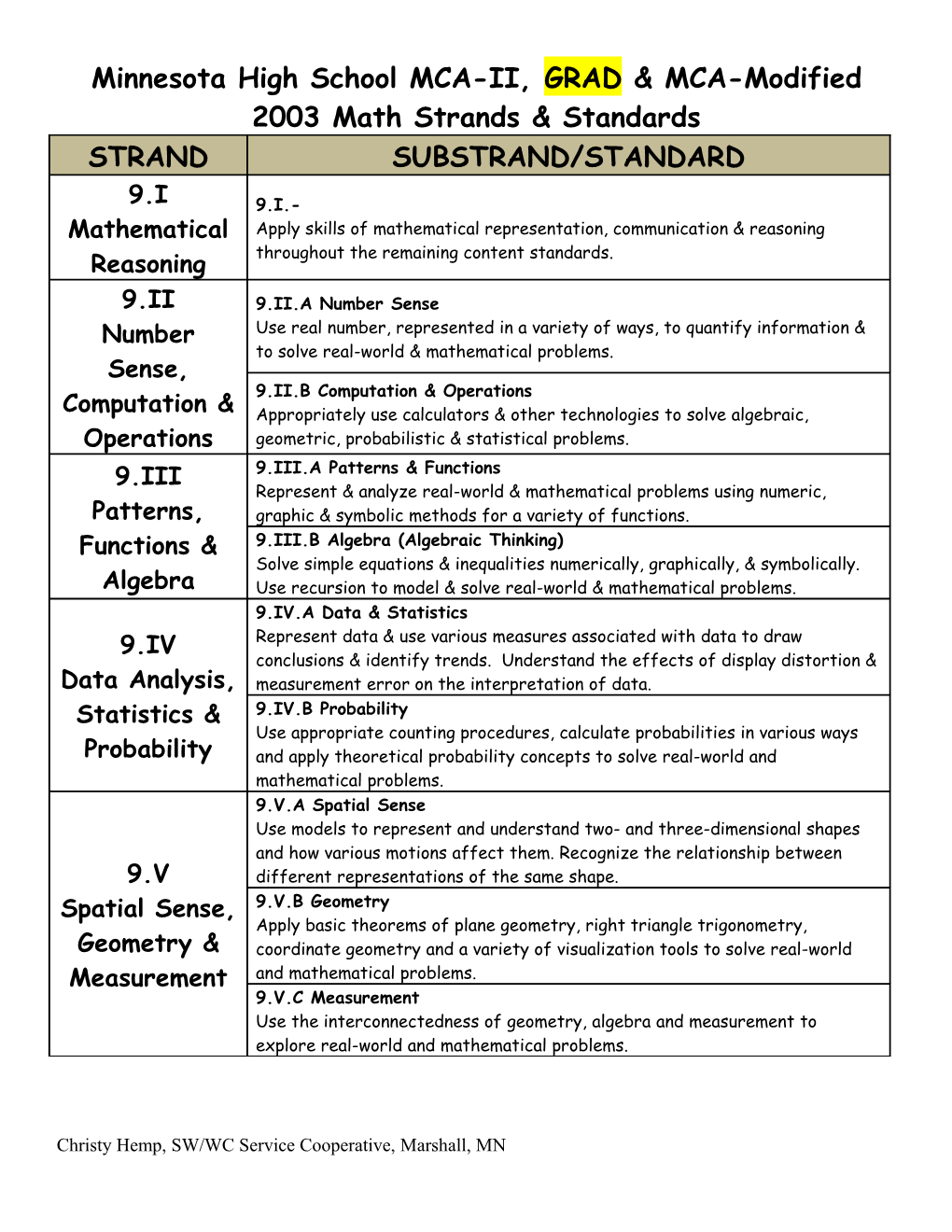
Minnesota High School MCA-II, GRAD & MCA-Modified 2003 Math Strands & Standards STRAND SUBSTRAND/STANDARD
9.I 9.I.- Mathematical Apply skills of mathematical representation, communication & reasoning Reasoning throughout the remaining content standards.
