Draft Example of Partial Mapping for AMSA CS Standards Crosswalk with CSTA K-12 Computer Science Standards for State/District/Course Standards http://csta.acm.org/Curriculum/sub/K12Standards.html
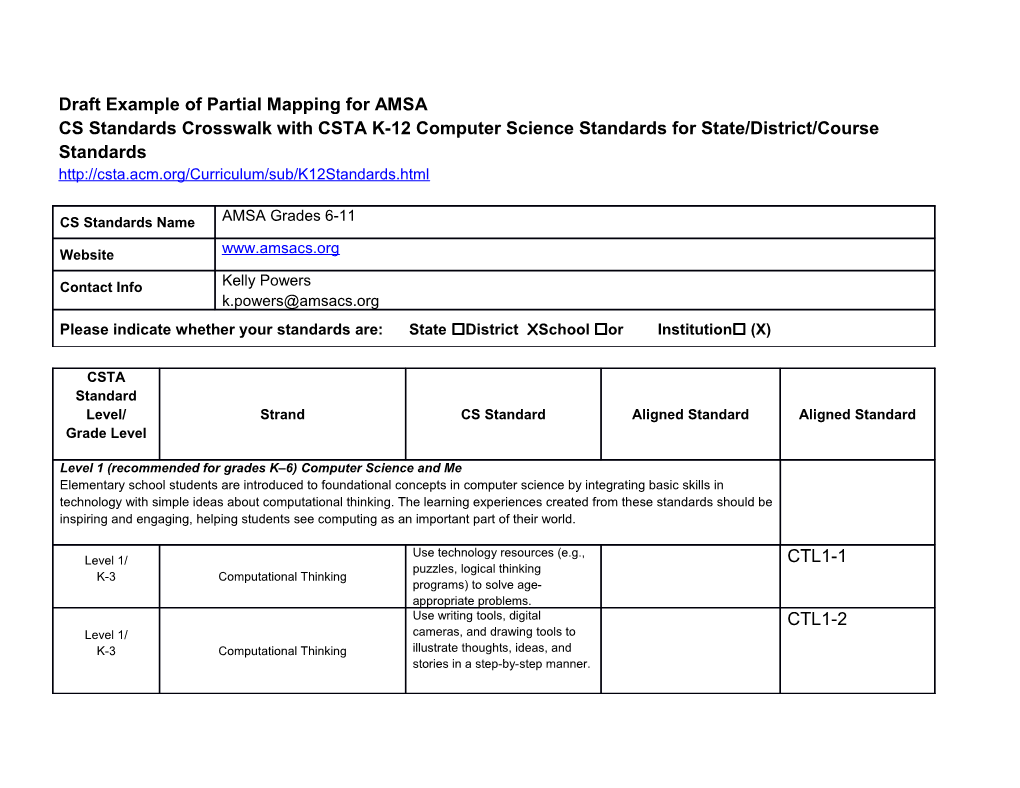
CS Standards Name AMSA Grades 6-11
Website www.amsacs.org
Contact Info Kelly Powers [email protected] Please indicate whether your standards are: State District XSchool or Institution (X)
CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 1 (recommended for grades K–6) Computer Science and Me Elementary school students are introduced to foundational concepts in computer science by integrating basic skills in technology with simple ideas about computational thinking. The learning experiences created from these standards should be inspiring and engaging, helping students see computing as an important part of their world.
Use technology resources (e.g., Level 1/ CTL1-1 puzzles, logical thinking K-3 Computational Thinking programs) to solve age- appropriate problems. Use writing tools, digital CTL1-2 Level 1/ cameras, and drawing tools to K-3 Computational Thinking illustrate thoughts, ideas, and stories in a step-by-step manner. CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 1 (recommended for grades K–6) Computer Science and Me Elementary school students are introduced to foundational concepts in computer science by integrating basic skills in technology with simple ideas about computational thinking. The learning experiences created from these standards should be inspiring and engaging, helping students see computing as an important part of their world.
Understand how to arrange (sort) CTL1-3 Level 1/ information into useful order, K-3 Computational Thinking such as sorting students by birth date, without using a computer.
Recognize that software is Level 1/ CTL1-4 created to control computer K-3 Computational Thinking operations.
