Environment: The Science Behind the Stories, 4e (Withgott) Chapter 8 Human Population
8.1 Graph and Figure Interpretation Questions
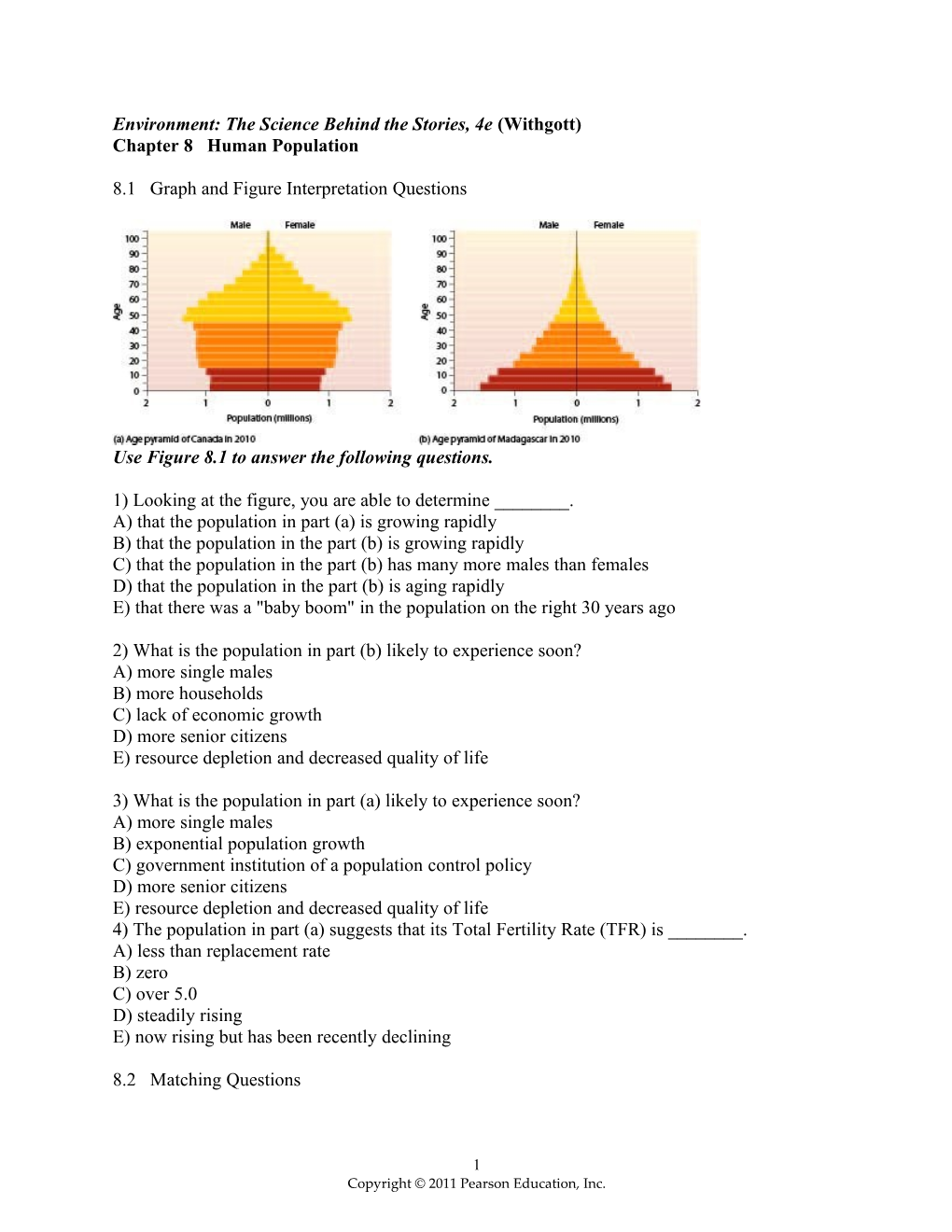
Use Figure 8.1 to answer the following questions.
1) Looking at the figure, you are able to determine ______. A) that the population in part (a) is growing rapidly B) that the population in the part (b) is growing rapidly C) that the population in the part (b) has many more males than females D) that the population in the part (b) is aging rapidly E) that there was a "baby boom" in the population on the right 30 years ago
2) What is the population in part (b) likely to experience soon? A) more single males B) more households C) lack of economic growth D) more senior citizens E) resource depletion and decreased quality of life
3) What is the population in part (a) likely to experience soon? A) more single males B) exponential population growth C) government institution of a population control policy D) more senior citizens E) resource depletion and decreased quality of life 4) The population in part (a) suggests that its Total Fertility Rate (TFR) is ______. A) less than replacement rate B) zero C) over 5.0 D) steadily rising E) now rising but has been recently declining
8.2 Matching Questions
1 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Match the following.