9.II 9.II.A Number Sense Number Use real number, represented in a variety of ways, to quantify information & to solve real-world & mathematical problems. Sense, 9.II.B Computation & Operations Computation & Appropriately use calculators & other technologies to solve algebraic, Operations geometric, probabilistic & statistical problems. 9.III 9.III.A Patterns & Functions Represent & analyze real-world & mathematical problems using numeric, Patterns, graphic & symbolic methods for a variety of functions. Functions & 9.III.B Algebra (Algebraic Thinking) Solve simple equations & inequalities numerically, graphically, & symbolically. Algebra Use recursion to model & solve real-world & mathematical problems. 9.IV.A Data & Statistics 9.IV Represent data & use various measures associated with data to draw conclusions & identify trends. Understand the effects of display distortion & Data Analysis, measurement error on the interpretation of data. Statistics & 9.IV.B Probability Use appropriate counting procedures, calculate probabilities in various ways Probability and apply theoretical probability concepts to solve real-world and mathematical problems. 9.V.A Spatial Sense Use models to represent and understand two- and three-dimensional shapes and how various motions affect them. Recognize the relationship between 9.V different representations of the same shape. Spatial Sense, 9.V.B Geometry Apply basic theorems of plane geometry, right triangle trigonometry, Geometry & coordinate geometry and a variety of visualization tools to solve real-world Measurement and mathematical problems. 9.V.C Measurement Use the interconnectedness of geometry, algebra and measurement to explore real-world and mathematical problems.
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN High School—Mathematical Reasoning Strand with MCA-II, GRAD & MCA-Modified Test Specifications 2003 MN Math Standard to Benchmarks
SUBSTRAND STANDARD BENCHMARK 9.I.-.1 Assess the reasonableness of a solution by comparing the solution to appropriate graphical or numerical estimates or by recognizing the feasibility of solutions in a given context & rejecting extraneous solutions. 9.I.-.2 Appropriately use examples & counterexamples to make & test conjectures, justify solutions, & explain results. 9.I.-.3 9.I.- Translate a problem described verbally or by tables, Apply skills of diagrams or graphs, into suitable mathematical language, mathematical solve the problem mathematically & interpret the result in 9.I representation, the original context. communication & Mathematical 9.I.-.4 reasoning Reasoning Support mathematical results by explaining why the steps throughout the in a solution are valid & why a particular method is remaining appropriate. content strands. 9.I.-.5 Determine whether or not relevant information is missing from a problem & if so, decide how to best express the results that can be obtained without that information. 9.I.-.6 Know & use the relationship that exists among a logical implication of the form “if A, then B,” its converse “if B, then A,” its inverse “if not A, then not B,” & its contrapositive “if not B, then not A.”
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN High School—Number Sense, Computation & Operations with MCA-II, GRAD & MCA-Modified Test Specifications 2003 MN Math Standard to Benchmarks (GRAD 5-8 items) *Item Type—Multiple Choice (MC) or Gridded Response (GR) *Cognitive Levels—Knowing (A), Understanding (B), Application, Analysis Synthesis & Evaluation (C) * Calculator Use—Item appears in calculator section of assessment (CL), Calculator Neutral, item appears in either section of assessment (CN) SUBSTRAND STANDARD * BENCHMARK
9.II.A Use real numbers, MC/GR 9.II.A.- represented in a 9.II.A N/A variety of ways, to ABC These benchmarks are continued from Number quantify information grade 8 & embedded in algebra, Sense & to solve real-world CL probability & geometry in grade 11. & mathematical problems.
