Draft proposal 12/14/2017 2008-09 New Mexico Expanded Grade Band Expectations Assessment Frameworks Social Studies – Grades 9 through 12
Strand: History Content Standard I: Students are able to identify important people and events in order to analyze significant patterns, relationships, themes, ideas, beliefs, and turning points in New Mexico, United States, and world history in order to understand the complexity of the human experience.
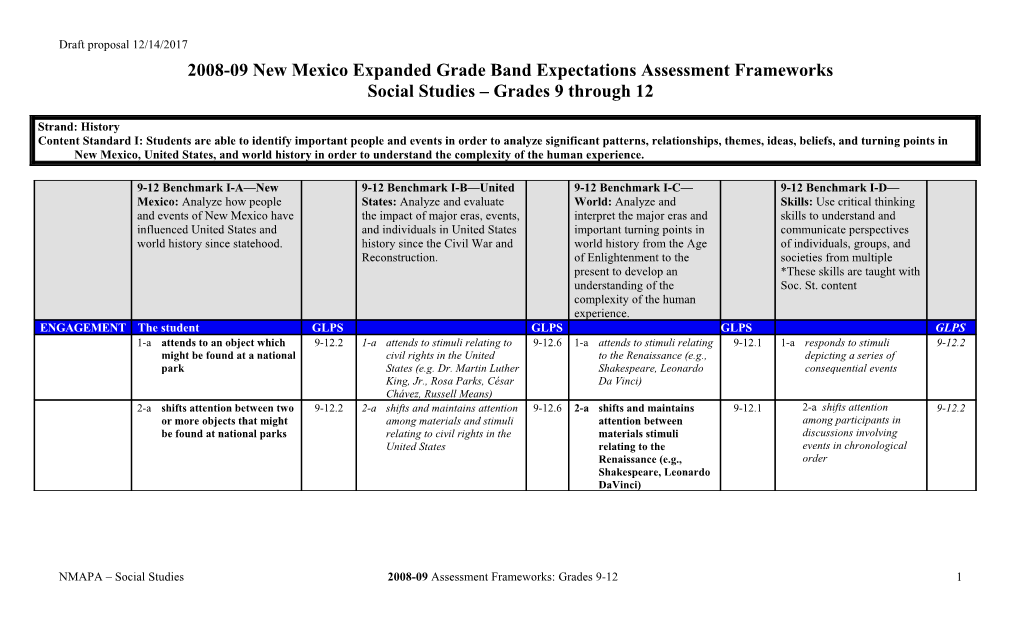
9-12 Benchmark I-A—New 9-12 Benchmark I-B—United 9-12 Benchmark I-C— 9-12 Benchmark I-D— Mexico: Analyze how people States: Analyze and evaluate World: Analyze and Skills: Use critical thinking and events of New Mexico have the impact of major eras, events, interpret the major eras and skills to understand and influenced United States and and individuals in United States important turning points in communicate perspectives world history since statehood. history since the Civil War and world history from the Age of individuals, groups, and Reconstruction. of Enlightenment to the societies from multiple present to develop an *These skills are taught with understanding of the Soc. St. content complexity of the human experience. ENGAGEMENT The student GLPS GLPS GLPS GLPS 1-a attends to an object which 9-12.2 1-a attends to stimuli relating to 9-12.6 1-a attends to stimuli relating 9-12.1 1-a responds to stimuli 9-12.2 might be found at a national civil rights in the United to the Renaissance (e.g., depicting a series of park States (e.g. Dr. Martin Luther Shakespeare, Leonardo consequential events King, Jr., Rosa Parks, César Da Vinci) Chávez, Russell Means) 2-a shifts attention between two 9-12.2 2-a shifts and maintains attention 9-12.6 2-a shifts and maintains 9-12.1 2-a shifts attention 9-12.2 or more objects that might among materials and stimuli attention between among participants in be found at national parks relating to civil rights in the materials stimuli discussions involving United States relating to the events in chronological Renaissance (e.g., order Shakespeare, Leonardo DaVinci)
NMAPA – Social Studies 2008-09 Assessment Frameworks: Grades 9-12 1 Draft proposal 12/14/2017 9-12 Benchmark I-A—New 9-12 Benchmark I-B—United 9-12 Benchmark I-C— 9-12 Benchmark I-D— Mexico: Analyze how people States: Analyze and evaluate World: Analyze and Skills: Use critical thinking and events of New Mexico have the impact of major eras, events, interpret the major eras and skills to understand and influenced United States and and individuals in United States important turning points in communicate perspectives world history since statehood. history since the Civil War and world history from the Age of individuals, groups, and Reconstruction. of Enlightenment to the societies from multiple present to develop an *These skills are taught with understanding of the Soc. St. content complexity of the human experience. PRE- SYMBOLIC The student GLPS GLPS GLPS GLPS 3-a matches objects or graphic 9-12.4 3-a matches graphic 9-12.6 3-a matches graphic 9-12. 11 3-a anticipates predictable 9-12.2 representations that representations of representations of effects of related causes represent NM’s artistic, important individuals in the various countries in the scientific, and technological civil rights movement in the Western Hemisphere contributions since World United States (e.g. Martin (e.g. Canada, United War II Luther King, Jr., Rosa States, Mexico) Parks, César Chávez) 4-a identifies New Mexicans who 9-12.3 4-a labels an event or an 9-12.6 4-a identifies historical 9-12.11 4-a identifies events 9-12.2 have contributed to the arts, individual important in the reasons for the migration chronologically sciences, and technology Civil Rights Movement in the of peoples between since World War II (e.g., US countries Georgia O’Keefe, Robert Oppenheimer)