Level 1/ Demonstrate how 0s and 1s can Computational Thinking CTL1-5 K-3 be used to represent information. Understand and use the basic CTL1-6 steps in algorithmic problem- Level 1/ Notion of algorithms solving (e.g., problem statement Grade 6, Topic 13, Designing 3-6 Computational Thinking and exploration, examination of Solutions, Pseudo Code, sample instances, design, Flowchart, Coding Algorithms implementation, and testing). Develop a simple understanding Notion of algorithms CTL1-7 Level 1/ of an algorithm (e.g., search, Grade 6, Topic 13, Designing 3-6 Computational Thinking sequence of events, or sorting) Solutions, Pseudo Code, using computer-free exercises. Flowchart, Coding Algorithms Level 1/ Computational Thinking Demonstrate how a string of bits Coding letters with CTL1-8 3-6 can be used to represent numbers alphanumeric information. ASCII and Unicode with binary & hex, RGB in HEX Grade 6, Topic 12, How CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 1 (recommended for grades K–6) Computer Science and Me Elementary school students are introduced to foundational concepts in computer science by integrating basic skills in technology with simple ideas about computational thinking. The learning experiences created from these standards should be inspiring and engaging, helping students see computing as an important part of their world.
Computers Think
Level 1/ Describe how a simulation can CTL1-9 3-6 Computational Thinking be used to solve a problem.
Make a list of sub-problems to Creating a Strategy, CTL1-10 consider while addressing a writing steps to solve a larger problem. problem Level 1/ Notion of algorithms 3-6 Computational Thinking Grade 6, Topic 13, Designing Solutions, Pseudo Code, Flowchart, Coding Algorithms
Understand the connections Babbage (analytic CTL1-11 between computer science and engine), Von Neumann, Level 1/ other fields. Harvard Mark I, analog 3-6 Computational Thinking computers. Grade 6, Unit 1: Topic 1History of Computers and Computation
Level 1/ Collaboration Gather information and COL1-1 K-3 communicate electronically with others with support from teachers, family members, or CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 1 (recommended for grades K–6) Computer Science and Me Elementary school students are introduced to foundational concepts in computer science by integrating basic skills in technology with simple ideas about computational thinking. The learning experiences created from these standards should be inspiring and engaging, helping students see computing as an important part of their world.
student partners.
Work cooperatively and COL1-2 Level 1/ collaboratively with peers, K-3 Collaboration teachers, and others using technology.
Use productivity technology tools Notion of an editor COL1-3 (e.g., word processing, Editing, formatting a spreadsheet, presentation project software) for individual and Using on line help, clip Level 1/ collaborative writing, art Collaboration 3-6 communication, and publishing Basic word functions activities. Grade 6, Topic 6, Word Processing Email etiquette Grade 6, Topic 8, Electronic Mail
Level 1/ Collaboration Use online resources (e.g., Notion of an editor COL1-4 3-6 email, online discussions, Editing, formatting a collaborative web environments) project to participate in collaborative Using on line help, clip problem-solving activities for the art purpose of developing solutions Basic word functions or products. Grade 6, Topic 6, Word Processing Email etiquette CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 1 (recommended for grades K–6) Computer Science and Me Elementary school students are introduced to foundational concepts in computer science by integrating basic skills in technology with simple ideas about computational thinking. The learning experiences created from these standards should be inspiring and engaging, helping students see computing as an important part of their world.
Grade 6, Topic 8, Electronic Mail
Identify ways that teamwork and Notion of an editor COL1-5 collaboration can support Editing, formatting a Level 1/ problem solving and innovation. project 3-6 Collaboration Using on line help, clip art Basic word functions Grade 6, Topic 6, Word Processing Use technology resources to Level 1/ CPPL1-1 Computing Practice and Programming conduct age-appropriate K-3 Research. Use developmentally appropriate CPPL1-2 Level 1/ multimedia resources (e.g., K-3 Computing Practice and Programming interactive books and educational software) to support learning across the curriculum. Create developmentally CPPL1-3 Level 1/ appropriate multimedia products K-3 Computing Practice and Programming with support from teachers, family members, or student partners. Construct a set of statements to Level 1/ CPPL1-4 be acted out to accomplish a K-3 Computing Practice and Programming simple task (e.g., turtle instructions). CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 1 (recommended for grades K–6) Computer Science and Me Elementary school students are introduced to foundational concepts in computer science by integrating basic skills in technology with simple ideas about computational thinking. The learning experiences created from these standards should be inspiring and engaging, helping students see computing as an important part of their world.
Level 1/ Identify jobs that use computing CPPL1-5 K-3 Computing Practice and Programming and technology.
Level 1/ Gather and organize information CPPL1-6 K-3 Computing Practice and Programming using concept-mapping tools.