9.II.B 9.II.B 9.II.B.1 Appropriately use MC/GR Apply the correct order of operations & Computation calculators & other grouping symbols when using calculators & Operations technologies to solve ABC & other technologies. algebraic, geometric, MCA-II probabilistic & CL This benchmark is assessed in grade 8 GRAD statistical problems. It is embedded in other grade 11 items 5-8 items 9.II.B.2 Know, use & translate calculator notational conventions to mathematical notation. MCA-II Assessed only at the classroom level MC/GR 9.II.B.3 Recognize the impact of units such as ABC degrees & radians on calculations. MCA-II CL This benchmark is embedded in grade 11 items from Strand V Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN 9.II.B.4 Recognize that applying an inverse function with a calculator may lead to extraneous or incomplete solutions. MCA-II Assessed only at the classroom level 9.II.B.5 Understand the limitations of calculators such as missing or additional features on graphs due to viewing parameters or misleading representations of zero or very large numbers. MCA-II Assessed only at the classroom level 9.II.B.6 Understand that use of a calculator requires appropriate mathematical reasoning & does not replace the need for mental computation. MCA-II Assessed only at the classroom level
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC 9.II.B.G7 Students will apply the correct order of CL operations to simplify & evaluate numeric expressions. GRAD GRAD 2-3 Items must use positive rational items numbers Items will use addition, subtraction, multiplication, division & grouping symbols only Fraction denominators are limited to 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10 & 12 Subtraction cannot be a mixed number minus a mixed number requiring 1 7 regrouping (e.g., 3- 1 is not 4 8 acceptable) Multiplication may be expressed as a raised dot, x, or ( ) (e.g., 5状 6, 5 6, 5(6) ) Division may be expressed using division symbol or fraction bar (e.g., 6 6 2 or ) 2 Division items must have a whole number divisor For multiplication & division items, mixed numbers must be expressed as improper fractions No nested grouping symbols are allowed (e.g., 3[ 292+ (100 / 2)] is not allowed) Items may require the identification of the correct order of operations shown (calculation not required) Items may require integer approximations of square roots of positive numbers Items may include exponents Problems may include context
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN 9.II.B.G8 Students will use rational numbers in complex ways to solve multi-step real- MC world & mathematical problems. GRAD CL Rationals are limited to positive rationals GRAD Non-integer rationals will be represented in decimal form 0-1 Items may require integer items approximations of square roots of positive integers Squares must be less than or equal to 150 MC 9.II.B.G9 Students will use fractions, decimals & CL percents in multiple representations for estimation & computation to solve real- GRAD world & mathematical problems. 1-2 GRAD items Fraction denominators are limited to 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 25 & 100. Restrictions on denominators apply to problem and answer options (e.g., 1/3 + 1/5 is not allowed; 1/15 – 1/3 is not allowed) Items may include positive & negative fractions, decimals & percents
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN 9.II.B.G10 Students will use proportional reasoning to solve real-world & mathematical problems. GRAD Items may involve: rates scale drawings & maps MC similar figures ratio CL unit pricing showing how changing one or more GRAD dimensions affect change in area 2-3 Shapes are limited to circles, items parallelograms & triangles Items are limited to two-dimensional figures Pictures or diagrams may be used but are note required Similarity may be shown using similarity symbol ( : ) or using markings on figures Items may include context
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN High School—Patterns, Functions & Algebra with MCA-II, GRAD & MCA-Modified Test Specifications 2003 MN Math Standard to Benchmarks (MCA-II 19-21 items) (GRAD 12-19 items) (MCA-Modified 16-18 items) *Item Type—Multiple Choice (MC) or Gridded Response (GR) *Cognitive Levels—Knowing (A), Understanding (B), Application, Analysis Synthesis & Evaluation (C) * Calculator Use—Item appears in calculator section of assessment (CL), Calculator Neutral, item appears in either section of assessment (CN) SUBSTRAND STANDARD * BENCHMARK 9.III.A 9.III.A MC 9.III.A.1 Represent & analyze Students will know the numeric, graphic Patterns & real-world & ABC & symbolic properties of linear, step, Functions mathematical absolute value & quadratic functions. problems using CL MCA-II/MCA-M numeric, graphic & Items may include rates of change, MCA-II symbolic methods MCA- intercepts, maxima & minima 7-9 items for a variety of II/ Items may include intersection functions. GRAD between two graphs Step functions must model real-world 1-2 situations GRAD items 5-7 items Step functions will not be represented symbolically MCA-M GRAD 1-2 MCA-M Items may not include step or absolute items value functions 6-7 items Items may include rates of change & intercepts Items that assess quadratics are limited to graphical properties Increments of x & y axes must be integers
