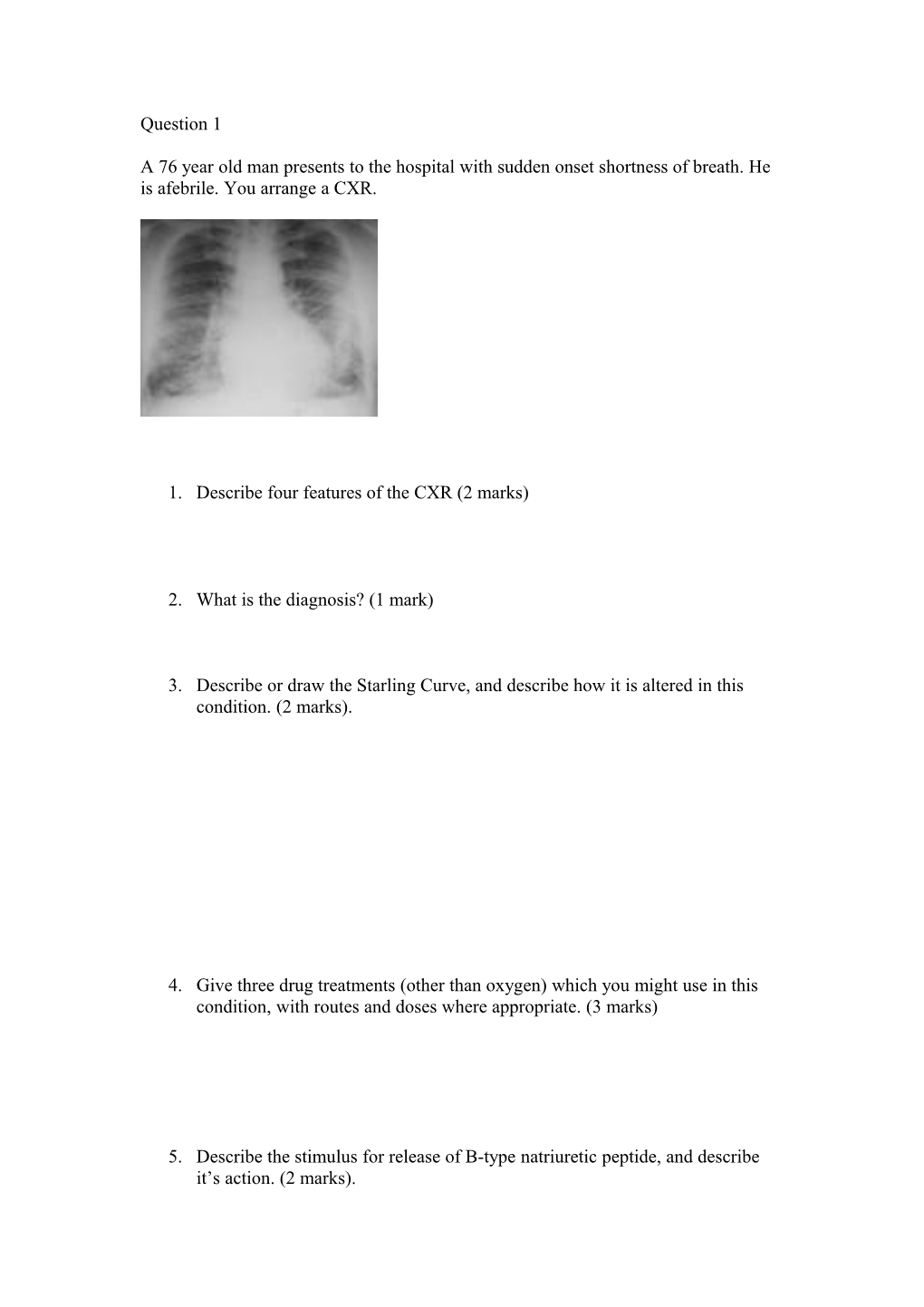
Question 1
A 76 year old man presents to the hospital with sudden onset shortness of breath. He is afebrile. You arrange a CXR.
