Confidential: Not for duplication, dissemination, or citation.
Table e-1: Plasmapheresis Evidence Table
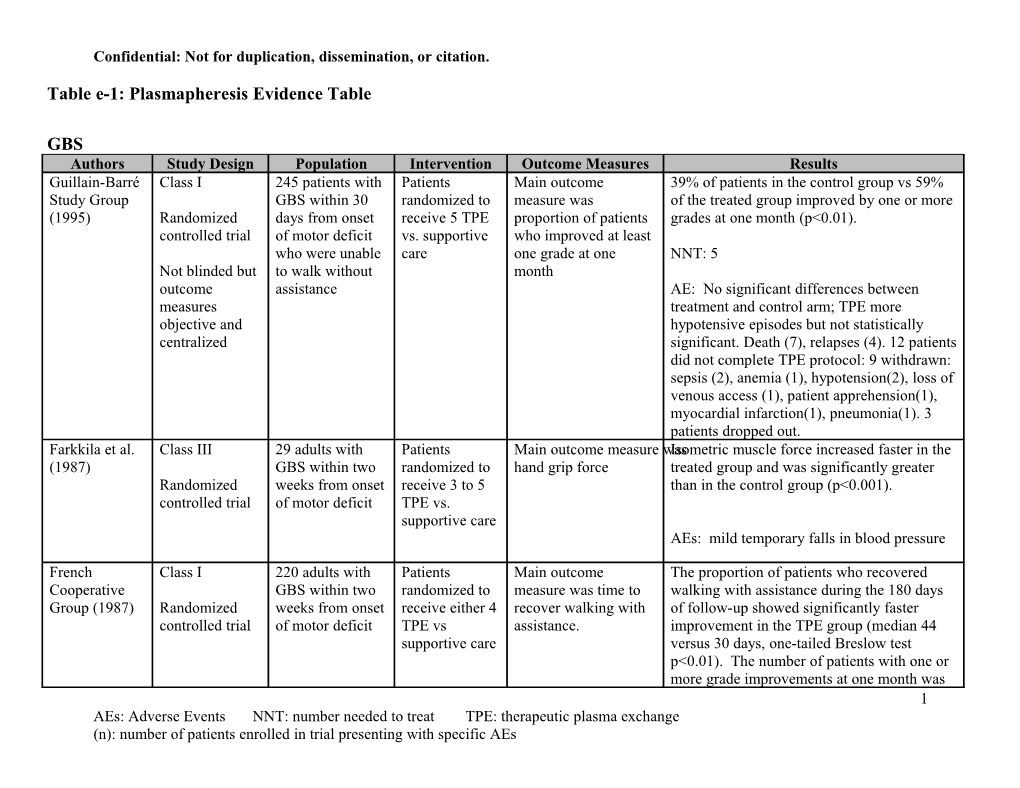
GBS Authors Study Design Population Intervention Outcome Measures Results Guillain-Barré Class I 245 patients with Patients Main outcome 39% of patients in the control group vs 59% Study Group GBS within 30 randomized to measure was of the treated group improved by one or more (1995) Randomized days from onset receive 5 TPE proportion of patients grades at one month (p<0.01). controlled trial of motor deficit vs. supportive who improved at least who were unable care one grade at one NNT: 5 Not blinded but to walk without month outcome assistance AE: No significant differences between measures treatment and control arm; TPE more objective and hypotensive episodes but not statistically centralized significant. Death (7), relapses (4). 12 patients did not complete TPE protocol: 9 withdrawn: sepsis (2), anemia (1), hypotension(2), loss of venous access (1), patient apprehension(1), myocardial infarction(1), pneumonia(1). 3 patients dropped out. Farkkila et al. Class III 29 adults with Patients Main outcome measure wasIsometric muscle force increased faster in the (1987) GBS within two randomized to hand grip force treated group and was significantly greater Randomized weeks from onset receive 3 to 5 than in the control group (p<0.001). controlled trial of motor deficit TPE vs. supportive care AEs: mild temporary falls in blood pressure
French Class I 220 adults with Patients Main outcome The proportion of patients who recovered Cooperative GBS within two randomized to measure was time to walking with assistance during the 180 days Group (1987) Randomized weeks from onset receive either 4 recover walking with of follow-up showed significantly faster controlled trial of motor deficit TPE vs assistance. improvement in the TPE group (median 44 supportive care versus 30 days, one-tailed Breslow test p<0.01). The number of patients with one or more grade improvements at one month was 1 AEs: Adverse Events NNT: number needed to treat TPE: therapeutic plasma exchange (n): number of patients enrolled in trial presenting with specific AEs Confidential: Not for duplication, dissemination, or citation.
