Study guide unit 2
_____1) If a gas pressure gauge reads 15 mm Hg, what is the pressure in atmospheres? A) 0.020 atm B) 0.20 atm C) 15 atm D) 1100 atm E) 11,000 atm
____2) Which of the following changes increases the pressure of a gas? A) increasing the volume B) decreasing the temperature C) decreasing the number of gas molecules D) all of the above E) none of the above
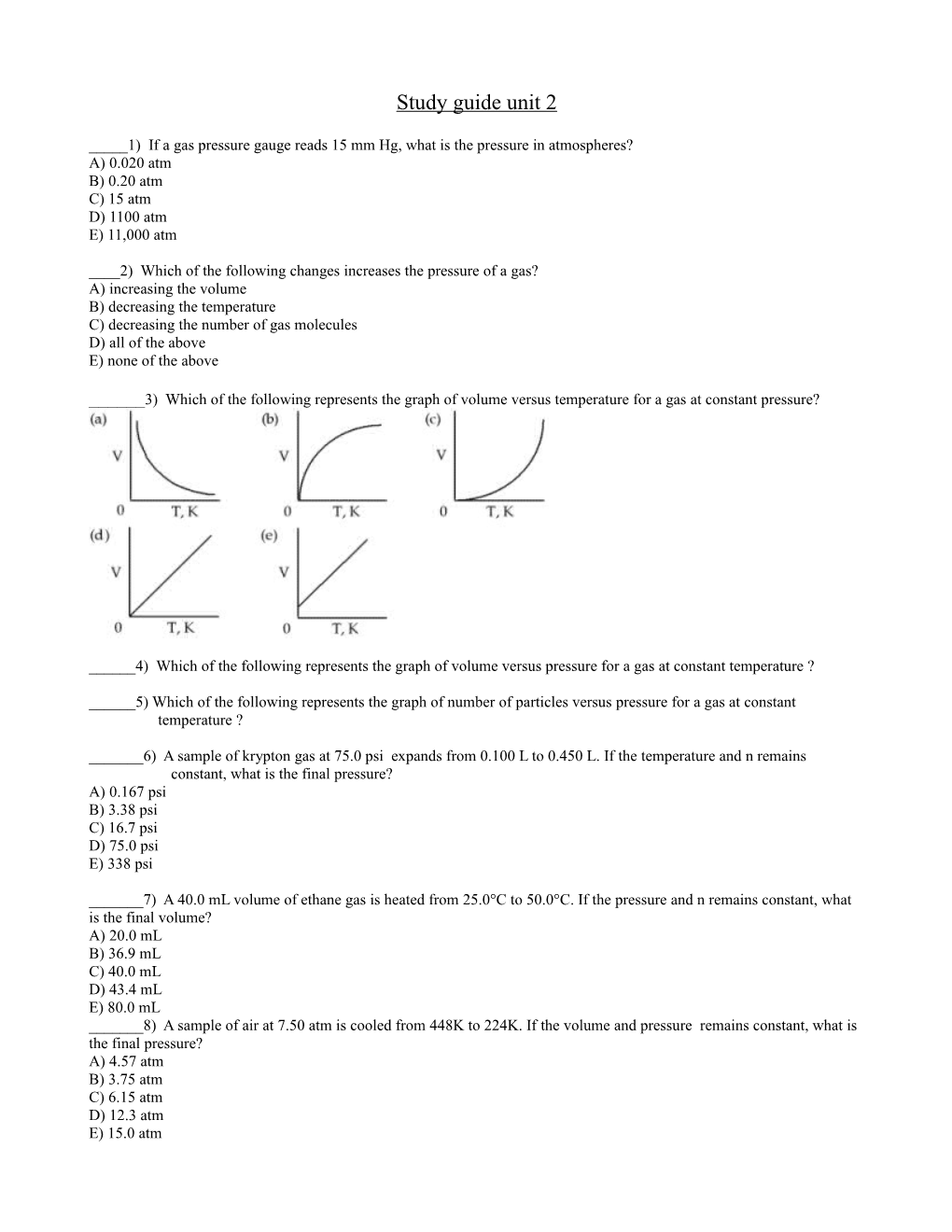
______3) Which of the following represents the graph of volume versus temperature for a gas at constant pressure?
______4) Which of the following represents the graph of volume versus pressure for a gas at constant temperature ?
______5) Which of the following represents the graph of number of particles versus pressure for a gas at constant temperature ?