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC 9.III.A.2 Students will model exponential growth ABC & decay. MCA-II/MCA-M CL Models may be numeric, graphic & symbolic MCA- When calculation is required, II/ exponents must be integers Items may have real-world context GRAD (e.g., bacterial growth, half-life, 1-2 compound interest) items GRAD Models may be numeric or graphic MCA-M Items may have real-world context 1-2 (e.g., bacterial growth, half-life, items compound interest) MC 9.III.A.3 Students will analyze the effects of ABC coefficient changes on linear & quadratic functions & their graphs. CL MCA-II/MCA-M Changes to coefficients in ax2 + bx + c MCA- are limited to a & c II 1-2 items
MCA-M 1-2 items
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC/GR 9.III.A.4 Students will apply basic concepts of ABC linear, quadratic & exponential expressions or equations in real-world CL problems. MCA-II/MCA-M MCA- Exponents must be integers II/ GRAD GRAD Items will be limited to linear & 1-2 exponential items Expressions & equations must be able to be solved numerically. Table or MCA-M graph required 1-2 Items will not require expressions or items equations to be solved symbolically MC 9.III.A.5 Students will distinguish functions from A other relations using graphic & symbolic methods. CN MCA-II/MCA-M Not more than 10 increments on either MCA- side of axes II 1-2 items
MCA-M 1-2 items
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN 9.III.A.G6 Students will generate a table of values from a formula or equation. Students will graph the result of a formula or linear equations in ordered pair format on a grid. GRAD MC x & y axes may have different scales items do not require students to graph CL or generate a table of a non-linear relation GRAD formulas will only have unknowns to the first degree 1-2 items may not require generating a items linear equation from a table of values items may include real-world context (e.g., converting temperature) given a continuous (i.e., individual points not indicated) linear graph, student will generate a table of values linear equations will be given in y= mx + b form 9.III.A.G7 MC Students will translate a problem described verbally or by tables, CL diagrams or graphs, into suitable mathematical language, solve the GRAD problem mathematically & interpret the 1-2 result in the original context. items GRAD items may include real-world context
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN 9.III.B 9.III.B MC 9.III.B.1 Solve simple Students will translate among equivalent Algebra equations & A forms of expressions. (Algebraic inequalities MCA-II/MCA-M Thinking) numerically, CN Items may include: graphically & simplifying algebraic expressions symbolically. Use MCA- involving nested pairs of MCA-II recursion to model & II/ parentheses & brackets simplifying rational expressions solve real-world & GRAD 12-14 items factoring a common monomial term mathematical 1-2 from an expression problems. items applying associative, commutative GRAD & distributive laws 7-12 items MCA-M A simplified expression should contain, 1-2 at most, four terms with, at most, two items variables per term MCA-M GRAD 10-11 items Items may include: simplifying algebraic expressions involving nested pairs of parentheses & brackets simplifying rational expressions factoring a common monomial term from an expression applying associative, commutative & distributive laws When applying distributive law, expressions may not contain 2 binomials Expressions may not include nested pairs of parentheses or brackets A simplified expression should contain at most two terms with at most one variable per term
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC 9.III.B.2 AB Students will understand the relationship between absolute value & CN distance on the number line. Students will graph simple expressions involving MCA- absolute value. II MCA-II/MCA-M 1-2 At most, one absolute value on each items side of the equation or inequality Absolute values will be in the form of x- b = c; x - b < c ; x - b > c ; x - b� c ; x b c MCA-M 1-2 (e.g., x -3 = 6 or x +2 < 5 ) items MC 9.III.B.3 Students will find equations of a line. AB MCA-II/MCA-M Items will provide two points on the CN line, a point & the slope of the line or the slope & y-intercept of the line MCA- All answer options will be given in the same form within a MC item, either II/ slope-intercept ( y= mx + b ) or GRAD standard form ( ax+ by = c ) 1-2 GRAD items Items may require the student to generate the equation from the graph MCA-M or identify the graph given the 1-2 equation items Items will provide the slope & y- intercept of the line, when graph is not provided Equations must be presented in slope- intercept form
