Test 4 - Sections 3 & 4 - MC Questions for Web Site
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
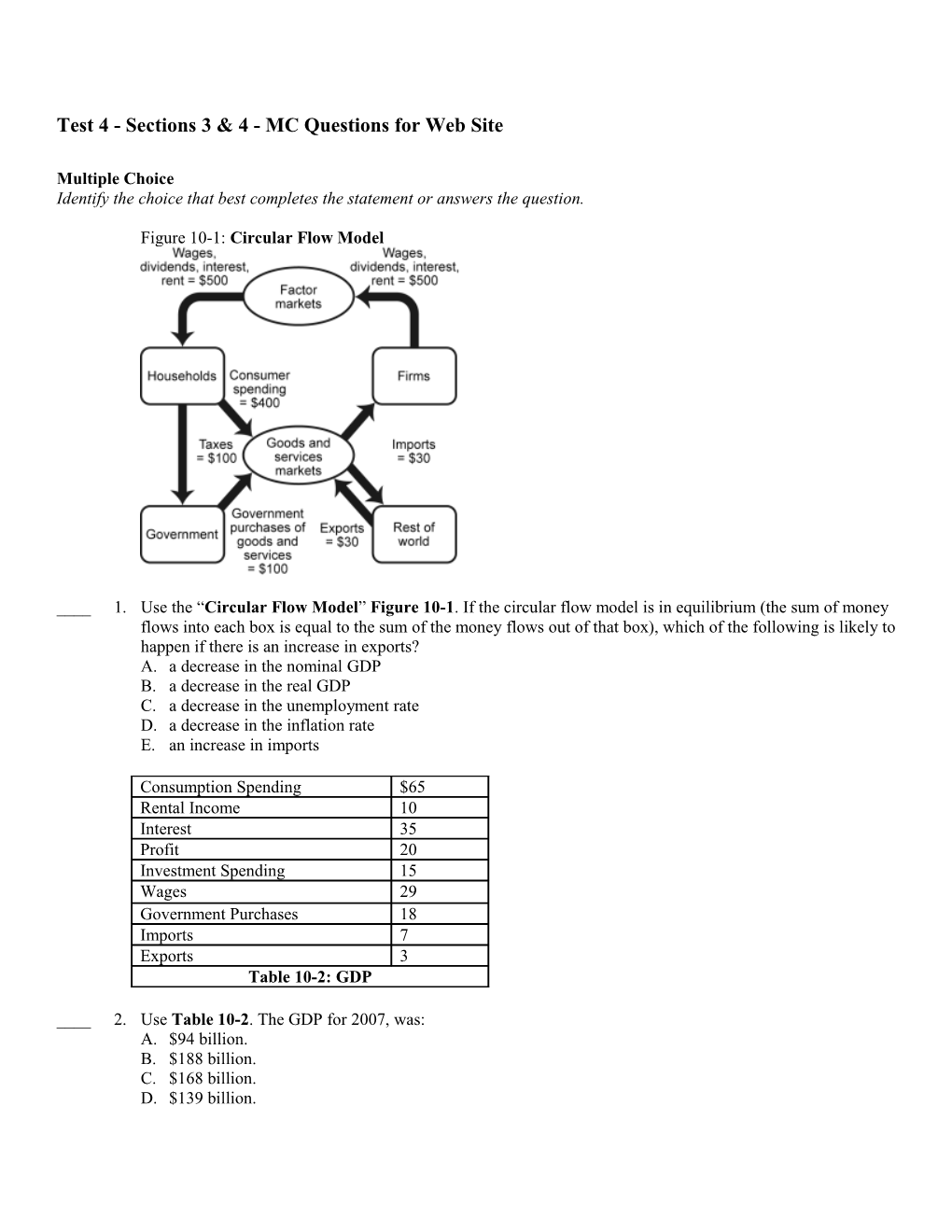
Figure 10-1: Circular Flow Model
____ 1. Use the “Circular Flow Model” Figure 10-1. If the circular flow model is in equilibrium (the sum of money flows into each box is equal to the sum of the money flows out of that box), which of the following is likely to happen if there is an increase in exports? A. a decrease in the nominal GDP B. a decrease in the real GDP C. a decrease in the unemployment rate D. a decrease in the inflation rate E. an increase in imports
Consumption Spending $65 Rental Income 10 Interest 35 Profit 20 Investment Spending 15 Wages 29 Government Purchases 18 Imports 7 Exports 3 Table 10-2: GDP
____ 2. Use Table 10-2. The GDP for 2007, was: A. $94 billion. B. $188 billion. C. $168 billion. D. $139 billion. E. $108 billion. ____ 3. A laptop computer purchased by a private individual is considered to be: A. consumption spending. B. investment spending. C. private saving. D. a transfer of income. E. a financial investment. ____ 4. Unemployment rates tend to decrease when: A. there is an expansion in the economy. B. discouraged workers become active job seekers. C. underemployed workers become unemployed. D. a contraction in the economy occurs. E. the business cycle is approaching the trough. ____ 5. People who are in the process of changing jobs are accounted for in the category of: A. frictional unemployment. B. involuntary unemployment. C. structural unemployment. D. cyclical unemployment. E. underemployed. ____ 6. If the actual unemployment rate is 7% and the cyclical unemployment rate is 2%, then the natural rate of unemployment is: A. 2%. B. 5%. C. 7%. D. 9%. E. 3.5%
Figure 13-1: Minimum Wage
____ 7. Use the “Minimum Wage” Figure 13-1. When the government introduces the binding minimum wage of P3, the quantity of labor supplied rises by:
A. Q4 – Q1. B. Q3 – Q2. C. Q2 – Q1. D. Q4 – Q2. E. zero.
Figure 13-2: Effect of Minimum Wage
____ 8. Use the “Effect of Minimum Wage” Figure 13-2. Suppose the labor market is in equilibrium at E when the
government introduces a minimum wage of WF. One problem that may arise is that the quantity of labor supplied would ______, resulting in structural unemployment.