______6) A sample of krypton gas at 75.0 psi expands from 0.100 L to 0.450 L. If the temperature and n remains constant, what is the final pressure? A) 0.167 psi B) 3.38 psi C) 16.7 psi D) 75.0 psi E) 338 psi
______7) A 40.0 mL volume of ethane gas is heated from 25.0°C to 50.0°C. If the pressure and n remains constant, what is the final volume? A) 20.0 mL B) 36.9 mL C) 40.0 mL D) 43.4 mL E) 80.0 mL ______8) A sample of air at 7.50 atm is cooled from 448K to 224K. If the volume and pressure remains constant, what is the final pressure? A) 4.57 atm B) 3.75 atm C) 6.15 atm D) 12.3 atm E) 15.0 atm ______9) If a 50.0 mL sample of xenon gas is at 0.921 atm and 27°C, what is the volume of the gas at 0 C and 1atm? n is constant. A) 41.9 mL B) 49.4 mL C) 50.6 mL D) 54.9 mL E) 59.7 mL
______10) An atmospheric sample is composed of nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and traces of other gases. If the partial pressure of nitrogen is 587 torr, oxygen is 158 torr, and argon is 7 torr, what is the observed barometric pressure? A) 8 torr B) 100 torr C) 422 torr D) 752 torr E) 1512 torr
______11) At the same temperature, which of the following gases contains molecules with the fastest average velocity? A) hydrogen, H2 B) nitrogen, N2 C) oxygen, O2 D) ozone, O3 E) The average velocity is the same.
______12) Which of the following explains why the volume of a gas increases when the temperature increases, and the pressure remains constant? A) The kinetic energy of gas molecules increases. B) The velocity of gas molecules increases. C) The collision frequency increases. D) all of the above E) none of the above
_____13) What happens to the pressure of carbon dioxide gas if the number of molecules increases by two (volume and temperature remain constant)? A) Pressure decreases by two. B) Pressure decreases by four. C) Pressure increases by two. D) Pressure increases by four. E) none of the above
_____14) Which of the following changes decreases the pressure of a gas? A) increasing the volume B) decreasing the temperature C) decreasing the number of gas molecules D) all of the above E) none of the above For each statement below write true or false.
1. If you increase the number of particles gas pressure increases.------
2. If you increase the temperature pressure increases.------
3. If you increase the volume pressure increases. ------
4. According to the kinetic theory gas particles are attracted to each other.------
5.Pressure is caused by the collision of gas particles.------
6.When the volume is decreased, pressure increases if the temperature is kept constant. --
7. Gas particles are always in constant random motion.------
8. Absolute zero is the temperature at which kinetic energy of the particles is zero, so all motion of gas particles stops.------
9. Absolute zero is 273K.------For problems 10-14 , Show work and label.
10. A sample of gas occupies a volume of 3.2L at 1.3 atm and 20 0C. If the volume of the gas is 5.0L at 25 0C, what is the pressure? n is constant.
P V T n Initial
Effect
Final
11. A sample of carbon dioxide gas is at 273K and 244kpa. What will its pressure be at 400K? V and n are constant.
P V T n Initial
Effect
Final
12. The volume of a gas at 4.00 atm is 600 ml. If the pressure is increased to 5.00 atm, what will be the new volume? T and n are constant.
P V T n Initial
Effect
Final 13. A 6.00L volume of methane gas is cooled from 120 0C to 90 0C. If the pressure and n remains constant, what is the final volume?
P V T n Initial
Effect
Final
14. A sample of gas occupies a volume of 4.0L at 2.3 atm and 30 0C. If the volume of the gas is 6.0L at 45 0C, what is the pressure?
P V T n Initial
Effect
Final
15. Convert 44.5kPa to atmospheres.
16. Convert 5 atms to psi.
17. what is STP? 1 18. .Label the following examples as being representative of a direct or inverse relationship.
a) pressure versus volume of a gas ------
b) volume versus temperature ------
c) pressure versus temperature ------
d) number of particles versus pressure------
19. If two variables have a direct relationship, what happens to the value of one as the value of the other is increased? Draw arrows to represent this. P T V T P n
20. If two variables have an inverse relationship, what happens to the value of one as the value of the other increases? P V
21. Explain why an unopened bag of potato chips left in a hot car appears to become larger?
22. What do we mean by atmospheric pressure? What causes this pressure?
23. How do we measure atmospheric measure? Is atmospheric pressure the same everywhere on the surface of the earth?
24. Explain why the alcohol level in a thermometer rises when it is placed in a warmer fluid.
25. Explain why the alcohol level in a thermometer falls when it is placed in a cooler fluid. 26. Ethyl salicylate is an organic liquid used in industry as a wintergreen scent. The liquid is volatile(easily evaporates) at room temperature. a) A bottle of ethyl salicylate is opened at the front of the classroom. Explain how someone at the back of the classroom can eventually smell the scent.
b) Draw diagrams (at the particle level) of your explanation.
c) Diffusion is easily observed with liquids and gases. Explain why diffusion is not usually observed in solid substances.
10. The gas in the box at left has a higher pressure than the gas in the box at the right. Draw “whooshies” on the particles in each box to represent their relative motion. Explain.
10. The gas in the box at left has a higher temperature than the gas in the box at the right. Draw “whooshies” on the particles in each box to represent their relative motion. Explain.