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC 9.III.B.4 AB Students will translate among equivalent forms of linear equations & inequalities. CN MCA-II/MCA-M Translating may require simplification (2x+ 2) + 2( x - 4) = y MCA- (e.g., translates to y=4 x - 6 ) II Equivalent forms may be slope- 1-2 intercept, standard or two-point items All answer options will be given in the same form within a MC item, either MCA-M slope-intercept ( y= mx + b ) or 1-2 standard form ( ax+ by = c ) items MC 9.III.B.5 Students will use a variety of models to ABC represent functions & patterns in real- world & mathematical problems. CN MCA-II/MCA-M Models may include equations, MCA- inequalities, algebraic formulas, II written statements, tables, graphs or 2-3 spreadsheets of linear, quadratic, exponential, absolute value & step items functions. Step functions must model real-world MCA-M situations 1-2 Step functions will not be represented items symbolically
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC 9.III.B.6 A Students will apply the laws of exponents to perform operations on CN expressions with integer exponents. MCA-II/MCA-M MCA- A simplified expression should contain, II at most, two variables 1-2 Multiplication & division operations items should only be performed on monomials Items may include scientific notation MCA-M with appropriate treatment of 1-2 significant digits items MC/GR 9.III.B.7 Students will solve linear equations & AB inequalities in one variable with numeric, graphic & symbolic methods. CN MCA-II/MCA-M Forms of the linear equations or MCA- inequalities are not limited (e.g., II/ 4(x+ 5) - 3 x = 6( x + 10) is acceptable) GRAD Items may include context 1-2 GRAD items Items may include at most one application of the distributive property MCA-M Items will not include inequalities 1-2 Forms of the linear equations are items limited to at most a binomial equaling a binomial Items must have a numeric solution
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC/GR 9.III.B.8 AB Students will determine solutions to quadratic equations in one variable with CL numeric, graphic & symbolic methods. MCA-II/MCA-M MCA- All solutions are real II/ Solutions determined from a graph will GRAD be integer solutions 1-2 Items may include context items GRAD All solutions are integer MCA-M Coefficient on second-degree term will 1-2 always be 1 items MC 9.III.B.9 Students will use appropriate A terminology & mathematical notation to define & represent recursion. CN MCA-II/MCA-M
x1 is the initial term in the sequence
MCA- xn+1 is the next term
II The term an is also included in 0-1 appropriate terminology items Items require only addition & multiplication to find the nth term MCA-M (arithmetic & geometric only) 0-1 9.III.B.9 & 9.III.B.10 will not both items have 0 items in the same administration
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC 9.III.B.10 AB Students will create & use recursive formulas to model & solve real-world & CL mathematical problems. MCA-II/MCA-M MCA- Progressions are limited to arithmetic II & geometric 0-1 Items will not require identification items past tenth term 9.III.B.10 & 9.III.B.9 will not both MCA-M have 0 items in the same 0-1 administration items MC/GR 9.III.B.11 Students will solve systems of two ABC linear equations & inequalities with 2 variables using numeric, graphic & CL symbolic methods. MCA-II/MCA-M MCA- Inequalities will only be solved II/ graphically GRAD Items may include context 1-2 GRAD items Items may include at most one application of the distributive property MCA-M Items will not include inequalities 1-2 Forms of linear equations are limited items to at most a binomial equaling a binomial Systems may be represented using graph, slop-intercept & table format Systems are consistent & independent (i.e., solution is one ordered pair)
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN 9.III.B.12 Students will understand how slopes can be used to determine when lines are MC parallel or perpendicular & determine equations for parallel lines & ABC perpendicular lines. MCA-II/MCA-M CL Items may provide a line & a point not on that line MCA- Items may require students to II/ determine the equation of the line GRAD passing through a given point & parallel to a given line 1-2 Items may require students to items determine the equation of the line passing through a given point MCA-M Items may include context 1-2 GRAD items Items may not require students to determine the equation of a line Equations in problem & answer options must be in slope-intercept form 9.III.B.G13 Students will use formulas with more than one variable to solve real-world & mathematical problems. MC GRAD Formulas must be from a real-world CL context & may include powers (e.g., area, volume, I= prt or d= rt ) GRAD Items may contain formulas with at 1-2 most four variables items Roots are limited to square roots Formula notation may not include subscripts Formulas must be included within the item