1. Describe four features of the CXR (2 marks)
2. What is the diagnosis? (1 mark)
3. Describe or draw the Starling Curve, and describe how it is altered in this condition. (2 marks).
4. Give three drug treatments (other than oxygen) which you might use in this condition, with routes and doses where appropriate. (3 marks)
5. Describe the stimulus for release of B-type natriuretic peptide, and describe it’s action. (2 marks). Question 2.
1. Give three predisposing factors to this condition (3 marks)
2. Give four signs on ocular examination which would assist in distinguishing between orbital and periorbital cellulitis. (4 marks)
3. Give three possible causative organisms (3 marks) Question 3
A 36 year old woman is brought to the department by police. She has a five week old baby. She is withdrawn and refuses to answer questions, and soon after presentation becomes aggressive and starts shouting and kicking walls. She has a bag which contains baby milk and nappies.
1. Outline the four principles of the treatment of violent patients in the ED according to NICE guideline.
2. How would you manage her acutely?
3. Give four possible organic causes of her presentation. Question 4
A 36 week old woman presents complaining of abdominal pain. Her urinalysis is suggestive of a UTI.
1. Outine three clinical features which would make you suspect pyelonephritis (3 marks).
2. In an otherwise healthy woman, what are the two commonest causative organisms? (2 marks)
3. Give three complications of pyelonephritis in pregnancy (3 marks). Question 5 An eight year old boy presents with a history of painful joints, associated with a rash. He had a sore throat two to three weeks ago. You suspect he has acute rheumatic fever.
1. List the features which make up the diagnosis of acute rheumatic fever (3 marks) – Whose criteria.
2. What single laboratory test is required to confirm the diagnosis (1 mark)
3. Outline four principles of treatment of acute rheumatic fever (four marks). Question 6
A 46 year old woman presents with a history of cramping lower abdominal pain, which has been coming on for the last few months. It is associated with her period, which has been getting heavier. She has been depressed, and has seen her GP who has commenced her on medication for this.
1. Give four of the recommendations concerning intimate patient examinations given in recent GMC guidance.
2. Give three possible diagnoses to explain her symptoms.
3. Give the dermatomal innervation for the following pelvic organs: a. Ovaries b. Uterine fundus c. Labia and perineum Question 7
A 16 year old girl is brought to the ED. She admits to taking some paracetamol tablets 30 minutes ago. Although she’s not exact about the number of tablets taken, three packets are missing, with 16 tablets in each.
1. What historical features would you wish to illicit? (3 marks)
2. What would be you immediate interventions? (2 marks)
3. What factors would result in her being in a high risk category for paracetamol poisoning? (2 marks)
4. What clinical and laboratory features would be consistent with a diagnosis of severe paracetamol poisoning (give six) (3 marks). Question 8
An elderly woman is brought into hospital from her nursing home, where she has been having bandage treatment of ‘infected leg ulcers.’ She’s become confused today, and has a GCS of 11/15 on arrival. Her investigation results are shown below:
Na 156; K 4.1; Urea 18; Creatinine 130; Chloride 120. pH 7.23; P02 8.6; PC02 3.2; HCO3 20; BE -8.0
1. What is the likely diagnosis? (1 mark)
2. Calculate the serum osmolality (show your working) (2 marks)
3. Outline the principles of fluid resuscitation in this case (2 marks)
4. Give two drug treatments you would use in this circumstances (2 marks) Question 9
A fifty six year old man is brought to the ED after an RTA. No other cars were involved, but he veered off the road, and hit a tree. There was fifty cm of intrusion of the car. Although restrained, he seems to have collided with the steering wheel, which is deformed. There was no air bag in the car.
1. What four additional features do you require in the history at this stage? (2 marks)
He begins to become more short of breath, and his respiratory rate increases to 32.
2. What is the most important diagnosis to exclude now? (1 mark)
3. Name six clinical signs of this diagnosis (3 marks)
4. He deteriorates further and a chest drain is inserted, which drains a haemothorax. What are the indications for a thoracotomy following a traumatic haemothorax? (4 marks) Question 10
A thirty seven year old woman presents with a short history of abdominal pain and nausea. She has become vomiting before presenting to the ED. She doesn’t remember when her bowels were last open, and she isn’t passing flatus. She had an appendicectomy aged six, but is otherwise fit and well.
1. Give two radiological abnormalities (2 marks)
2. Give four common causes (2 marks) Question 11
Give three diagnostic criteria for SIRS (3 marks)
Give the diagnostic criteria for severe sepsis(3 marks) Question 12
Pyeloneprhitis in pregnancy
1. Give two physiological reasons that pregnant women are more at risk of UTI. 2. In an otherwise healthy woman, name the two most likely causative organisms. 3. Give three clinical findings which would increase your suspicion of pyelonephritis. 4. Give three potential complications of pyelonephritis in pregnancy. Question 13
Neonatal jaundiced baby from Africa.
