Bushing analysis
Purpose: Identify the effect of corner fillet on contact pressure distribution.
Units: Length = mm, mass = kg, time = sec, force = mmN, pressure = kPa
Model: Bearing is modeled as a spring with stiffness = 106 mmN/mm
Boundary Condition: 1. Bushing is fixed in x and z direction. 2. 100 N (105 nnN) is applied to the bushing in y-direction. This force is evenly distributed on all the nodes at the outer surface of the bushing 3. Two bearings are fixed 4. Long end of the shaft is fixed in x- and z-directions.
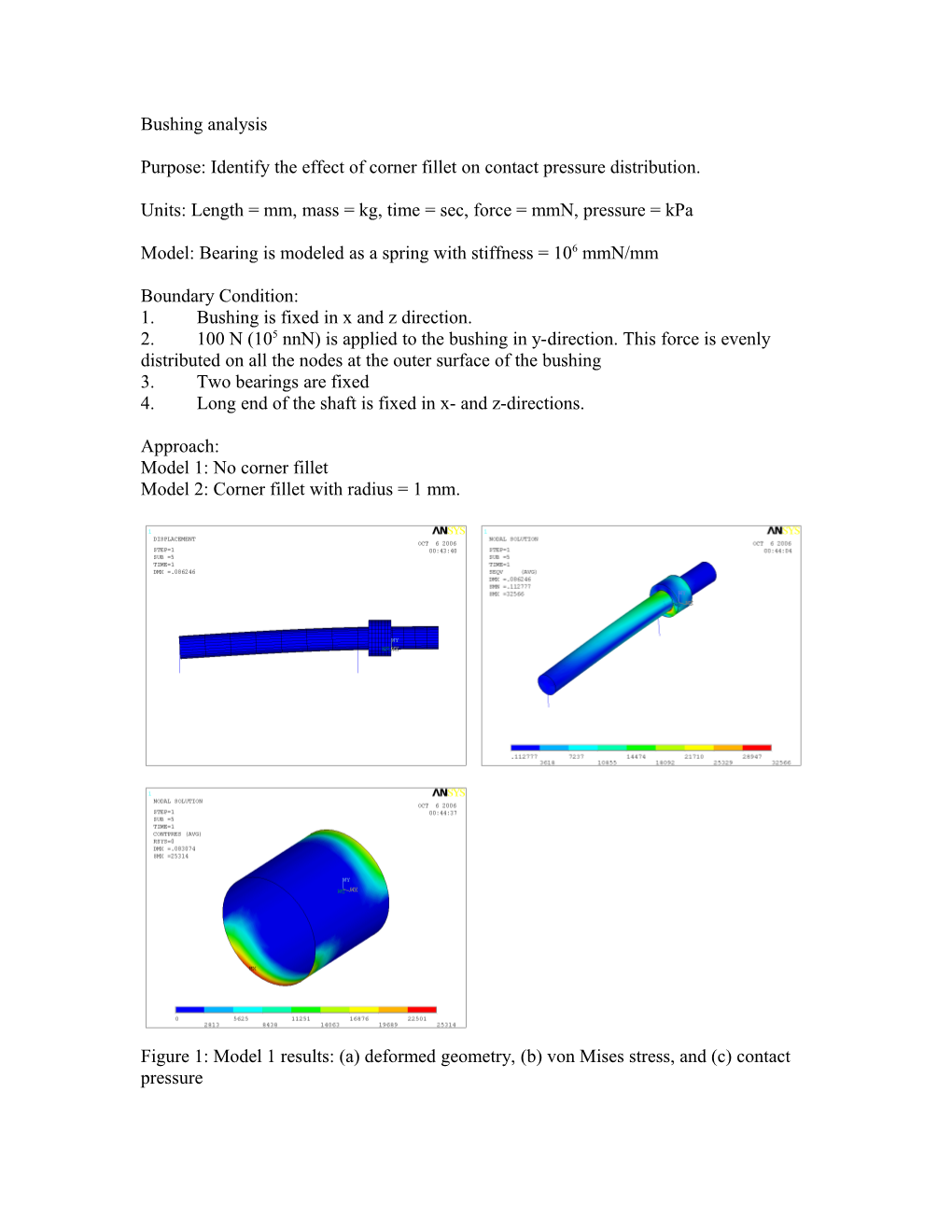
Approach: Model 1: No corner fillet Model 2: Corner fillet with radius = 1 mm.
Figure 1: Model 1 results: (a) deformed geometry, (b) von Mises stress, and (c) contact pressure Figure 2: Model 1 contact pressure distribution along the cordlength (a) Top (b) Bottom
Cordlength Top Bottom 0 17956 0 0.35379 14495 0 0.70757 11034 0 1.0614 7572.6 0 1.4151 4111.5 0 1.7689 3083.6 0 2.1227 2055.7 0 2.4765 1027.9 0 2.8303 1.37E-12 0 3.1841 0 0 3.5379 0 0 3.8916 0 0 4.2454 0 0 4.5992 0 0 4.953 0 0 5.3068 0 0 5.6606 0 0 6.0144 0 0 6.3681 0 0 6.7219 0 0 7.0757 0 0 7.4295 0 1867.6 7.7833 0 3735.2 8.1371 0 5602.8 8.4909 0 7470.4 8.8446 0 11808 9.1984 0 16146 9.5522 0 20484 9.906 0 24822 Figure 3: Model 2 results: (a) deformed geometry, (b) von Mises stress, (c) contact pressure, and (d) von Mises stress at bushing
Figure 4: Model 2 contact pressure distribution along the cordlength (a) Top (b) Bottom
Cordlength Top Bottom 0 0 0 0.25882 0 0 0.51764 14523 0 0.81225 27715 0 1.1069 16618 0 1.4363 4190.3 0 1.7657 2095.2 0 2.2598 0 0 2.7539 0 0 3.0834 0 0 3.4128 0 0 3.7422 0 0 4.0716 0 0 4.401 0 0 4.7304 0 0 5.0599 0 0 5.3893 0 0 5.7187 0 0 6.0481 0 0 6.3775 0 0 6.7069 0 0 7.2011 0 0 7.6952 0 4320.9 8.0246 0 8641.9 8.354 0 24087 8.6486 0 37877 8.9432 0 19766 9.2021 0 0 9.4609 0 0 9.5914 0 0 9.7219 0 0 9.8525 0 0 9.983 0 0 10.114 0 0 10.244 0 0 Conclusion: The bushing with fillet has higher contact stress than that without fillet. This possibly happens because the fillet reduces the actual length of contacting length of the bushing. This observation can be supported from the fact that the maximum displacement of the bushing with fillet is about 2.5% larger than that without fillet. The conclusion is that the fillet cannot reduce the concentration of contact pressure.
Using the optimization technique, the profile of the inner diameter can be determined so that the contact pressure is evenly distributed inside busing.