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN High School—Data Analysis, Statistics & Probability with MCA-II, GRAD & MCA-Modified Test Specifications 2003 MN Math Standard to Benchmarks (MCA-II 14-16 items) (GRAD 8-14 items) (MCA-Modified 13-15 items) *Item Type—Multiple Choice (MC) or Gridded Response (GR) *Cognitive Levels—Knowing (A), Understanding (B), Application, Analysis Synthesis & Evaluation (C) * Calculator Use—Item appears in calculator section of assessment (CL), Calculator Neutral, item appears in either section of assessment (CN) SUBSTRAND STANDARD * BENCHMARK 9.IV.A 9.IV.A MC 9.IV.A.1 Represent data & use Students will analyze graphs & Data & various measures AB demonstrate understanding of the Statistics associated with data strengths & weaknesses of each format to draw conclusions CL by choosing appropriately among them & identify trends. for a given situation. MCA-II Understand the MCA- MCA-II/MCA-M 8-10 items effects of display II Items may contain circle graphs, bar distortion & 1-2 graphs, histograms, box-&-whisker measurement error items plots, scatter plots, tables & stem-&- GRAD on the interpretation leaf plots Circle graphs may have, at most, eight 5-9 items of data. MCA-M sectors 1-2 Scales are in increments appropriate items to the application
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MCA-M MC 9.IV.A.2 Students will use measures of central 7-8 items AB tendency & variability to describe, compare & draw conclusions about sets CL of data. MCA-II/MCA-M MCA- Measures may be: II/ mean GRAD median 1-2 maximum minimum items range standard deviation MCA-M quartile 1-2 percentile items mode interquartile range (IQR) GRAD Measures may be: mean median maximum minimum range quartile mode interquartile range (IQR) The interquartile range may be referred to conceptually, but the terminology “interquartile range” will not be used
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC 9.IV.A.3 Students will determine approximate AB line of best-fit & use the line to draw conclusions. CL MCA-II/MCA-M Items will provide a scatter plot MCA- (coordinates of points on scatter plot II/ are integers) or data set GRAD GRAD Equations are limited to linear 1-2 equations only items Items will provide a scatter plot (coordinates of points on scatter plot MCA-M are integers) 1-2 Line of best fit may be provided & items asked to draw conclusions MC 9.IV.A.4 Students will know the influence of AB outliers on various measures & representations of data about real- CL world & mathematical problems. MCA-II/MCA-M MCA- Items may require students to II understand that the median is 1-2 resistant to outliers items Items may require students to understand that outliers affect the mean MCA-M Given a mathematical definition, items 1-2 may require students to verify that a items data point is an outlier
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC 9.IV.A.5 AB Students will distinguish between correlation & causation. CN MCA-II/MCA-M Items may provide several statements MCA- about correlation & causation of a II situation & require the student to 1-2 select the correct statement (e.g., items high correlation does not guarantee causation) MCA-M Items will not require calculation of 1-2 correlation coefficients items MC 9.IV.A.6 Students will interpret data credibility AB in the context of measurement error & display distortion. CL MCA-II/MCA-M Items will assess either measurement MCA- error or display distortion, but not II both in the same item 1-2 Items may address the effect of sample size on measurement error items
MCA-M 1-2 items
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC
AB 9.IV.A.7 Students will compare outcomes of CL voting methods. MCA-II/MCA-M MCA- Voting methods may include: II majority 1-2 plurality items ranked by preference run-off comparison MCA-M pair-wise comparison 1-2 items MC 9.IV.A.G8 Students will analyze histograms, bar CL graphs, circle graphs, stem-&-leaf plots & box-&-whisker plots. GRAD GRAD 2-3 Graphics may have at most ten data items categories Circle graphs may have a most eight sectors Scales are in increments appropriate to the application Histogram intervals must be consistent Items may involve: Reading & interpreting Identifying trends & patterns & make predictions Solve problems using information presented in the graph
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN 9.IV.A.G9 Students will understand the meaning of & be able to compute minimum, maximum, range, median, mean & mode of a data set. GRAD MC At most twenty numbers in the data set CL Numbers used are less than 300 Items may ask which values (mean, GRAD median, mode, range) “best” describes 1-2 a data set in context & identify items justification Items may require the calculation of quartiles The interquartile range may be referred to conceptually, but the terminology “interquartile range” will not be used MC/GR 9.IV.B 9.IV.B.1 Students will select & apply appropriate Probability 9.IV.B AB counting procedures to solve real-world Use appropriate & mathematical problems. counting procedures, CN MCA-II MCA-II/MCA-M calculate 6-8 items Items may involve computing probabilities in MCA- probabilities various ways & apply II/ Items may include combinations & GRAD theoretical GRAD permutations probability concepts 1-2 GRAD 3-5 items to solve real-world & items Items may involve determining sample mathematical space &/or computing probabilities Items may not include formulas MCA-M problems. MCA-M 1-2 Solutions may have at most 24 6-7 items items possibilities