67/109 in the treated group compared to 41/111 in the control group (p<0.001).
NNT: 4 (for the more than 1 grade improvement at 1 month outcome)
AEs: pneumopathies (87), systolic blood pressure instability (68), bradycardia (75), septicemia (19), pulmonary embolus (3), coronary insufficiency (2), digestive hemorrhage (9), complications of endotracheal tubing (5), relapses (7), death (14). French Class I 556 patients with Patients For mild disease, time Mild group: the median time to onset of Cooperative mild (n=91), randomized to motor recovery, recovery shortened compared to control group Group (1997) Randomized moderate according to defined as (8 vs 4 days, p=0.0002). Moderate group: controlled trial (n=304), and severity of improvement of at median time to recover walking with severe (n=161) disease: mild: 2 least two items of a assistance was shortened in the 4 TPE Outcome not GBS TPE vs functional muscular compared to 2 TPE (24 vs 20 days, p=0.04); masked observation; score or one item and median time on ventilator and median time to moderate: 2 improvement in hospital discharge shortened with 4 sessions TPE vs 4 TPE; cranial nerve function of TPE (37 vs 25 days, p=0.005, and 26 vs 21 severe: 4 TPE or trunk or respiratory days, p=0.04, respectively). Severe group: no vs 6 TPE involvement. significant differences between two arms for outcome measures. For moderate and severe disease, time to Mild group: recover walking with Clinical deterioration 39% 0 TPE, 4% 2 TPE assistance NNT 3
Moderate group: Full muscle strength recovery at one year 48% 2 TPE, 64% 4 TPE NNT 6 2 AEs: Adverse Events NNT: number needed to treat TPE: therapeutic plasma exchange (n): number of patients enrolled in trial presenting with specific AEs Confidential: Not for duplication, dissemination, or citation.
AEs: pneumonia (190), systolic BP instability (141), bradycardia (97), septicemia (40), pulmonary embolism (10), GI bleeding (14), complications of endotracheal tubing (25), hematoma at vein puncture site (52), relapses (19), death (21).
CIDP Authors Study Design Population Intervention Outcome Measures Results Dyck et al. Class I 34 patients with Patients Outcome measures 29 patients completed the trial; 4 patients (1986) presumed CIDP (4 randomized to used were Neuropathy removed for incorrect diagnosis, 1 for Randomized, later removed due TPE (n=15) or Disability Scale myocarditis. The plasma exchange group controlled to incorrect sham (NDS) and showed improvement in nerve conduction double-blind diagnosis) exchange neurophysiological parameters compared to sham exchange trial, with open (n=14) for parameters group, and improvement in NDS score in 5 crossover of three weeks patients (p=0.025) and in subset scores for control arm weakness and reflex in 4 patients (p<0.057).
AEs: myocarditis, possibly related to indwelling subclavian catheter (1)
Hahn et al. Class I 18 patients with Patients Outcome measures 15 patients completed the trial. The 3 drop (1996) newly or recently randomized to used were the outs were due to one patient who lost venous Randomized, diagnosed CIDP 10 TPE vs Neuropathy Disability access, one patient suffered a stroke, and one controlled, confirmed by sham Scale (NDS), a clinical patient left the trial to receive open treatment double-blind, nerve biopsy exchange, grade (CS) and a grip elsewhere. The TPE group showed significant crossover trial followed by a strength (GS) improvement in all clinical outcome measures 5-week wash- measurement, and (NDS by 38 points, p<0.001; CS by 1.6 out and then electrophysiological points, p<0.001; GS by +13kg, p<0.003) and cross-over parameters in selected electrophysiological measurements 3 AEs: Adverse Events NNT: number needed to treat TPE: therapeutic plasma exchange (n): number of patients enrolled in trial presenting with specific AEs Confidential: Not for duplication, dissemination, or citation.