NMAPA – Social Studies 2008-09 Assessment Frameworks: Grades 9-12 2 Draft proposal 12/14/2017 9-12 Benchmark I-A—New 9-12 Benchmark I-B—United 9-12 Benchmark I-C— 9-12 Benchmark I-D— Mexico: Analyze how people States: Analyze and evaluate World: Analyze and Skills: Use critical thinking and events of New Mexico have the impact of major eras, events, interpret the major eras and skills to understand and influenced United States and and individuals in United States important turning points in communicate perspectives world history since statehood. history since the Civil War and world history from the Age of individuals, groups, and Reconstruction. of Enlightenment to the societies from multiple present to develop an *These skills are taught with understanding of the Soc. St. content complexity of the human experience. SYMBOLIC The student GLPS GLPS GLPS GLPS 5-a explores the life of a NM 9-12.3 5-a identifies an event or the 9-12.6 5-a name an important 9-12.11 5-a arranges important 9-12.2 citizen who had a role or characteristics of an turning point in world world history events in impacted World War II (e.g., individual involved in the history which contributed chronological order Navajo Code Talkers, Bataan US Civil Rights Movement to mass migrations (e.g., Death March, Manhattan religious persecution, Project) growth of industrial cities, rural-to-urban migration) 6-a relates details about a NM 9-12.3 6-a describes events and 9-12.6 5-b identifies important 9-12.7 6-a describes events in a 9-12.2 citizen who had a role or individuals in US History individuals and events 9-12.9 historical timeline impacted World War II related to the Civil Rights of World War I and related to cause and (e.g., Navajo Code Talkers, Movement World War II effect Bataan Death March, Manhattan Project) 6-a describe a historical 9-12.11 event which caused mass migration
NMAPA – Social Studies 2008-09 Assessment Frameworks: Grades 9-12 3 Draft proposal 12/14/2017 9-12 Benchmark I-A—New 9-12 Benchmark I-B—United 9-12 Benchmark I-C— 9-12 Benchmark I-D— Mexico: Analyze how people States: Analyze and evaluate World: Analyze and Skills: Use critical thinking and events of New Mexico have the impact of major eras, events, interpret the major eras and skills to understand and influenced United States and and individuals in United States important turning points in communicate perspectives world history since statehood. history since the Civil War and world history from the Age of individuals, groups, and Reconstruction. of Enlightenment to the societies from multiple present to develop an *These skills are taught with understanding of the Soc. St. content complexity of the human experience.
EXTENDED SYMBOLIC The student GLPS GLPS GLPS GLPS 7-a describes the impact of a 9-12.3 7-a determines the relationship 9-12.6 7-a understand the 9-12. 11 7-a constructs a 9-12.2 NM citizen on world history between an event or an significance of shifting representation of an since statehood (e.g., Native individual in the US Civil world populations historical timeline Code Talkers, Bataan Rights Movement and the Death March) effect on US history 8-a evaluates the impact of a 9-12.3 8-a analyzes the impact of a 9-12.6 7-b researches causes, 9-12.7 8-a reflects on the causal 9-12.2 New Mexican citizen on single event on the US Civil events, and effects of 9-12.8 aspects of events in a world history since statehood Rights Movement world crises (e.g., World 9-12.9 given historical timeline War I, World War II, 9-12.10 Vietnam, Cold War) 8-a analyzes the impact of 9-12.11 shifting world populations 8-b presents research 9-12.7 findings related to 9-12.8 world crises (e.g., World 9-12.9 War I, World War II, 9-12.10 Vietnam, Cold War)
NMAPA – Social Studies 2008-09 Assessment Frameworks: Grades 9-12 4 Draft proposal 12/14/2017
Strand: Geography Content Standard II: Students understand how physical, natural, and cultural processes influence where people live, the ways in which people live, and how societies interact with one another and their environments.