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN 9.IV.B.2 MC/GR Students will calculate probabilities & relate the results in real-world & ABC mathematical problems. MCA-II/MCA-M CN Items may use area, trees, unions & intersections to calculate probabilities MCA- Items may involve both the concept of II/ mutually exclusive events or not mutually exclusive events GRAD Items may involve independent or 1-2 dependent events items Items may involve conditional probability MCA-M GRAD 1-2 Items may involve independent events items Items will not involve conditional probability MC 9.IV.B.3 Students will use probability models in ABC real-world & mathematical problems. MCA-II/MCA-M CN Models may include area & binomial models MCA- Binomial probabilities will involve, at II/ most, 4 events GRAD GRAD Binomial probabilities will involve at 1-2 most 3 events items
MCA-M 1-2 items
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC/GR
AB 9.IV.B.4 CL Students will determine the expected values of random variables for simple MCA- probability models. II MCA-II/MCA-M Sample spaces will include, at most, 1-2 four possible outcomes items Probabilities for each outcome may be given or may have to be computed MCA-M 1-2 items MC 9.IV.B.5 Students will know the effect of sample AB size on experimental & simulation probabilities. CL MCA-II/MCA-M Items may require the application of MCA- the Law of Large Numbers II Items will note require the application 1-2 of the Central Limit Theorem Items may require the interpretation items of confidence intervals, but will not require the calculation of confidence MCA-M intervals 1-2 items
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC/GR
ABC
CL 9.IV.B.6 Students will calculate probabilities. MCA- MCA-II/MCA-M II Items use a variety of experimental, 1-2 simulation & theoretical methods items
MCA-M 1-2 items
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN High School—Spatial Sense, Geometry & Measurement with MCA-II, GRAD & MCA-Modified Test Specifications 2003 MN Math Standard to Benchmarks (MCA-II 14-16 items) (GRAD 6-11 items) (MCA-Modified 9-12 items) *Item Type—Multiple Choice (MC) or Gridded Response (GR) *Cognitive Levels—Knowing (A), Understanding (B), Application, Analysis Synthesis & Evaluation (C) *Calculator Use—Item appears in calculator section of assessment (CL), Calculator Neutral, item appears in either section of assessment (CN) SUBSTRAND STANDARD * BENCHMARK 9.V.A.1 Students will use models & visualization to understand & represent various three-dimensional objects & their cross sections from different perspectives. MCA-II/MCA-M 9.V.A MC Items are limited to top view, side view, front view or net Spatial 9.V.A AB Shapes are limited to polyhedra, Sense Use models to combinations of polyhedra, cylinders & represent & cones CN understand two- & Not figures will be oblique MCA-II three-dimensional All visible sides of views are clearly MCA- 1-2 items shapes & how various labeled II/ motions affect them. Prisms will have a base with, at most, GRAD six sides Recognize the 1-2 Pyramids will have a base with, at GRAD relationship between items most, six sides 1-2 items different Cross sections are limited to representations of MCA-M rectangular prisms, cones, cylinders, the same shape. MCA-M 1-2 rectangular pyramids & triangular pyramids items 1-2 items GRAD Shapes are limited to prisms, pyramids, cylinders & cones Prisms will have a base with at most four sides Pyramids will have a base with at most four sides
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN 9.V.B 9.V.B 9.V.B.1 Apply basic Students will know & use theorems Geometry theorems of plane about triangles & parallel lines in geometry, right MC elementary geometry to justify facts MCA-II triangle about various geometric figures & solve trigonometry, ABC real-world & mathematical problems. 11-13 items coordinate geometry MCA-II/MCA-M & a variety of CN Theorems may include criteria for two GRAD visualization tools to triangles to be congruent or similar solve real-world & MCA- Theorems may include facts about 4-7 items mathematical II/ angles formed by parallel lines cut by a transversal problems. GRAD Items may involve the application of 1-2 MCA-M these theorems to solve real-world & items 7-8 items mathematical problems involving other plane figures MCA-M GRAD 1-2 Items will require knowledge & use of items theorems Items will not require students to use theorems for justification Items must include context or diagram MC 9.V.B.2 Students will know & use theorems ABC about circles to justify geometrical facts & solve real-world & mathematical CN problems. MCA-II/MCA-M MCA- Theorems may include the relationship II involving tangent lines & radii 1-2 Theorems may include the relationship items between inscribed & central angles Theorems may include the relationship between the measure of the central MCA-M angle & the length of the related arc 1-2 Items may involve the application of items these theorems to solve real-world 7 mathematical problems