A. decrease to QD B. stay at QE C. increase to QS D. stay at WE E. decrease to zero. ____ 9. The natural rate of employment is achieved when: A. the actual rate of unemployment is equal to zero. B. the natural rate of unemployment is equal to the frictional rate of unemployment. C. the quantity of labor supplied is equal to the quantity of labor demanded. D. there is no cyclical unemployment. E. there is no cyclical unemployment and no frictional unemployment. ____ 10. Which of the following is true concerning interest rates? A. The nominal interest rate can be negative. B. The real interest rate cannot be negative. C. The real interest rate can only be positive. D. The real interest rate can be zero, positive, or negative. E. The real interest rate is equal to the sum of the nominal interest rate and expected inflation rate. ____ 11. If the multiplier is 4, and investment spending falls by $100 billion, the change in equilibrium income will be: A. -$40 billion. B. $400 billion. C. $25 billion. D. –$25 billion. E. –$400 billion. ____ 12. An upward shift in the consumption function can be caused by: A. an increase in consumer wealth. B. a drop in consumer wealth. C. pessimistic expectations about the future. D. an increase in current disposable personal income. E. a stock market crash. ____ 13. If real GDP is less than aggregate expenditure, then inventories will: A. increase and firms will cut back on future production. B. fall and firms will decrease the prices of their products. C. increase and firms will decrease the prices of their products. D. fall and firms will increase their future production. E. increase and firms will increase the prices of their products. ____ 14. Alice's disposable income increases by $1,000, and she spends $600 of this increase in disposable income. For Alice, her: A. MPS is 0.40 and she saves $400. B. MPC is 0.40 and she saves $400. C. MPS is 0.40 and she saves $600. D. MPC is 0.60 and she consumes $400. E. MPC is 0.60 and she consumes $1,000 ____ 15. A decrease in aggregate demand is seen as a(n): A. downward movement along the aggregate demand curve. B. upward movement along the aggregate demand curve. C. shift to the left in the aggregate demand curve. D. shift to the right in the aggregate demand curve. E. movement from a vertical to a horizontal aggregate demand curve.
Figure 18-1: Aggregate Supply Movements ____ 16. Use the “Aggregate Supply Movements” Figure 18-1. Using the accompanying figure we can safely conclude that: A. an increase in the price level is responsible for pushing the SRAS curve to the right. B. a decrease in the price level is responsible for pushing the SRAS curve to the right. C. there has been an increase in the SRAS supply curve. D. there has been a decrease in the SRAS supply curve. E. an increase in the price level has caused an upward movement along the SRAS curve. ____ 17. An increase in the short-run aggregate supply curve may be caused by: A. a decrease in income taxes. B. an increase in productivity. C. an increase in the price of inputs. D. an increase in wages. E. an increase in government spending.
Figure 19-6: AD–AS Model I
____ 18. Use the “AD–AS Model I” Figure 19-6. If the economy is at point X, there is: A. an inflationary gap with low unemployment. B. an inflationary gap with high unemployment. C. a recessionary gap with low unemployment. D. a recessionary gap with high unemployment. E. long-run equilibrium with full employment. ____ 19. Contractionary fiscal policy includes: A. decreasing taxes. B. increasing taxes. C. increasing the money supply. D. increasing government expenditures. E. increasing the discount rate. ____ 20. Assume that marginal propensity to consume is 0.8, and potential output is $800 billion. If current GDP is $850 billion: A. there is an inflationary gap. B. there is a recessionary gap. C. the economy is in long-run equilibrium. D. taxes should be decreased. E. transfer payments should be increased. Test 4 - Sections 3 & 4 - MC Questions for Web Site Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 10 SKL: Critical Thinking 2. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 10 SKL: Critical Thinking 3. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 10 SKL: Concept-Based 4. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 12 SKL: Concept-Based 5. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: E REF: Module 13 SKL: Definitional 6. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 13 SKL: Concept-Based 7. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 13 SKL: Critical Thinking 8. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 13 SKL: Concept-Based 9. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 13 SKL: Concept-Based 10. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: E REF: Module 14 SKL: Critical Thinking 11. ANS: E PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 16 SKL: Critical Thinking 12. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 16 SKL: Critical Thinking 13. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 16 SKL: Critical Thinking 14. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 16 SKL: Critical Thinking 15. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 17 SKL: Concept-Based 16. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18 SKL: Concept-Based 17. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 18 SKL: Critical Thinking 18. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 19 SKL: Critical Thinking 19. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: E REF: Module 20 SKL: Fact-Based 20. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: M REF: Module 21 SKL: Critical Thinking