(E proximal CMAP, p<0.01; E motor conduction velocities, p<0.006; E distal motor latencies, p<0.01) as compared to the sham controls. 8/12 responders relapsed (7 within 7-14 days and 1 within 5 weeks after stopping plasma exchange; all these patients improved with subsequent open plasma exchange; 2 patients however required long-term immunosuppression for stabilization.
AEs: 3 drop-outs due to failed venous access (1), stroke (1), drop-out (1). Otherwise AEs included MI (1).
Dysimmune Neuropathies
Authors Study Design Population Intervention Outcome Measures Results Dyck et al. Class I 39 patients with Patients Outcome measures 29 patients completed the trial; 4 patients (1991) neuropathy and randomized to used were Neuropathy removed for incorrect diagnosis, 1 for Randomized, MGUS TPE (n=19) or Disability Scale myocarditis. The plasma exchange group controlled sham (NDS) and showed improvement in NDS score patients double-blind exchange neurophysiological (p=0.06), weakness score (p=0.07), and trial with open (n=20) twice parameters summed compound muscle action potentials crossover weekly for 3 of motor nerves (p=0.07). Subgroup analysis weeks. showed those with IgG or IgA gammopathy had better response.
AEs: One drop out due to osteosclerotic myeloma. Otherwise AEs not discussed.
4 AEs: Adverse Events NNT: number needed to treat TPE: therapeutic plasma exchange (n): number of patients enrolled in trial presenting with specific AEs Confidential: Not for duplication, dissemination, or citation.
Oksenhendler Class III 44 patients with Patients Outcome measures No differences found between the two groups. et al., 1995 polyneuropathy randomized to used including the Randomized, associated with chlorambucil Neuropathy Disability AEs: 8 drop-outs due to clinical worsening (5) controlled, not monoclonal IgM (0.1mg/kg/day Scale (NDS) and or no improvement (1), death due to bowel blinded gammopathy ) or electrophysiological occlusion (1), emergency vascular surgery (1). chlorambucil parameters Otherwise AEs included hepatotoxicity (10). with TPE
Demyelinating CNS Disease
Authors Study Design Population Intervention Outcome measures Results Weinshenker Class II 22 patients with Patients Primary outcome was Five patients who received active treatment in et al. (1999) clinically definite randomized to the TNDs the first treatment period improved compared Randomized, or lab supported 7 TPE (n=11) to 1 who received sham treatment (mean z controlled, definite MS or vs sham score 0.4 +/- 0.5). Of 14 who crossed over, 3 double-blind, idiopathic exchange who received active treatment in second crossover trial inflammatory (n=11). On period improved compared with none who demyelinating day 14, two received sham (mean z score -0.2 +/- 0.6) CNS diseases, neurologist confirmed by investigators For improvement in the first treatment period: biopsy when after TPE 45.5%, SPE 9.1% necessary and independently Difference 36.4% acute neurologic scoring the 95% CI (-1.1 to 64%) deficit affecting TND consciousness, following NNT: 3 (not significant) language, specific brainstem function scales, decide AEs: treatment complications included the or spinal cord by consensus need for central venous access (13), nausea function with whether (6), symptomatic hypotension (6), impairment in one sustained paresthesias (2), anemia (4), severe or more of the moderate or thrombocytopenia (2), elevated creatine targeted marked kinase (1) 5 AEs: Adverse Events NNT: number needed to treat TPE: therapeutic plasma exchange (n): number of patients enrolled in trial presenting with specific AEs Confidential: Not for duplication, dissemination, or citation.
neurological improvement deficits (TNDs): had occurred. coma, aphasia, If not, patients acute severe were crossed cognitive over to dysfunction, opposite hemiplegia, treatment arm. paraplegia, or quadriplegia.