1. Give four causes which should be considered in any neonate presenting with jaundice. 2. Give six investigations which you would consider in the ED. 3. Give six supplements or replacements which you would give to a neonate with jaundice in the emergency department. Question 14
A sixty five year old man presents to the ED with a painful swollen 1st MTPJ. He’s had gout before, and you suspect this is the diagosis now.
1. Give the biochemical abnormality in gout and pseudogout.
2. Give two classes of drug, and an example of each, which may precipitate an acute attack of gout.
You decide to offer him some dietary advice to try and reduce further attacks.
3. Give three foods which you would advise him to avoid, and give the reason behind this.
Food:
Food:
Food:
Reason:
Allopurinol and colchicine may both be used to prevent attacks of gout. By what mechanism do they do this?
Colchicine:
Allopurinol: Question 15
A seventy six year old woman comes into the department complaining of sudden onset shortness of breath. She has had numerous previous admissions and is on inhalers for COPD. Her observations are: P – 110; BP – 140/85; Sp02 – 94% on 24% 02
1. Give two drug treatments which will be effective in the next five minutes (give names, routes and doses where appropriate).
You do an ABG which shows: pH 7.25; p02 7.9; pC02 8.4; HC03 36. You decide to commence NIV.
2. What type of NIV would you commence?
3. You have a medical student with you. Give four points which you would make in describing the type of NIV which you have commenced: i) ii) iii) iv)
She suddenly deteriorates and you arrange a CXR.
4. Give four abnormalities on the CXR (can’t get a picture to match theirs)
5. Give the next two steps which you would carry out. Question 16
A thirty six year old woman presents to the ED with cramping abdominal pain and diarrhoea. Although she feels nauseated, she hasn’t vomited. The diarrhoea is not bloody. She’s just returned from holiday in North Africa, and the night before leaving had a Bedouin barbeque on the beach.
1. What’s the commonest causative organism in travellers diarrhoea.
2. Give two organisms which might cause bloody diarrhoea.
3. Give four worrying clinical features in a patient with a history of bloody diarrhoea. i) ii) iii) iv)
4. She still has some crampy abdominal pain, but a non-tender abdomen, her temperature is 37.3, and her pulse is 90. You decide to treat her. Give two treatment options.
i)
ii) Question 17
A seventy six year old man presents with difficulty passing urine. Clinically he has a palpable bladder. He is on lisinopril, aspirin and ‘a diuretic.’ His urea and electrolytes are shown below: Na 135; K 5.6; Urea 17; Creatinine 180.
1. Give four steps, in order of priority, which you would carry out after catheterisation
i) ii) iii) iv)
2. Give four causes for his renal impairment. i) ii) iii) iv) Question 18
A fifty six year old woman presents to the ED complaining of extreme nausea, and an abnormal gait. Every time she tries to sit up, her symptoms get worse.
1. Give three features on clinical examination which would help to distinguish a central from a peripheral cause of her vertigo.
i) ii) iii)
2. You decide that her vertigo has a peripheral cause. Give two differential diagnoses.
i)
ii)
3. Give the name of a diagnostic test to determine between the two of these, and describe how to carry it out. Question 19 (Part a)
You receive a call about a nineteen year old man who is being brought to the department. His temperature is 26 degrees, but he still has a palpable carotid pulse.
1. Except for resuscitation equipment, name four items which you would ensure were present in the department prior to his arrival.
i) ii) iii) iv)
En route to the ED he loses his output.
2. Give four changes to the standard cardiac arrest protocol for patients who arrest with a temperature below 30 degrees.
i) ii) iii) iv)
Question 19 (part b)
A different patient is brought to the department, having spent three nights living rough in extremely cold weather. This is his hand:
1. Give two interventions which are indicated, and two which are contraindicated. Question 20
A nineteen year old gardener presents to the department, having cut his top lip on a branch. You decide to repair his lip under a nerve block.
1. Describe how you would carry out this block
He didn’t have an initial tetanus course as a baby, but thinks he had a pre-school booster 12 years ago.
2. Describe four actions which would reduce his risk of tetanus.
i) ii) iii) iv)
Describe four features which make a wound ‘tetanus prone.’
i) ii) iii) iv)