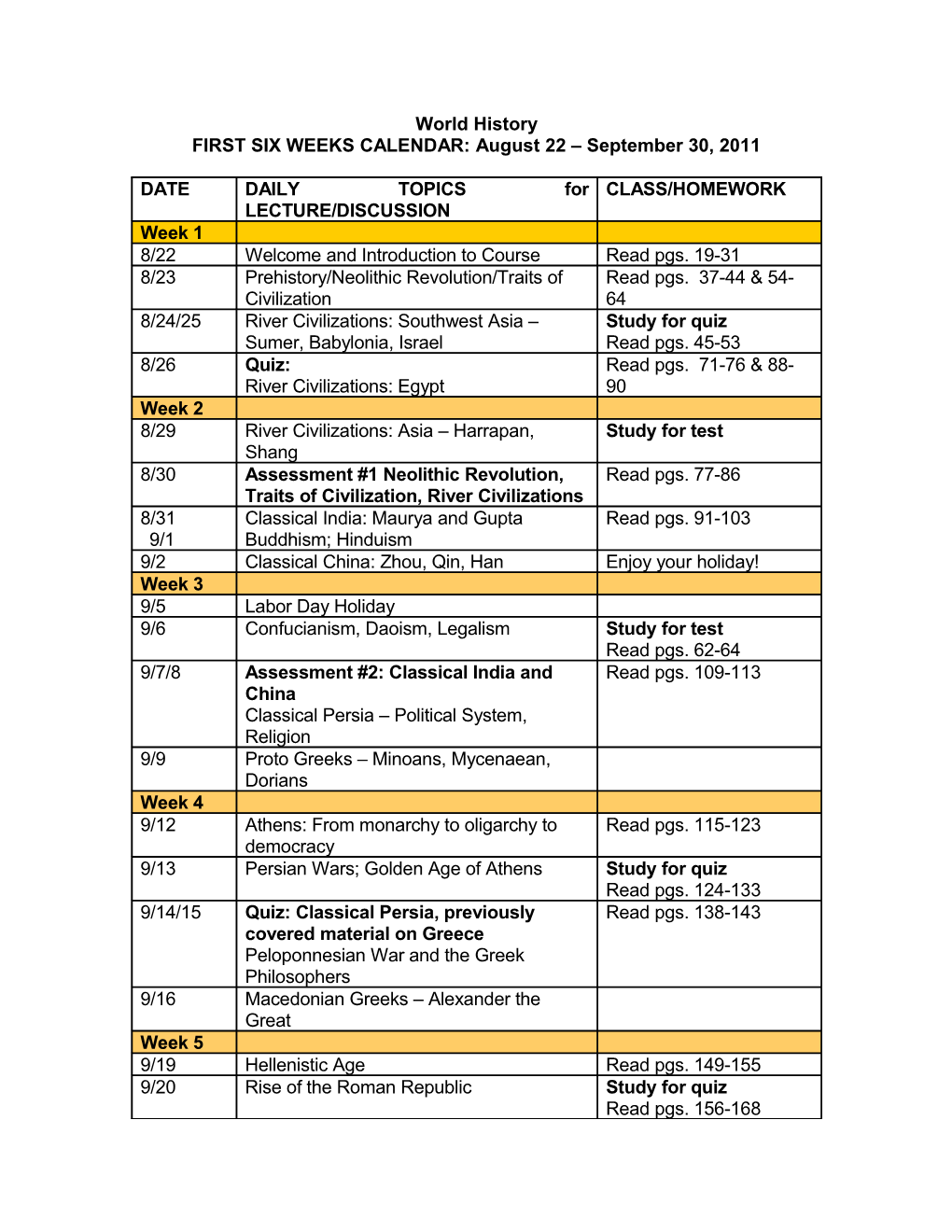
World History FIRST SIX WEEKS CALENDAR: August 22 – September 30, 2011
DATE DAILY TOPICS for CLASS/HOMEWORK LECTURE/DISCUSSION Week 1 8/22 Welcome and Introduction to Course Read pgs. 19-31 8/23 Prehistory/Neolithic Revolution/Traits of Read pgs. 37-44 & 54- Civilization 64 8/24/25 River Civilizations: Southwest Asia – Study for quiz Sumer, Babylonia, Israel Read pgs. 45-53 8/26 Quiz: Read pgs. 71-76 & 88- River Civilizations: Egypt 90 Week 2 8/29 River Civilizations: Asia – Harrapan, Study for test Shang 8/30 Assessment #1 Neolithic Revolution, Read pgs. 77-86 Traits of Civilization, River Civilizations 8/31 Classical India: Maurya and Gupta Read pgs. 91-103 9/1 Buddhism; Hinduism 9/2 Classical China: Zhou, Qin, Han Enjoy your holiday! Week 3 9/5 Labor Day Holiday 9/6 Confucianism, Daoism, Legalism Study for test Read pgs. 62-64 9/7/8 Assessment #2: Classical India and Read pgs. 109-113 China Classical Persia – Political System, Religion 9/9 Proto Greeks – Minoans, Mycenaean, Dorians Week 4 9/12 Athens: From monarchy to oligarchy to Read pgs. 115-123 democracy 9/13 Persian Wars; Golden Age of Athens Study for quiz Read pgs. 124-133 9/14/15 Quiz: Classical Persia, previously Read pgs. 138-143 covered material on Greece Peloponnesian War and the Greek Philosophers 9/16 Macedonian Greeks – Alexander the Great Week 5 9/19 Hellenistic Age Read pgs. 149-155 9/20 Rise of the Roman Republic Study for quiz Read pgs. 156-168 9/21/22 Quiz: Classical Greece and Rise of Read pgs. 169-174 Roman Republic From Republic to Empire; Pax Romano 9/23 Rise of Christianity Read pgs. 175-178 Week 6 9/26 Fall of Rome and its Legacy 9/27 Comparing the fall of Rome and Han Study for test China Read pgs. 191-195 9/28/29 Assessment #3 (including CBA Read pgs. 199-202 #1)Classical Persia, Greece, Rome The Rise of Islam – Muhammad and Islamic Faith 9/30 Spread of Arab empire and its impact on Afroeuroasia
Schedule subject to change to meet the needs of the class. TEKS for First Six Weeks 8000 BC to 500 BC Identify major causes and describe the major effects of the development of agriculture and the development of the river valley civilizations Summarize the impact of the development of farming (Neolithic Revolution) on the creation of river valley civilizations Identify the characteristics of civilization Explain how major river valley civilizations influenced the development of the classical civilizations Identify important changes in human life caused by the Neolithic Revolution Summarize the role of economics in driving political changes as related to the Neolithic Revolution Identify the characteristics of monarchies and theocracies as forms of government in early civilizations Identify the characteristics of the political system – theocracy Explain the development of democratic-republican government from its beginnings in the Judeo legal tradition Identify the