A) Canada B) Sweden C) 2050 D) Latin America and the Caribbean E) European nations F) Great Britain G) 2011 H) United States I) African nations J) India
1) This region has been hit the hardest by the HIV/AIDS epidemic
2) Second most populous region on Earth 3) Year when we expect the 7 billionth human 4) TFR is 2.5 in this region 5) Nation where a very high percentage of women hold national parliamentary seats 8.3 Multiple-Choice Questions
1) The human population is approximately ______. A) 1.5 million B) 6.9 million C) 1.5 billion D) 6.9 billion E) 10 billion 2) During which time period did the world's population more than double? A) 1750–1800 B) 1800–1850 C) 1850–1900 D) 1900–1950 E) 1950–2000 3) If a population roughly doubles in the course of 50 years, its growth rate would be close to ______%. A) 1.5 B) 5 C) 10 D) 20 E) 25 4) ______is the world's most populous nation, home to ______of the people living on Earth. A) China; half B) China; one-fifth C) The United States; half D) The United States; one-fifth
2 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. E) India; one-third 5) Which of the following is not one of the world's top five most populous nations? A) Vietnam B) United States C) Indonesia D) Brazil E) India 6) Replacement fertility ______. A) restores population size after a catastrophic event B) is a contraceptive technique C) is below 2 in Latin America and the Caribbean D) is below 2 in Africa E) is equal to 2.1 in stable populations 7) The 1994 Cairo, Egypt, conference was organized ______. A) by President Clinton to seek world funding for family-planning initiatives B) to lower the world's population to preset targets by advocating the use of contraceptives C) to urge governments to better address social issues such as poverty and disease as potential sources of population problems D) to address the growing AIDS epidemic in Africa E) to reevaluate the effectiveness of China's one-child policy 8) Life expectancy in parts of southern Africa ______. A) has fallen dramatically since 1990 B) is starting to fall C) is on the rise D) has stabilized due to population control E) cannot be determined due to lack of adequate methods for data collection 9) Declining death rates due to increased food production and improved medical care while birth rates remain high is characteristic of the ______stage. A) pre-industrial B) stabilization C) transitional D) post-industrial E) revolutionary 10) Areas with the least dense human populations are in ______. A) agricultural areas B) temperate areas C) Europe D) Mexico E) the suburbs 11) Which of the following countries has the highest population growth rate? A) Spain B) Italy C) Pakistan D) Canada E) United States 12) Which of the following factors drives TFR down?
3 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. A) rural lifestyle B) social and economic security C) poverty D) history and tradition E) high infant mortality 13) The transitional stage in Frank Notestein's demographic model is initiated by ______. A) government intervention B) the increased use of contraceptives C) epidemics D) industrialization E) resource depletion 14) The richest one-fifth of the world's population possess approximately ______times the income of the poorest one-fifth, and the richest one-fifth use over 86% of the world's resources. A) 10 B) 20 C) 40 D) 60 E) 80 15) If global fertility rates remain at 2008 levels, the United Nations predicts that world population will be approximately ______billion in 2050. A) 11 B) 10 C) 7 D) 5 E) 4 16) The annual global growth rate of the human population peaked in the ______and has been declining ever since. A) early 1900s B) 1950s C) 1960s D) 1990s E) year 2000 17) A country with ______is not expected to grow quickly in the near future. A) a pyramid-shaped age-structure diagram B) high female literacy C) a female to male ratio of 1.2 to 1 D) growing industrialization E) many developing regions 18) In a country where there are increasingly more households, ______. A) consumption should decrease B) consumption should increase C) birth rates should increase D) birth rates should remain constant E) population growth rates should increase
4 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 19) As of 2008, total HIV infections are estimated at nearly ______million. A) 33 B) 100 C) 25 D) 10 E) 1 20) Demographic effects of AIDS are most significant because ______. A) AIDS strikes affluent people more than poor people B) it is caused by a virus C) it is not known who is resistant to AIDS D) AIDS leaves behind orphans E) AIDS sickens and kills the youngest and most productive members of society 21) America's age-structure diagram ______. A) looks like a pyramid B) reflects unequal distribution of males and females at all age groups C) reflects a "baby boom" in the early 1980s D) reflects an aging population E) reflects a population with a high growth rate 22) The world population growth rate is currently close to ______%. A) 20 B) 10 C) 5 D) 2.5 E) 1.2 : 8.1 Scope of human population growth
23) According to the IPAT model, technology that enhances our acquisition of minerals, fossil fuels, timber, and ocean fish ______. A) increases environmental impact B) decreases environmental impact C) increases population D) increases sensitivity E) decreases sensitivity 24) The Cornucopian view held by many economists suggests that resource depletion due to greater numbers of people ______. A) is not a problem if new resources can be found to replace depleted ones B) is not a problem because disease will limit population size C) is not a problem because humans are too intelligent to allow it to be D) will lead to natural selection of the most fit individuals E) will cause a population crash
5 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 25) The "sensitivity factor" in the model used to represent human environmental impact denotes ______. A) human sensitivity to what needs to be done to protect the environment B) the sensitivity of an environment to human pressures C) the sensitivity of endangered species to human population infringement D) the sensitivity of governments to carrying capacity demands E) economic sensitivity to resource use 26) The most accurate terms describing the trend over the past 50 years in resource use for human energy and agricultural systems are ______. A) increasing and unsustainable B) decreasing and sustainable C) steady state - no change D) from unsustainable to sustainable E) rapidly increasing, moving from unsustainable to sustainable 27) Malthus was responsible for ______. A) the book The Population Bomb, which described the disastrous effects of human population growth B) the idea that without social strictures increasing human population would lead to famine and war C) the idea that population growth would lead to greater industry and prosperity D) recognizing the demographic transition effect in developing nations E) defining the concept of ecosystem services 28) A population which is not growing will have a TFR of ______. A) zero B) 1.2 C) 2.1 D) 5 or higher E) less than 1.0 29) Not surprisingly, the nation with the highest rate of contraceptive use (90%) is ______. A) South Africa B) United States C) New Zealand D) China E) Australia 30) Helmut Haberl and colleagues have compiled data on ______as a measure of the human population's growth on earth's natural resources and ecosystem services. A) industrial pollution B) loss of biodiversity, especially pollinators C) water quality D) invasive exotic species E) consumption of net primary productivity
6 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.