Weiner et al. Class I 116 patients with Patients were Changes on modified Trend toward improvement in TPE-treated (1989) clinically definite randomized to EDSS score patients at week 2 and 1 month; subgroup Randomized, MS presenting true (n=59) vs analysis of RRMS showed improvement at controlled, with a clinical sham TPE one month (p< .04). double-blind exacerbation (n=57), given defined as a with ACTH Improvement at 1 month: decline of at least plus oral SPE 41% vs TPE 58% (estimated from graph) one grade on the cyclophospha- Kurtzke Disability mide. ACTH NNT: 6 (not significant) Status Scale was given as lasting longer than 40 U IM AEs: 13 patients dropped out (6 true TPE; 7 5 days but less twice daily for sham TPE) for poor venous access (5), than 8 weeks 7 days, 20 U pulmonary embolus (1), fatigue (1), IM twice noncompliance with oral medication (1), drop daily for 4 out (1), elevated LFTs (1), days, and 20 hypofibrinogenemia (1), nausea and vomiting U IM once (1), and abdominal pain (1). daily for 3 days. Cyclophospha -mide was given 2mg/kg orally daily for 12 weeks. 6 AEs: Adverse Events NNT: number needed to treat TPE: therapeutic plasma exchange (n): number of patients enrolled in trial presenting with specific AEs Confidential: Not for duplication, dissemination, or citation.
True TPE was performed 5 times during the first 14 days, then weekly for 6 weeks. Canadian Class I 168 patients with Patients Change in EDSS at 6- Slight trend favoring TPE group seen at 12-24 Cooperative clinical or randomized to month intervals and/or months. MS Study Randomized, laboratory- receive at final assessment Group (1991) controlled, supported definite intravenous (mean 30.4 months) Primary analysis “Treatment Failures” single-masked MS in progressive cyclophospha- 35% cyclophosphamide phase mide and oral 32% TPE (deterioration by at prednisone 29% placebo least 1.0 on EDSS (n=55), daily in previous year) oral There is no trend favoring TPE by primary cyclophospha- analysis. Therefore NNT not calculated. mide, alternate day AEs: death (2), hemorrhagic cystitis (2), prednisone sepsis (3), vascular collapse (1), diabetes (22 weeks) mellitus (1), herpes zoster (1), pulmonary and weekly embolism (1), depression requiring plasma psychiatric hospitalization (3), angina (2), exchange (20 alopecia (38), amenorrhea (44) weeks) (n=57); or placebo medications and sham plasma exchange (n=56)
7 AEs: Adverse Events NNT: number needed to treat TPE: therapeutic plasma exchange (n): number of patients enrolled in trial presenting with specific AEs Confidential: Not for duplication, dissemination, or citation.
Khatri et al., Class I 54 patients with Patients EDSS and the Canter 11/26 improved in TPE group vs 8/29 in the (1985) clinically definite randomized to Scale (measuring sham TPE group; one TPE patient worsened Randomized, chronic receive TPE ADL); follow-up over vs 3 sham TPE patients. controlled, progressive MS (n=30; 26 11 months. Differences not significant. double-blind with continuous completed worsening on study) or For improvement: serial neurologic sham TPE TPE 42.3% examinations in (n=29) once SPE 27.6% preceding 12 per week for Risk difference 14.7% months 20 weeks. All (95% CI -10 to 37.5%) patients received oral NNT: 7 (not significant) cyclophospha- mide daily AEs: 4 drop-outs in PP arm (urosepsis, spinal (1.5mg/kg), fracture following fall, cervical meningioma, prednisone drop-out). Otherwise, treatment related AEs (1mg/kg) on included vascular access difficulty (18), alternate days transient hypotension(13), DVT (2), fatigue and pooled (20). human immune serum globulin (40ml in by IM injection)
8 AEs: Adverse Events NNT: number needed to treat TPE: therapeutic plasma exchange (n): number of patients enrolled in trial presenting with specific AEs Confidential: Not for duplication, dissemination, or citation.
Gordon et al. Class II 20 patients with Patients Neurological exam, No significant improvement. (1985) chronic randomized to EDSS, evaluation of Randomized, progressive MS TPE or sham ADL Improvement Clinical Immediate post PE: controlled, and continuous TPE SPE 30%, TPE 70% double-blind decline over the performed 3 Difference 40% preceding 2 years. times/week 95% CI 2.9 to 67.2% for 2 weeks, then 2/week NNT: 3 (not significant) for 3rd week, for total of 8 3-6 months post PE exchanges. TPE 20%, SPE 10% All patients Difference 10%, Not significant received prednisone NNT: 10 (not significant) (30-50mg QOD) and AEs: not discussed azathioprine (150mg QD). Follow-up for 3-6 months. Sorensen et al., Class II 11 patients with Patients Number of No evidence of beneficial effect 1996) clinically definite randomized to gadolinium-enhancing Randomized, secondary receive active lesions by MRI controlled, progressive MS treatment (3 AEs: GI toxicity (2), withdrawal (1), transient single-masked with two or more month run-in hypotension (1), hyperpyrexia (2). crossover acute treatment with exacerbations or at azathioprine least 1-point 2mg/kg worsening on followed by 6 EDSS in preceding month period 12 months of AZA+TPE) or no treatment (6 months no 9 AEs: Adverse Events NNT: number needed to treat TPE: therapeutic plasma exchange (n): number of patients enrolled in trial presenting with specific AEs Confidential: Not for duplication, dissemination, or citation.