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN 9.V.B.3 Students will use properties of two- & three-dimensional figures to solve real- MC/GR world & mathematical problems. MCA-II/MCA-M AB Use 3.14 as an approximation for p Situations may include finding area, CL perimeter, volume & surface area Situations may include applying direct MCA- or indirect methods of measurement II/ Situations may include applying the GRAD Pythagorean theorem & its converse 2-3 Situations may include properties of items 45-45-90 & 30-60-90 triangles GRAD MCA-M Situations may include applying the 2-3 Pythagorean theorem but not its items converse Situations will not include properties of 45-45-90 & 30-60-90 triangles Limits on shapes in 9.V.C.G2 apply MC 9.V.B.4 Students will apply the basic concepts ABC of right triangle trigonometry to determine unknown sides or unknown CN angles when solving real-world & mathematical problems. MCA- MCA-II/MCA-M II/ Concepts may include sine, cosine & GRAD tangent 1-2 Items will not require the use of the items reciprocals or inverses of sine, cosine & tangent Items will provide a table of decimal MCA-M approximations of three trigonometry 1-2 values for each angle given in the item items or students may use trigonometry values from a calculator GRAD Items must include diagram
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC
ABC 9.V.B.5 CL Students will use coordinate geometry. MCA-II/MCA-M MCA- Concepts may include distance between two points or midpoint of a II line segment 1-2 Concepts may include slope of a line, items slopes of parallel lines or slopes of perpendicular lines MCA-M 1-2 items MC 9.V.B.6 Students will use numeric, graphic & ABC symbolic representations of transformations to solve real-world & CL mathematical problems. MCA-II/MCA-M MCA- Transformations may include rotations, II reflections translations & change of 1-2 scale items
MCA-M 1-2 items
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN 9.V.B.7 MC Students will perform basic constructions with a straightedge & AB compass. MCA-II/MCA-M CN Items may require analysis or justification of the steps in a MCA- construction II Items may provide construction diagrams for midpoint of a line 0-1 segment, perpendicular bisector of a items line segment, the perpendicular to a line through a point not on the line, the MCA-M perpendicular to a line through a point 0-1 on the line & angle bisector items Constructions are best assessed in the classroom MC
AB
9.V.B.8 CN Students will draw accurate representations of planar figures using MCA- a variety of tools. II MCA-II/MCA-M 0-1 This benchmark is best assessed in the items classroom
MCA-M 0-1 items
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN MC/GR
ABC 9.V.C.1 CN Students will demonstrate an understanding of the interconnectedness MCA- of geometry, algebra & measurement. II MCA-II/MCA-M 1-2 Measurements will be provided with 9.V.C items the item Items may include context Measurement MCA-M 1-2 9.V.C items MCA-II Use the 9.V.C.G1 interconnectedness 1-2 items Students will make calculations involving of geometry, algebra time, length, area, volume, weight & & measurement to mass choosing appropriate unites to GRAD explore real-world & calculate, measure & record. mathematical 1-2 items GRAD problems. MC Appropriate U.S. customary unties are MCA-M inches, feet, yards, miles, fluid ounces, CL cups, pints, quarts, gallons, ounces & 1-2 items pounds GRAD Metric prefixes may include milli, centi & kilo 0-1 Items may not combine systems within items one item Time units are years, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes & seconds Time problems may include reading arrival/departure schedules Items may include measurement conversions
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN 9.V.C.G2 Students will use formulas to solve real-world & mathematical problems. GRAD Items may include determining the surface area or volume of shapes Shapes are limited to cubes, prisms & cylinders Pictures or diagrams may be used but are not required The radius or diameter is supplied for cylinders Answer options may be left in terms of p (e.g., 7p ) Non-rectangular prisms must MC provide the area of the base Items may include calculating CL perimeter & area of two-dimensional figures obtained by putting together GRAD triangles, parallelograms & sectors of 0-1 circles to solve real-world & items mathematical problems. Items must provide a picture or diagram Items may include calculating the radius, diameter, circumference & area of a circle Given the diameter or radius, items may require students to determine area or circumference Given the circumference, items may require students to determine radius, diameter or area Radii must be greater than 2 Grade 11 Formula Sheet will be provided (See copy of grade 11 formula sheet in Grade 11 Item Sampler)
Christy Hemp, SW/WC Service Cooperative, Marshall, MN