impact of political and legal ideas contained in the following significant historic documents: including, Hammurabi's Code, the Jewish Ten Commandments Summarize trace the historical development of the rule of law during antiquity Describe and compare the historical origins, central ideas, and the spread of major religious and philosophical traditions, including the development of monotheism (Zoroastrianism) Identify examples of religious influence on various events referenced during antiquity Describe the changing roles of women, children, and families during antiquity Identify significant examples of art and architecture that demonstrate an artistic ideal or visual principle from antiquity Identify the origin and diffusion of major new ideas in mathematics, science, and technology that occurred in river valley civilizations 500 BC BCE to AD 600 Identify major causes and describe the major effects of the following events: The development of the classical civilizations of Greece, Rome, Persia, India (Maurya and Gupta), China (Zhou, Qin, and Han) the development of major world religions Summarize fundamental ideas and institutions of Eastern civilizations that originated in China and India Describe the major political, religious/philosophical, and cultural influences of Persia, India, China, Israel, Greece, and Rome, including the development of monotheism, Judaism, and Christianity Identify the characteristics of the following political systems: democracy, republic, oligarchy, and totalitarianism Explain the development of democratic-republican government from its beginnings in classical Greece and Rome Identify the influence of ideas regarding the right to a “trial by a jury of your peers”, and the concepts of “innocent until proven guilty” and “equality before the law” that originated in Greece and Rome Describe the historical origins, central ideas, and the spread of major religious and philosophical traditions, including Christianity Identify the contributions of significant scientists such as Archimedes, Eratosthenes, Pythagoras Compare the factors that led to the collapse of Rome and Han China Analyze how the Silk Road and the African gold-salt trade facilitated the spread of ideas and trade Describe how people have participated in supporting or changing their governments Describe the different roles rights and responsibilities of citizens and noncitizens in historical cultures, especially as the roles pertain to civic participation throughout history Describe the specific changing roles of women, children, and families from 500 BC to AD 600 Identify significant examples of art and architecture that demonstrate an artistic ideal or visual principle from 500 BC to AD 600 Identify the origin and diffusion of major new ideas in mathematics, science, and technology that occurred from 500 BC to AD 600
Required Historical Personalities: Hammurabi Archimedes Erastothenes Pythagoras