Version FINAL rev 140813
Electronic Supplementary Material
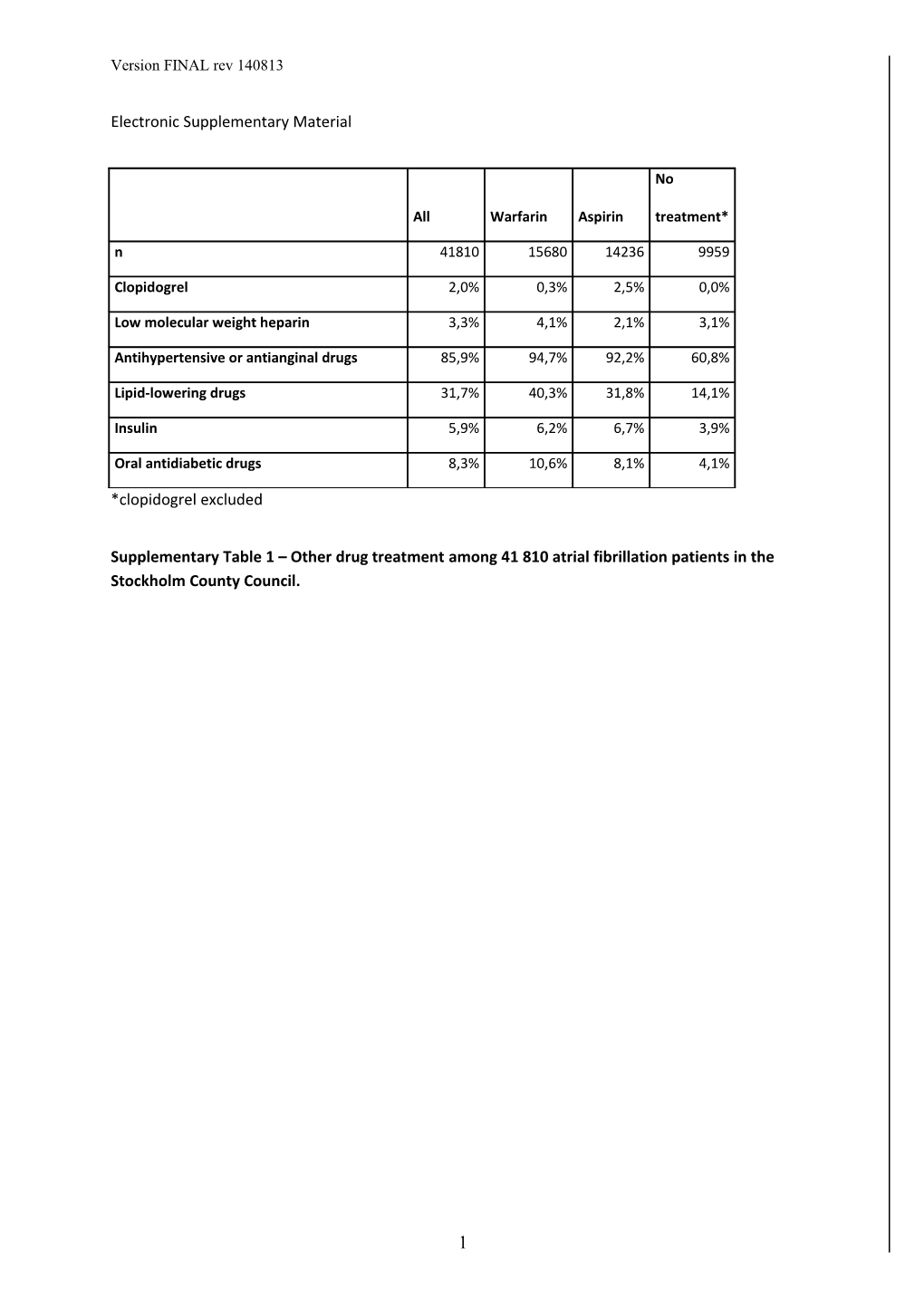
No
All Warfarin Aspirin treatment*
n 41810 15680 14236 9959
Clopidogrel 2,0% 0,3% 2,5% 0,0%
Low molecular weight heparin 3,3% 4,1% 2,1% 3,1%
Antihypertensive or antianginal drugs 85,9% 94,7% 92,2% 60,8%
Lipid-lowering drugs 31,7% 40,3% 31,8% 14,1%
Insulin 5,9% 6,2% 6,7% 3,9%
Oral antidiabetic drugs 8,3% 10,6% 8,1% 4,1%
*clopidogrel excluded
Supplementary Table 1 – Other drug treatment among 41 810 atrial fibrillation patients in the Stockholm County Council.