treatment, then 3 month washout followed by active treatment). TPE was performed once per week for 1 month, then Q2weeks for 5 months.
PANDAS Authors Study Design Population Intervention Outcome Measures Results Perlmutter et Class III 30 patients with Patients were Outcome measures were 29 patients completed the study. al. (1999) severe, infection- randomized to improvement on standard The IGIV- and TPE-treated patients Randomized triggered TPE (5 assessment scales for OCD showed improvement in OCD controlled trial exacerbations of exchanges) vs (Yale-Brown obsessive symptoms (45% and 58%), anxiety obsessive- IVIg (1g/kg compulsive scale score), tics (31% and 47%), overall functioning compulsive for 2 days) vs (Tourette syndrome unified (33% and 35%), and tics (49%). disorder (OCD) or placebo rating scale), anxiety (NIMH Benefits were maintained at 1 year. tic disorders, (saline anxiety scale), depression and including Tourette solution given global function (NIMH global AEs: pallor, dizziness, and nausea syndrome as IGIV) scale). (7)
Sydenham’s Chorea 10 AEs: Adverse Events NNT: number needed to treat TPE: therapeutic plasma exchange (n): number of patients enrolled in trial presenting with specific AEs Confidential: Not for duplication, dissemination, or citation.
Authors Study Design Population Intervention Outcome measures Results Garvey et al. Class III 18 patients with Patients Outcome measure was mean At 1 month follow-up, there was (2005) Sydenham’s randomized to chorea severity using chorea overall 48% improvement for all Randomized chorea based on TPE vs. IGIV rating scale. arms with no superiority of any controlled trial, Jones criteria vs. treatment. At one year follow-up not blinded corticosteroids there was no difference in severity scores between the three groups.
AEs: brief vaso-vagal episodes, mild citrate-induced circumoral paresthesias. Only SAE in TEP arm gram-negative sepsis (1)
Myasthenia Gravis Authors Study Design Population Intervention Outcome Measures Results Goti et al. Class III 9 patients with Baseline of Pulmonary volumes, inspiratory Decrease in FRC and RV, and (1995) grade IIb treatment with and expiratory muscle force, increase in FEV1, MIP, and Non- myasthenia pyridostig- respiratory muscle strength, increase in MEP in TPE vs randomized, mine ventilatory pattern (inspiratory pyridostigmine (p<0.05). baseline to compared to time, expiratory time, total time treatment treatment with of respiratory cycle, and tidal TPE volume) Nagayasu et al. Class III 51 patients with 19 patients Incidence of MG crisis, Incidence of crisis within 1 year (2004) MG treated with pretreated pharmacologic remission rate after thymectomy was decreased in Retrospective, transsternal with one TPE and improvement rate, evaluated the TPE group (5.3% vs 28.1%) cohort study thymectomy prior to by graded scale (p=0.049); no evidence of crisis thymectomy; within 30 days after thymectomy in 32 patients TPE group vs 15.6% crises in treated with control group (p=0.0724). In the thymectomy TPE group, greater improvement alone. rate (100% vs 81.3%, p=0.0466) and complete remission rate (79% 11 AEs: Adverse Events NNT: number needed to treat TPE: therapeutic plasma exchange (n): number of patients enrolled in trial presenting with specific AEs Confidential: Not for duplication, dissemination, or citation.
vs 50%, p=0.0427) at 5-7 years.
NNT: 4 for avoiding crisis within 30 days 5 for improvement 3 for remission
12 AEs: Adverse Events NNT: number needed to treat TPE: therapeutic plasma exchange (n): number of patients enrolled in trial presenting with specific AEs