Supplementary Information
Film squeezing process for generating oblate spheroidal particles with high yield and uniform sizes
Sang Jae Ahn 1, Kyung Hyun Ahn 2, Seong Jae Lee *,1
1 Department of Polymer Engineering, The University of Suwon, Hwaseong, Gyeonggi 445- 743, Republic of Korea
2 School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical Process, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-744, Republic of Korea
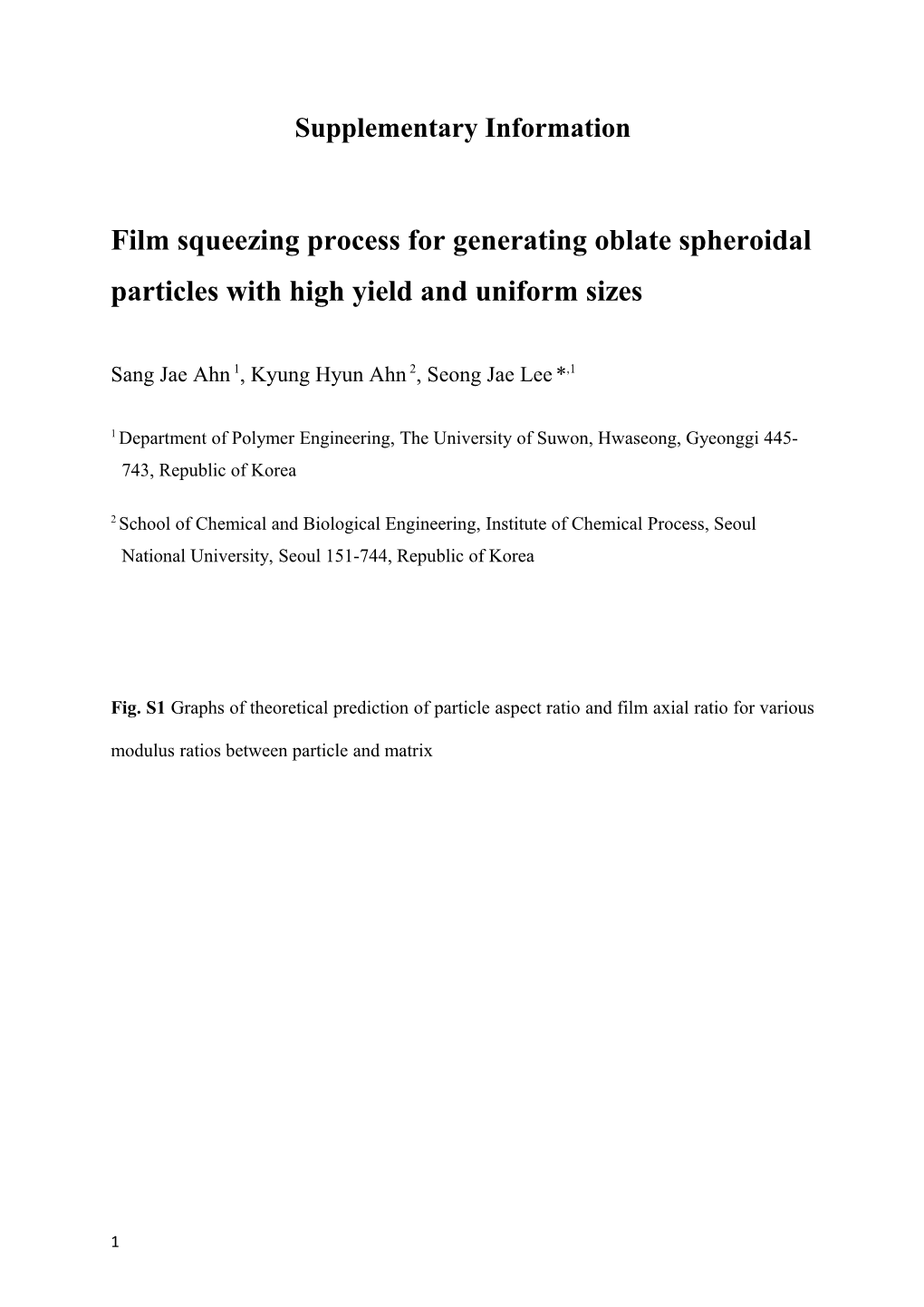
Fig. S1 Graphs of theoretical prediction of particle aspect ratio and film axial ratio for various modulus ratios between particle and matrix
1 Fig. S2 Loss moduli (a) and complex viscosities (b) of silicone rubber sheet, PVA film, and three kinds of PS seed spheres as a function of temperature
2
3 Fig. S3 Examples of shape and size changes before and after squeezing for a couple of films with non-circular geometry: (a) square, (b) triangle, (c) heart, (d) pentagon shaped films
4 Fig. S4 Shapes and sizes of oblate spheroidal particles collected from different locations on a circular film containing PS seed spheres after the film squeezing process: (a) Oblate particles squeezed from DS microspheres at an axial ratio of 0.83, (b) Oblate particles squeezed from
DS microspheres at an axial ratio of 0.5, (c) Oblate particles squeezed from DM microspheres at an axial ratio of 0.83, (d) Oblate particles squeezed from DM microspheres at an axial ratio of 0.17. The scale bars are 500 nm in (a) and (b), and 2 m in (c) and (d)
5 Uniformity of the particles used in this study
To check the uniformity of the particles used in this study, the number-average diameter, , the standard deviation, , and the coefficient of variation of particle size distribution, , of the deformed particles as well as their seed spheres were determined and summarized in Tables S1-S3.
Table S1 Number-average diameter and coefficient of variation of PS seed particles Average diameter Standard Deviation Coefficient of Sample code () () variation (%)
