Name : ______Date : ______Chemical Compounds – WATER -Notes
Backgrounds Information: Life as we know it, is based on the chemistry of organic molecules. ______
______
______.
For example;______
______,
The organic molecules in living things are easily grouped into four types. An understanding of these four biochemical compounds is the purpose of the next unit.
1. ______3. ______
2. ______4. ______
Why is water so incredibly important? What happens to the quality of life if the chemical conditions of living things change?
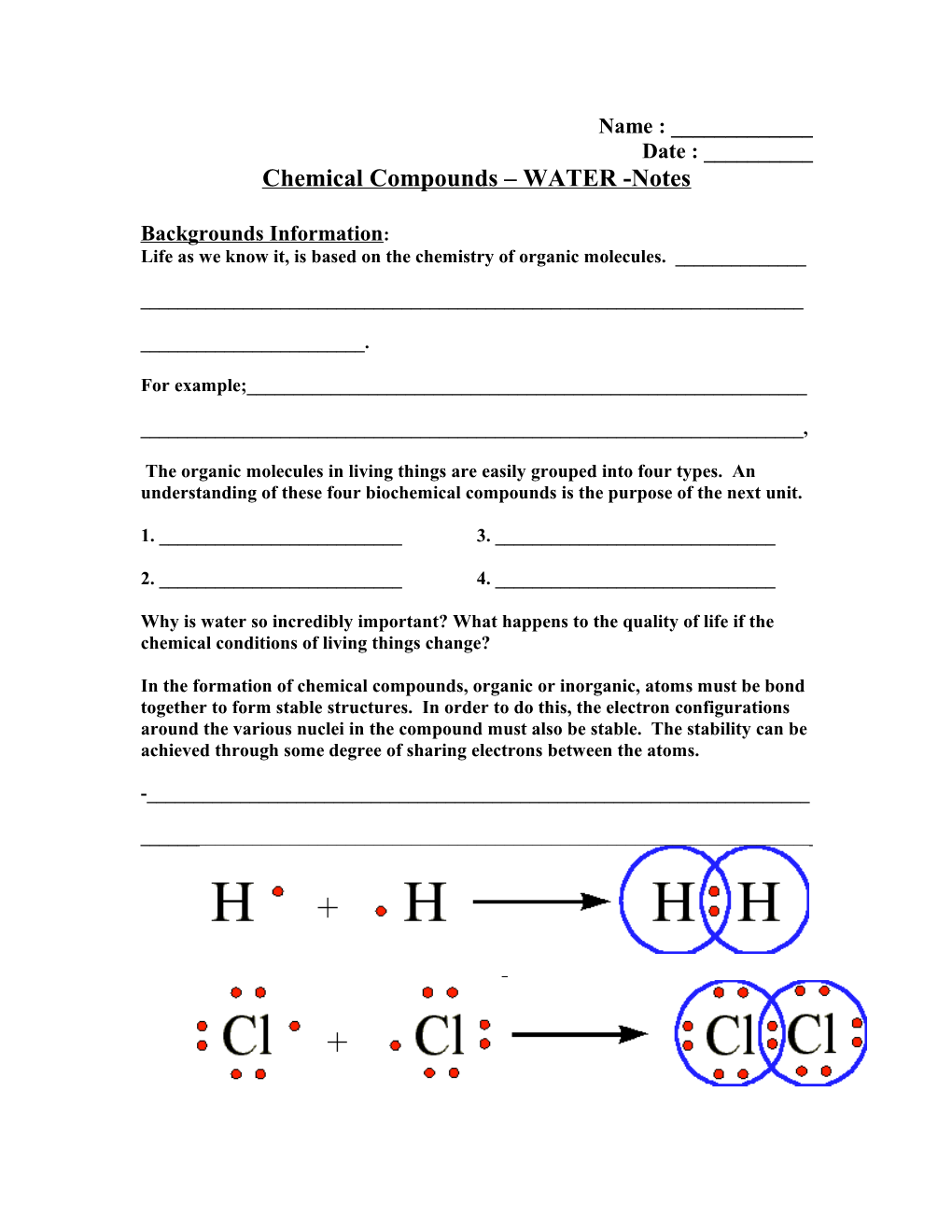
In the formation of chemical compounds, organic or inorganic, atoms must be bond together to form stable structures. In order to do this, the electron configurations around the various nuclei in the compound must also be stable. The stability can be achieved through some degree of sharing electrons between the atoms.
-______
______
-The alternative is a very unequal sharing. ______
______
______
- In between these two extremes is what is termed polar covalent. ______
______
______
______
Water Structure of water:
In a covalent bond atoms share electrons to become stable. ______
______
______
______
Any molecule that ends up with different charged regions is called a polar molecule. Hence it would be a dipole.
______
______
- ______
______
______
______
Therefore, water tends to clump together. Although the bond is weak, the vast number of these bonds gives water its unique properties.
Roles of Water 1) ______
______
______
Since blood is mainly water, the ability of water to dissolve and transport substances greatly aids in bringing about necessary chemical reactions in the body.
2) Moderates Climate (both internal and external climates) due to high Specific Heat Capacity
- ______
______
Example: Oceans keep surrounding land masses cool in summer and warmer in winter. Example: ______
______
3) Liquid water is more dense than ice. (very rare for compounds).
______
______. Hydrogen bonding allows molecules to come closer together.
If ice formed at the bottom, all lakes and oceans would freeze solid in the winter.
4) Water is transparent.
______
______.
5) Water molecules are cohesive.
They stick to each other and to other surfaces. This keeps surfaces moist and lubricated. ______
______.
Acids, Bases and Buffers
Acids are molecules that dissociate to release hydrogen ions. HCl (Hydrocholoric
Acid) is a strong acid because ______
______.
Bases : ______
______
______
______
At pH 7, the concentration of hydrogen ions = the concentration of hydroxide ions. [ H+ ] = [ OH- ]
At pH 6 : ______pH 3 has 100 times more H+ than Ph 5
The pH scale is just a comparison between the [ H+ ] and [ OH- ].
______
Most enzymes, which control the chemical reactions in your body, can only operate at certain pH levels.
Example: ______
______
Buffers : ______
______
______
- + Example: Bicarbonate (HCO3 ) absorbs excess acid (H ions)
______Note: The buffer keeps pH constant despite adding more and more acid.
Example of Buffering System
# 2 #1 ______ _____ + ______
Carbonic Hydrogen Bicarbonate Acid Ion Ion
If H+ is added, ______
If OH- is getting too high, the ______
______
______