9-12 Benchmark II-A: 9-12 Benchmark II-B: 9-12 Benchmark II-C: 9-12 Benchmark II-E: NOTE* Analyze and evaluate the Analyze natural and Analyze the impact of people, Analyze and evaluate characteristics and man-made places, and natural how economic, political, purposes of geographic characteristics of environments upon the past cultural, and social tools, knowledge, skills, worldwide locales; and present in terms of our processes interact to and perspectives, and describe regions, their ability to plan for the future. shape patterns of human apply them to explain the interrelationships, and populations, and their past, present, and future patterns of change. interdependence, in terms of patterns, cooperation, and events, and issues. conflict. ENGAGEMENT The student GLPS GLPS GLPS GLPS 1-a attends to stimuli in 9-12.1 1-a attends to an object 9-12.2 1-a attends to stimuli and 9-12.1 1-a attends to stimuli 9-12.2 discussions related to of cultural 9-12.4 materials involving and materials while geographic significance (e.g. geographical participating in representations drums, pottery) characteristics discussions of geographical factors influencing activities in New Mexico 2-a shifts and maintains 9-12.1 2-a responds to an object 9-12.2 2-a jointly attends to 9-12.1 2-a jointly attends to 9-12.2 attention among of cultural 9-12.4 materials and peers while materials and peers while peers in discussions significance participating in participating in related to geographic discussions of the discussions of representations geographical geographical factors characteristics affecting influencing activities in historical events New Mexico
NMAPA – Social Studies 2008-09 Assessment Frameworks: Grades 9-12 5 Draft proposal 12/14/2017 9-12 Benchmark II-A: 9-12 Benchmark II-B: 9-12 Benchmark II-C: 9-12 Benchmark II-E: NOTE* Analyze and evaluate the Analyze natural and Analyze the impact of people, Analyze and evaluate characteristics and man-made places, and natural how economic, political, purposes of geographic characteristics of environments upon the past cultural, and social tools, knowledge, skills, worldwide locales; and present in terms of our processes interact to and perspectives, and describe regions, their ability to plan for the future. shape patterns of human apply them to explain the interrelationships, and populations, and their past, present, and future patterns of change. interdependence, in terms of patterns, cooperation, and events, and issues. conflict. PRE- GLPS SYMBOLIC The student GLPS GLPS GLPS 3-a explores 9-12.1 3-a matches objects of 9-12.2 3-a matches objects that 9-12.1 3-a matches objects 9-12.1 geographical cultural significance 9-12.4 represent like that represent economic representations geographical activities in NM (e.g., characteristics mining, ranching, agriculture, tourism) 4-a identifies features of 9-12.1 4-a labels graphic 9-12.2 4-a gathers information 9-12.1 4-a compares regional 9-12.1 relevant representations of 9-12.4 involving geographical economic activities in geographical cultural significance characteristics that have New Mexico representations (e.g., drums, affected historical events pottery) SYMBOLIC The student GLPS GLPS GLPS GLPS 5-a lists information 9-12.1 5-a identifies cultural 9-12.2 5-a identifies geographical 9-12.1 5-a predicts the impact 9-12.1 contained in a aspects of his/her 9-12.4 characteristics that have of regional development geographical environment (e.g., affected historical events on local resources (e.g., representation sacred tribal lands) drought, depletion of resources) 6-a describes the 9-12.1 6-a describes the cultural 9-12.2 6-a draws conclusions about 9-12.1 6-a makes connections 9-12.1 relationship significance of a 9-12.4 how geographical between specific between a map and specific place or characteristics can effect geographical regions in its key region historical outcomes NM and their respective economic activities
NMAPA – Social Studies 2008-09 Assessment Frameworks: Grades 9-12 6 Draft proposal 12/14/2017 9-12 Benchmark II-A: 9-12 Benchmark II-B: 9-12 Benchmark II-C: 9-12 Benchmark II-E: NOTE* Analyze and evaluate the Analyze natural and Analyze the impact of people, Analyze and evaluate characteristics and man-made places, and natural how economic, political, purposes of geographic characteristics of environments upon the past cultural, and social tools, knowledge, skills, worldwide locales; and present in terms of our processes interact to and perspectives, and describe regions, their ability to plan for the future. shape patterns of human apply them to explain the interrelationships, and populations, and their past, present, and future patterns of change. interdependence, in terms of patterns, cooperation, and events, and issues. conflict. EXTENDED GLPS SYMBOLIC The student GLPS GLPS GLPS 7-a identifies issues and 9-12.1 7-a describes the cultural 9-12.2 7-a uses technology to study 9-12.4 7-a determines the 9-12.1 problems based on significance of an 9-12.4 geography impact of depleted information gathered important place or resources on economic from geographical person activity in a given representations region of NM 8-a interprets 9-12.2 8-a reflect on the 9-12.2 8-a describes outcomes that 9-12.3 8-a evaluates the 9-12.1 population personal 9-12.4 were influenced by impact of resource distributions and significance of a geographical features changes in given regions settlement patterns specific cultural of NM that are on a geographical person or place dependent on specific representation economic resources (e.g., human, natural)
NOTE* The EGBE development panel determined that benchmarks “9-12 Benchmark II-D: Analyze how physical processes shape the Earth’s surface patterns and biosystems and 9- 12 Benchmark II-F: Analyze and evaluate the effects of human and natural interactions in terms of changes in the meaning, use, distribution, and importance of resources in order to predict our global capacity to support human activity,” provided inappropriate assessment targets for students with significant cognitive disabilities. Thus, no Assessment Frameworks were developed within these benchmarks.
