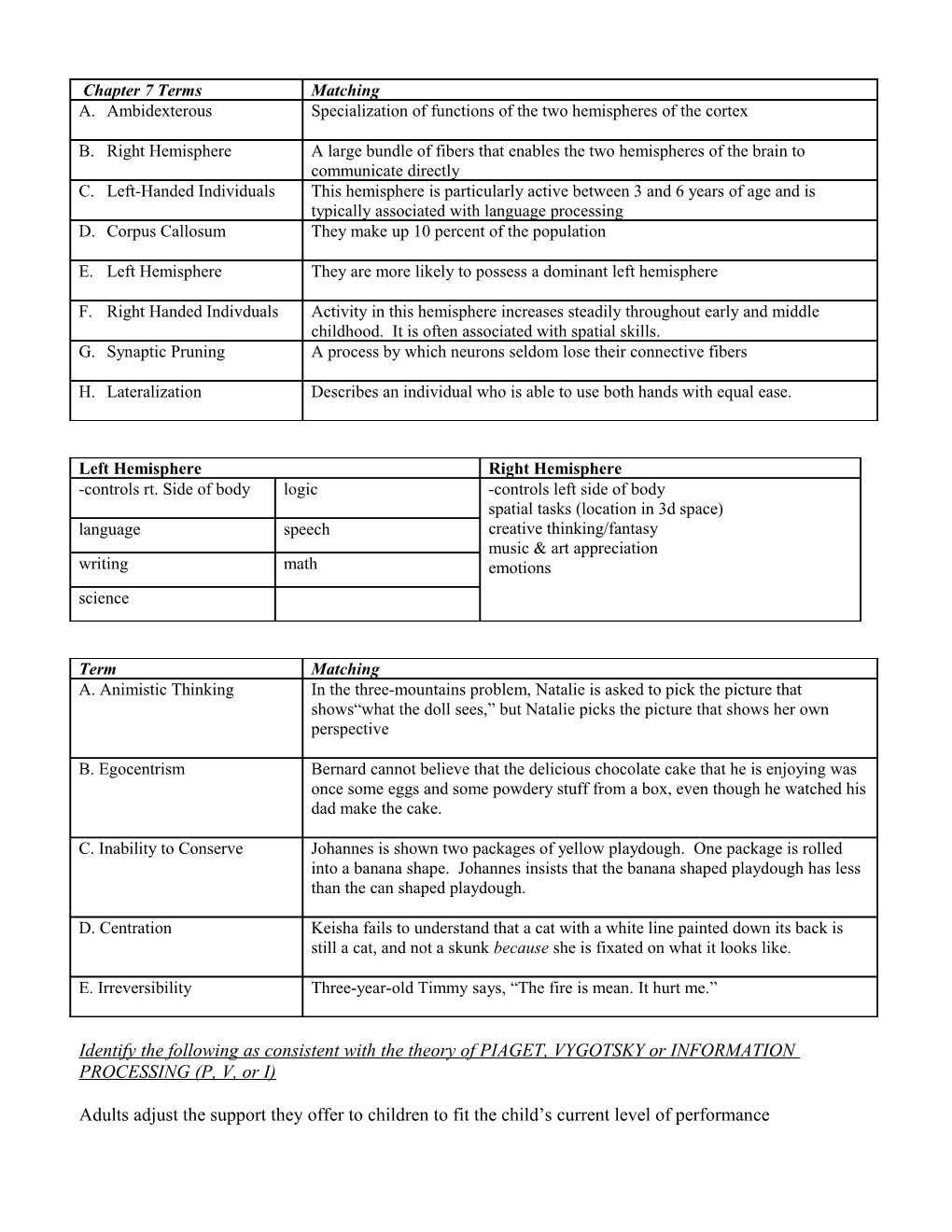
Chapter 7 Terms Matching A. Ambidexterous Specialization of functions of the two hemispheres of the cortex
B. Right Hemisphere A large bundle of fibers that enables the two hemispheres of the brain to communicate directly C. Left-Handed Individuals This hemisphere is particularly active between 3 and 6 years of age and is typically associated with language processing D. Corpus Callosum They make up 10 percent of the population
E. Left Hemisphere They are more likely to possess a dominant left hemisphere
F. Right Handed Indivduals Activity in this hemisphere increases steadily throughout early and middle childhood. It is often associated with spatial skills. G. Synaptic Pruning A process by which neurons seldom lose their connective fibers
H. Lateralization Describes an individual who is able to use both hands with equal ease.
Left Hemisphere Right Hemisphere -controls rt. Side of body logic -controls left side of body spatial tasks (location in 3d space) language speech creative thinking/fantasy music & art appreciation writing math emotions science
Term Matching A. Animistic Thinking In the three-mountains problem, Natalie is asked to pick the picture that shows“what the doll sees,” but Natalie picks the picture that shows her own perspective
B. Egocentrism Bernard cannot believe that the delicious chocolate cake that he is enjoying was once some eggs and some powdery stuff from a box, even though he watched his dad make the cake.
C. Inability to Conserve Johannes is shown two packages of yellow playdough. One package is rolled into a banana shape. Johannes insists that the banana shaped playdough has less than the can shaped playdough.
D. Centration Keisha fails to understand that a cat with a white line painted down its back is still a cat, and not a skunk because she is fixated on what it looks like.
E. Irreversibility Three-year-old Timmy says, “The fire is mean. It hurt me.”
Identify the following as consistent with the theory of PIAGET, VYGOTSKY or INFORMATION PROCESSING (P, V, or I)
Adults adjust the support they offer to children to fit the child’s current level of performance Young children are not capable of operations (mental actions that obey logical rules). Preschoolers cannot use memory strategies such as rehearsal or categorization because such strategies tax a young child’s limited working memories. Young children egocentrically assign human purposes to physical events. There is an abrupt change toward logical reasoning at around age 6 or 7 Stresses the social context of cognitive development A classroom based on this approach relies upon assisted discovery and peer collaboration Around age 4, children realize that false beliefs – ones that do not represent reality accurately – can guide people’s actions Focuses on the mental strategies that child use to transform the stimuli following their mental systems Children’s self-directed speech is the foundation for all higher cognitive processes Preschoolers rely on scripts to remember familiar, repeated events In a classroom in this tradition, children are encouraged to discover for themselves through spontaneous interaction with the environment