Use technology resources (e.g., CPPL1-7 calculators, data collection Level 1/ probes, mobile devices, videos, 3-6 Computing Practice and Programming educational software, and web tools) for problem-solving and self-directed learning.
Use general-purpose productivity Use proven typing CPPL1-8 Level 1/ tools and peripherals to support program 3-6 Computing Practice and Programming personal productivity, remediate Grade 6, Topic 4,Typing Skills skill deficits, and facilitate learning. Use technology tools (e.g., Use Paint and web tools CPPL1-9 multimedia and text authoring, to build and create animation Level 1/ presentation, web tools, digital Grade 6, Topic 6, Elementary 3-6 Computing Practice and Programming cameras, and scanners) for Computer Graphics individual and collaborative writing, communication, and publishing activities. CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 1 (recommended for grades K–6) Computer Science and Me Elementary school students are introduced to foundational concepts in computer science by integrating basic skills in technology with simple ideas about computational thinking. The learning experiences created from these standards should be inspiring and engaging, helping students see computing as an important part of their world.
Level 1/ Gather and manipulate data CPPL1-10 3-6 Computing Practice and Programming using a variety of digital tools.
Construct a program as a set of Notion of algorithms CPPL1-11 Level 1/ step-by-step instructions to be Grade 6, Topic 13, Designing 3-6 Computing Practice and Programming acted out (e.g., make peanut Solutions, Pseudo Code, butter and jelly sandwich Flowchart, Coding Algorithms activity). Implement problem solutions Using Alice visual CPPL1-12 using a block based visual programming programming language. Programming as steps to Level 1/ solve a problem 3-6 Computing Practice and Programming Concept of an object, methods, looping Grade 6, Topic 14, Intro to Programming
Use computing devices to CPPL1-13 access remote information, Level 1/ communicate with others in 3-6 Computing Practice and Programming support of direct and independent learning, and pursue personal interests. Level 1/ Computing Practice and Programming Navigate between webpages URLS, domains, CPPL1-14 3-6 using hyperlinks and conduct hyperlinks simple searches using search CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 1 (recommended for grades K–6) Computer Science and Me Elementary school students are introduced to foundational concepts in computer science by integrating basic skills in technology with simple ideas about computational thinking. The learning experiences created from these standards should be inspiring and engaging, helping students see computing as an important part of their world.
engines. Comparison of search engines Relevance of search Boolean search strings Grade 6, Topic 9, WWW & Browsers
Identify a wide range of jobs that what computers are CPPL1-15 require knowledge or use of used for Level 1/ computing. Grade 6, Unit 1 Topic 2: Computer 3-6 Computing Practice and Programming Usage and Terminology
Level 1/ Gather and manipulate data CPPL1-16 3-6 Computing Practice and Programming using a variety of digital tools.
Use standard input and output Level 1/ CCDL1-1 devices to successfully operate K-3 Computers and Communication Devices computers and related technologies.
Level 1/ Demonstrate an appropriate level CCDL1-2 3-6 Computers and Communication Devices of proficiency with keyboards and other input and output devices. CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 1 (recommended for grades K–6) Computer Science and Me Elementary school students are introduced to foundational concepts in computer science by integrating basic skills in technology with simple ideas about computational thinking. The learning experiences created from these standards should be inspiring and engaging, helping students see computing as an important part of their world.
Understand the pervasiveness of CCDL1-3 computers and computing in daily life (e.g., voicemail, Level 1/ downloading videos and audio 3-6 Computers and Communication Devices files, microwave ovens, thermostats, wireless Internet, mobile computing devices, GPS systems). Apply strategies for identifying Level 1/ CCDL1-4 simple hardware and software 3-6 Computers and Communication Devices problems that may occur during use. Level 1/ Identify that information is CCDL1-5 3-6 Computers and Communication Devices coming to the computer from many sources over a network. Level 1/ Identify factors that distinguish CCDL1-6 3-6 Computers and Communication Devices humans from machines.
Recognize that computers model CCDL1-7 intelligent behavior (as found in Level 1/ robotics, speech and language 3-6 Computers and Communication Devices recognition, and computer animation).
Level 1/ Community, Global, and Ethical Impacts Practice responsible digital CGEL1-1 CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 1 (recommended for grades K–6) Computer Science and Me Elementary school students are introduced to foundational concepts in computer science by integrating basic skills in technology with simple ideas about computational thinking. The learning experiences created from these standards should be inspiring and engaging, helping students see computing as an important part of their world.
citizenship (legal and ethical K-3 behaviors) in the use of technology systems and software. Identify positive and negative CGEL1-2 Level 1/ social and ethical behaviors for Community, Global, and Ethical Impacts K-3 using technology.