1 Version FINAL rev 140813
Supplementary Figure 1 – Factors contributing to CHA2DS2VASc scores 1 and 2 in 9 032 AF patients with warfarin, aspirin or no treatment*.
*clopidogrel excluded
2 Version FINAL rev 140813
Supplementary Figure 2 –Risks of suffering ischemic (IS) and hemorrhagic stroke (HS) during 2010 in 41810 AF patients, warfarin vs. no warfarin (i.e. aspirin or no treatment according to [3]).
Patients who had claimed prescriptions of both warfarin and aspirin are included in the warfarin group.
The patients having claimed both warfarin and aspirin between between July 1st 2009 and Dec 31st
2009 (n=1574) represented 3.8% of the total atrial fibrillation cohort. They were younger than the patients in the warfarin and aspirin groups: their mean age was 72.3 years and 71.1 % were under
the age of 80. The majority were men (63.0%). The mean CHA2DS2VASc score was 4.0 and 47.9% had vascular disease, which was more common than in the other treatment groups. Also, diabetes
(24.5%) and hypertension (72.2%) were slightly more common. Other co-morbidity was similar to the warfarin treated patients, while clopidogrel (5.8%) and lipid lowering treatment (53.2%) were more common.
Their risk of suffering ischemic stroke was 5.2%, thromboembolism 7.2%, hemorrhagic stroke 0.8%, traumatic intracranial bleeding 0.3%, any severe bleed 3.4%, and death 9.0%
3 Version FINAL rev 140813
Supplementary Text – Characteristics and Outcomes of 1574 AF Patients Claiming both Warfarin and Aspirin
4 Version FINAL rev 140813
Diagnosis ICD-code beginning with
Alcohol abuse E244, F10, G312, G621, G721, I426, K292, K70,
K860, O354, P043, Q860, T51, Y90-91, Z502, Z714
Anemia D50-64
Any severe bleed I60-62, I690-I692,, S064-S066, I850, I983, K25-28
(subcodes 0-2 and 4-6 only), K625, K922, D629
Atrial fibrillation I48
Cancer entire C-series
Cardioversion Procedure codes DF026, DF027
COPD/Emphysema J43-44
Dementia F00-F03
Diabetes E10-E14
Frequent falls (more than one W00-19 registration)
Gastric duadenal bleeding K25-28 (subcodes 0-2 and 4-6 only)
Heart failure I50
Hypertension I10-I15
Ischemic stroke, arterial I63, I64, I679, I693, I694, I698, I67-, I69-, Z866, embolism, and stroke, Z867, G450, G451, G452, G453, G458, G45.9, unspecified G45-, I74
Intracranial bleeding I60-I62, I690-I692, S064-S066
Liver disease K70-77
Mechanical valve Procedure codes FCA60, FCA70, FDC10, FGE00,
FGE10, FGE20, FGE96, FJF00, FJF10, FJF12, FJF20,
FJF96, FKD00, FKD10, FKD20, FKD96, FMD00,
FMD10, FMD12, FMD13, FMD20, FMD30, FMD40,
5 Version FINAL rev 140813
FMD96
Mitral stenosis I050, I052, I342
Obesity E65-66
Renal disease N17-19
Vascular disease I20-I25, I70, I739
Venous thromboembolism I26, I80-I82
Outcomes
(only inpatient care or specialist ambulatory care)
Any severe bleed I60-62, S064-S066, I850, I983, K25-28 (subcodes
0-2 and 4-6 only), K625, K922, D629
Intracranial bleeding I60-I62, S064-S066
Ischemic stroke I63
Hemorrhagic stroke I60-I62
Thromboembolism I63, I64, G450, G451, G452, G453, G458, G459,
I74
Traumatic intracranial bleeding S064-S066
Supplementary Appendix A - Definitions of co-morbidities and outcomes by ICD-10, primary care codes and procedure codes.
Treatment ATC-code beginning with
Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) B01AC06
Antihypertensive drugs C03, C07, C08, C09
Clopidogrel B01AC04
Insulin A10A
Lipid-lowering treatment C10
Low molecular weight heparin B01AB04, B01AB05
Oral antidiabetic treatment A10B
Warfarin B01AA
6 Version FINAL rev 140813
Supplementary Appendix B – ATC-codes of concomitant treatments.
7