DS 0.530 0.008 1.5
DM 1.9 0.03 1.6
DL 4.3 0.07 1.6
Table S2 Number-average diameter and coefficient of variation of prolate spheroidal particles Axial Average Standard Particle Coefficient of Sample code ratio diameter () deviation () aspect ratio variation (%) 1.5 0.391 0.0093 2.48 2.3 2 0.344 0.0072 3.64 2.0 D S 3 0.289 0.0069 6.11 2.3 4 0.257 0.0074 8.75 2.8 1.5 1.392 0.028 2.54 2.0 2 1.186 0.029 4.11 2.4 D M 3 0.998 0.027 6.9 2.7 4 0.879 0.023 10.09 2.6 1.5 3.131 0.069 2.59 2.2 2 2.682 0.064 4.12 2.3 D L 3 2.235 0.068 7.12 3.0 4 2.008 0.061 9.82 3.0
Table S3 Number-average diameter and coefficient of variation of oblate spheroidal particles Axial Average Standard Particle Coefficient of Sample code ratio diameter () deviation () aspect ratio variation (%) 0.83 0.656 0.017 1.9 2.5
DS 0.5 0.772 0.020 3.1 2.5 0.17 1.320 0.054 15.46 4.0 0.83 2.336 0.051 1.86 2.1
DM 0.5 2.876 0.094 3.47 3.2 0.17 5.258 0.171 21.2 3.2 0.83 5.325 0.127 1.9 2.3
DL 0.5 7.172 0.172 4.64 2.3 0.17 12.631 0.409 25.35 3.2
6 The uniformity of particles can be classified as monodisperse when the value is less than 2%
[S1], 3% [S2], or 4% [S3]. Based on these criteria, all the PS seed particles (DS, DM, DL) show highly monodisperse state. Although the spheroidal particles show a little higher values due to the accumulated errors by additional deformation, it can be said that the particles are still very uniform even after stretching or squeezing.
References S1. Nisisako T, Torii T, Takahashi T, Takizawa Y (2006) Synthesis of monodisperse bicolored Janus particles with electrical anisotropy using a microfluidic co-flow system. Adv Mater 18:1152-1156. S2. Li K, Stover HDH (1993) Synthesis of monodisperse poly(divinylbenzene) microspheres. J Polym Sci Polym Chem 31: 3257-3263. S3. Nagao D, Anzai N, Kobayashi Y, Gu S, Konno M (2006) Preparation of highly monodisperse poly(methyl methacrylate) particles incorporating fluorescent rhodamine 6G for colloidal crystals. J Colloid Interf Sci 298: 232-237.
7