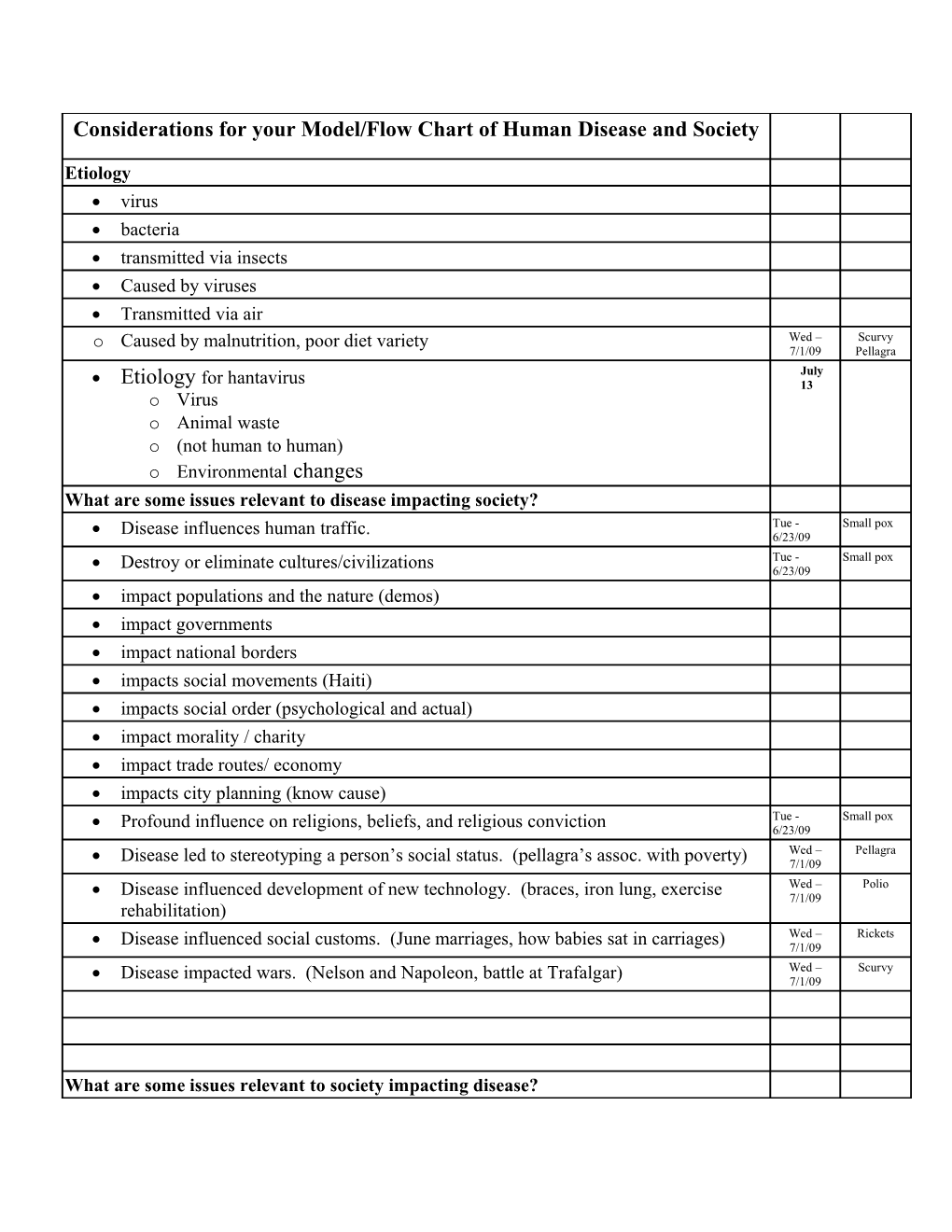
Considerations for your Model/Flow Chart of Human Disease and Society
Etiology virus bacteria transmitted via insects Caused by viruses Transmitted via air Caused by malnutrition, poor diet variety Wed – Scurvy o 7/1/09 Pellagra July Etiology for hantavirus 13 o Virus o Animal waste o (not human to human) o Environmental changes What are some issues relevant to disease impacting society? Tue - Small pox Disease influences human traffic. 6/23/09 Tue - Small pox Destroy or eliminate cultures/civilizations 6/23/09 impact populations and the nature (demos) impact governments impact national borders impacts social movements (Haiti) impacts social order (psychological and actual) impact morality / charity impact trade routes/ economy impacts city planning (know cause) Tue - Small pox Profound influence on religions, beliefs, and religious conviction 6/23/09 Wed – Pellagra Disease led to stereotyping a person’s social status. (pellagra’s assoc. with poverty) 7/1/09 Wed – Polio Disease influenced development of new technology. (braces, iron lung, exercise 7/1/09 rehabilitation) Wed – Rickets Disease influenced social customs. (June marriages, how babies sat in carriages) 7/1/09 Wed – Scurvy Disease impacted wars. (Nelson and Napoleon, battle at Trafalgar) 7/1/09
What are some issues relevant to society impacting disease? Tue - Small pox Religion and church against using vaccines 6/23/09 Tue - Small pox Morality of society 6/23/09 (+) society decided to eradicate small pox Tue - Small pox o 6/23/09 (-) putting animal parts into people was viewed as wrong, deterred use of Tue - Small pox o 6/23/09 variolation Tue - Small pox Authority figures (+/-) influence on dealing w/ disease 6/23/09 Human traffic influences spread of disease. trade (brought mosquitoes on ships) quarantine public policy social attitude about disease political pressure population density immigration and emigration spread disease Wed – Pellagra Technology influences disease. (New food processing lead to removing essential 7/1/09 nutrients) Wed – Yellow Social customs influenced disease. (standing water)/ (consuming lots of 7/1/09 Fever/ Gout wine/moonshine) Wed – - Epidemiology 7/1/09 Society’s misuse of correlations led to misdiagnoses. (sailors had lots of Wed – Scurvy o 7/1/09 STDS) Wed – Gout Trade/Treaties impacted disease. (Treaty allowed export of wine from Portugal to 7/1/09 England) Wed – Gout Social Status impacted who got the disease. (wealthy men) 7/1/09 Wed – Pellagra Political influence impacted disease. (Firing of Babcock due to ‘embarrassing’ the 7/1/09 state) Wed – Pellagra Current science often influenced the research focus of the etiology of the disease. 7/1/09 Beriberi (Originally, some of the metabolic diseases were thought to be caused by bacteria, a popular and frequently used hypothesis at the time) Stereotypes (Navajo disease) July 13 Institutions (CDC) Emotional reactions (panic and fear) Culture conflicting with the discovery of the disease Environment cont. July 13 o Hospitals (infected people in one area) July 13 o Sharing needles ( third world countries) July 13 o Financial status July 13 o Bacteria and virus mutations/ different strains o Industry (changes of making a product)
Important points: Tue - Small pox 6/23/09 Tue - Small pox Significance of moral conviction for a cause 6/23/09 Wed – Beriberi Dumb Luck often led to breakthroughs in understanding the etiology and treatment of 7/1/09 a disease. (Eijkman/Chickens)