NMAPA – Social Studies 2008-09 Assessment Frameworks: Grades 9-12 7 Draft proposal 12/14/2017 Strand: Civics and Government Content Standard III: Students understand the ideals, rights, and responsibilities of citizenship and understand the content and history of the founding documents of the United States with particular emphasis on the United States and New Mexico constitutions and how governments function at local, state, tribal, and national levels.
9-12 Benchmark III-A: Compare and 9-12 Benchmark III-B: Analyze how the 9-12 Benchmark III-D: Understand NOTE* analyze the structure, power, and purpose of symbols, icons, songs, traditions, and how to exercise rights and government at the local, state, tribal, and leaders of New Mexico and the United responsibilities as citizens by national levels as set forth in their respective States exemplify ideals and provide participating in civic life and using skills constitutions or governance documents. continuity and a sense of unity. that include interacting, monitoring, and influencing. ENGAGEMENT The student GLPS GLPS GLPS 1-a attends to stimuli and materials 9-12.2 1-a responds to songs and symbols that 9-12.4 1-a responds to stimuli and materials that 9-12.2 involving the President of the United represent NM and the US are reflective of basic rights and States responsibilities of US citizens 2-a jointly attends to stimuli and materials 9-12.5 2-a shifts and maintains attention to songs 9-12.4 2-a shifts and maintains attention 9-12.2 involving the Constitution and Bill of and various symbols of NM and the US among peers in discussions involving Rights basic rights and responsibilities of US citizens PRE- SYMBOLIC The student GLPS GLPS GLPS 3-a matches objects which represent the 9-12.2 3-a matches objects which represent NM and 9-12.4 3-a attends to personal role in activities 9-12.2 office of the President of the United the US involving group membership States. 4-a identifies a personal freedom 9-12.5 4-a identifies symbols that are reflective of 9-12.4 4-a labels the basic rights and 9-12.2 guaranteed by the Bill of Rights NM and the US responsibilities of US citizens (e.g., voting, obeying the law, paying taxes)
NMAPA – Social Studies 2008-09 Assessment Frameworks: Grades 9-12 8 Draft proposal 12/14/2017 9-12 Benchmark III-A: Compare and 9-12 Benchmark III-B: Analyze how the 9-12 Benchmark III-D: Understand NOTE* analyze the structure, power, and purpose of symbols, icons, songs, traditions, and how to exercise rights and government at the local, state, tribal, and leaders of New Mexico and the United responsibilities as citizens by national levels as set forth in their respective States exemplify ideals and provide participating in civic life and using skills constitutions or governance documents. continuity and a sense of unity. that include interacting, monitoring, and influencing. SYMBOLIC The student GLPS GLPS GLPS 5-a broadly defines the role of the executive 9-12.2 5-a distinguishes symbols that are reflective 9-12.4 5-a identifies basic rights and 9-12.2 branch in government of NM compared to those reflective of responsibilities of US citizens (e.g., the US voting, obeying the law, taxes) 5-b broadly defines the rights, protection, 9-12.5 6-a produces symbols that are reflective of 9-12.4 6-a describes the basic rights and 9-12.2 limits and freedoms included in the US NM and the US responsibilities of US citizens Constitution 6-a identifies the powers of the legislative 9-12.1 branch of the US government 6-b cites an example of the rights, 9-12.5 protection, limits and freedoms included in the US Constitution 6-c defines the role of the judicial branch of 9-12.4 the US government EXTENDED SYMBOLIC The student GLPS GLPS GLPS 7-a broadly defines the rights, protection, 9-12.1 7-a describes symbols that are reflective of 9-12.4 7-a evaluates candidates for public 9-12.3 limits and freedoms included in the US 9-12.5 NM and the US positions based upon their platform Constitution 8-a identifies the structure, powers, and roles 9-12. 8-a explains the significance of symbols of 9-12.3 8-a discusses factors that influence the of the three branches of government 9-12.2 NM and the US 9-12.4 formation of public opinion (e.g., 9-12.2 9-12.4 media, news, radio)
*NOTE: The EGBE development panel determined that benchmark “9-12 Benchmark III-C: Compare and contrast the philosophical foundations of the United States political system in terms of the purpose of government, including its historical sources and ideals, with those of other governments in the world,” provided inappropriate assessment targets for students with significant cognitive disabilities. Thus, no Assessment Frameworks were developed within this benchmark.
