(s) of the IB learner profile that you will identify.
Topic Contribution to the development of the attribute(s) of the IB learner profile
Random sampling from Contribution to the development of the attribute(s) of the IB learner profile: Inquiry, risk-taking, reflection. populations; graphical displays of data Sampling from populations and then displaying the results requires a fundamental knowledge of the tools necessary to achieve accurate results. Clear presentation is also necessary. The impact of displaying accurate versus inaccurate results on public opinion and elections throughout the world will be discussed. Suggestions for presenting and displaying clear and meaningful results will be debated.
6. Resources
Describe the resources that you and your student will have to support the subject. Indicate whether they are sufficient in terms of quality, quantity and variety. Briefly describe what plans are in place if changes are needed.