Discuss basic issues related to CGEL1-3 responsible use of technology Level 1/ and information, and the 3-6 Community, Global, and Ethical Impacts consequences of inappropriate use.
Identify the impact of technology CGEL1-4 (e.g., social networking, cyber bullying, mobile computing and Level 1/ communication, web 3-6 Community, Global, and Ethical Impacts technologies, cyber security, and virtualization) on personal life and society.
Level 1/ Community, Global, and Ethical Impacts Evaluate the accuracy, CGEL1-5 3-6 relevance, appropriateness, comprehensiveness, and biases that occur in electronic CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 1 (recommended for grades K–6) Computer Science and Me Elementary school students are introduced to foundational concepts in computer science by integrating basic skills in technology with simple ideas about computational thinking. The learning experiences created from these standards should be inspiring and engaging, helping students see computing as an important part of their world.
information sources. Understand ethical issues that Personal safety CGEL1-6 relate to computers and networks Cyber Bullying (e.g., equity of access, security, Level 1/ Social Networking privacy, copyright, and 3-6 Community, Global, and Ethical Impacts Concept of an object, intellectual property). methods, looping Grade 6, Topic 12, internet Safety CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 2 (recommended for grades 6–9) Computer Science and Community Middle school/junior high school students begin using computational thinking as a problem-solving tool. They begin to appreciate the ubiquity of computing and the ways in which computer science facilitates communication and collaboration. Students begin to experience computational Thinking as a means of addressing issues relevant, not just to them, but to the world around them.
Level 2/ Computational Thinking Use the basic steps in algorithmic Notion of algorithms CTL2-1 6-9 problem-solving to design solutions Problem solving techniques (e.g., problem statement and Grade 6, Topic 14, Designing Solutions, exploration, examination of sample Pseudo Code, Flowchart, Coding Algorithms instances, design, implementing a Programming as steps to solve a solution, testing, and evaluation). problem Using Alice Visual Programming Looping Branching, Storyboarding Testing Grade 6, Topic 14, Introduction to Programming
What is an algorithm and how can we represent it? Reading and Understanding a problem CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 2 (recommended for grades 6–9) Computer Science and Community Middle school/junior high school students begin using computational thinking as a problem-solving tool. They begin to appreciate the ubiquity of computing and the ways in which computer science facilitates communication and collaboration. Students begin to experience computational Thinking as a means of addressing issues relevant, not just to them, but to the world around them.
Designing Solutions Grade 7, Unit2, Algorithms & Computational Thinking
Various Scripting Languages Revisited Introduction to SQL with databases Database Concepts Design, Reports, Forms Data Modeling Desktop Databases (MS Access) Database Queries Relate SQL with HTML + JavaScript Grade 8, Unit 4, Intro of SQL Fundamental Concepts Learning Algorithms in the world CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 2 (recommended for grades 6–9) Computer Science and Community Middle school/junior high school students begin using computational thinking as a problem-solving tool. They begin to appreciate the ubiquity of computing and the ways in which computer science facilitates communication and collaboration. Students begin to experience computational Thinking as a means of addressing issues relevant, not just to them, but to the world around them.
(Review of algorithms discussed) Python Programming Revisited Revisit more algorithm examples (e.g. Cryptology algorithms from CS Unplugged) Revisit Sorting Algorithms Notion of algorithmic complexity and CS Unplugged intractable problem games Relationship between algorithms, flowcharts, pseudo code and programs using Python Grade8, Unit 5, Computer Programming Using Python
Discussion of U Can Do It Writing procedures with not CSTA Standard Level/ Strand CS Standard Aligned Standard Grade Level
Level 2 (recommended for grades 6–9) Computer Science and Community Middle school/junior high school students begin using computational thinking as a problem-solving tool. They begin to appreciate the ubiquity of computing and the ways in which computer science facilitates communication and collaboration. Students begin to experience computational Thinking as a means of addressing issues relevant, not just to them, but to the world around them.
reinventing the wheel Creating Repeat structures ( Loops) Identifying the Problem, Design, Code, Test, Revisit Making your code efficient Grade9, Unit 4, Designing Solutions, Pseudo code, Flowchart, Coding Algorithms
Web Site Storyboard/Map Designing navigation Defining Site Characteristics, Headings, Color Scheme Refining a Database Query Grade 10, Designing Solutions, Pseudo code, Flowchart, Coding Algorithms