NMAPA – Social Studies 2008-09 Assessment Frameworks: Grades 9-12 9 Draft proposal 12/14/2017 Strand: Economics Content Standard IV: Students understand basic economic principles and use economic reasoning skills to analyze the impact of economic systems (including the market Economicseconomy) on individuals, families, businesses, communities, and governments.
9-12 Benchmark IV-A: Analyze the ways 9-12 Benchmark IV-B: Analyze and NOTE* individuals, households, businesses, evaluate how economic systems impact governments, and societies make decisions, are the way individuals, households, influenced by incentives (economic and businesses, governments, and societies intrinsic) and the availability and use of scarce make decisions about resources and the resources and that their choices involve costs production and distribution of goods and and varying ways of allocating. services. ENGAGEMENT The student GLPS GLPS 1-a attends to activities involving work force 9-12.9 1-a attends to activities involving 9-12.5 requirements technology, transportation, and communication systems 2-a shifts and maintains attention in activities 9-12.9 2-a shifts and maintains attention among 9-12.5 involving work force requirements. peers in activities involving technology, transportation, and communication systems PRE- SYMBOLIC GLPS GLPS 3-a explores graphic representations and 9-12.9 3-a explores objects and graphic 9-12.6 objects which represent workforce representations involving the roles requirements played by local, state, and tribal governments in NM’s economic system 4-a discusses essential learning skills that are 9-12.9 4-a labels changes in the areas of 9-12.15 necessary for participation in the technology, transportation, and workforce communication that have affected economic activities in NM
NMAPA – Social Studies 2008-09 Assessment Frameworks: Grades 9-12 10 Draft proposal 12/14/2017 9-12 Benchmark IV-A: Analyze the ways 9-12 Benchmark IV-B: Analyze and NOTE* individuals, households, businesses, evaluate how economic systems impact governments, and societies make decisions, are the way individuals, households, influenced by incentives (economic and businesses, governments, and societies intrinsic) and the availability and use of scarce make decisions about resources and the resources and that their choices involve costs production and distribution of goods and and varying ways of allocating. services. SYMBOLIC GLPS GLPS 5-a identifies the essential learning skills that 9-12.9 5-a identifies changes in the areas of 9-12.5 are necessary for a personal employment technology, transportation, and selection communication that have affected economic activities in NM 6-a describes the relationship between essential 9-12.9 6-a makes connections between changes in 9-12.5 learning skills and workforce requirements the areas of technology, transportation, related to a specific employment application and communication and specific effects on economic activities in NM 6-b identifies aspects of personal financing 9-12.13 (e.g., banking, credit, debit) EXTENDED SYMBOLIC GLPS GLPS 7-a defines appropriate strategies of 9-12.13 7-a investigates technology, 9-12.5 maintaining personal finances (e.g., transportation, and communication banking, credit, debit) systems in NM 8-a explains the relationship between essential 9-12.9 8-a describes the roles played by local, 9-12.6 learning skills and workforce requirements state, and tribal governments in NM’s economic system
*NOTE: The EGBE development panel determined that benchmark “9-12 Benchmark IV-C: Analyze and evaluate the patterns and results of trade, exchange, and interdependence between the United States and the world since 1900,” provided inappropriate assessment targets for students with significant cognitive disabilities. Thus, no Assessment Frameworks were developed within this benchmark.
NMAPA – Social Studies 2008-09 Assessment Frameworks: Grades 9-12 11