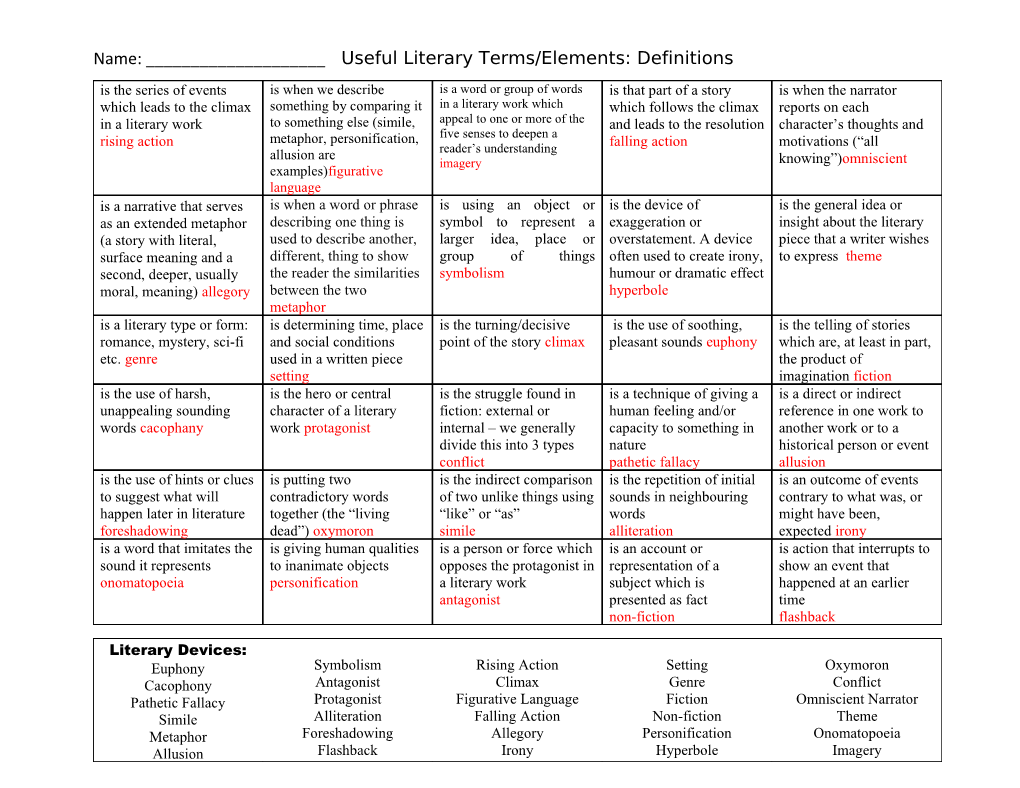
Name: ______Useful Literary Terms/Elements: Definitions is the series of events is when we describe is a word or group of words is that part of a story is when the narrator which leads to the climax something by comparing it in a literary work which which follows the climax reports on each in a literary work to something else (simile, appeal to one or more of the and leads to the resolution character’s thoughts and five senses to deepen a rising action metaphor, personification, falling action motivations (“all allusion are reader’s understanding imagery knowing”)omniscient examples)figurative language is a narrative that serves is when a word or phrase is using an object or is the device of is the general idea or as an extended metaphor describing one thing is symbol to represent a exaggeration or insight about the literary (a story with literal, used to describe another, larger idea, place or overstatement. A device piece that a writer wishes surface meaning and a different, thing to show group of things often used to create irony, to express theme second, deeper, usually the reader the similarities symbolism humour or dramatic effect moral, meaning) allegory between the two hyperbole metaphor is a literary type or form: is determining time, place is the turning/decisive is the use of soothing, is the telling of stories romance, mystery, sci-fi and social conditions point of the story climax pleasant sounds euphony which are, at least in part, etc. genre used in a written piece the product of setting imagination fiction is the use of harsh, is the hero or central is the struggle found in is a technique of giving a is a direct or indirect unappealing sounding character of a literary fiction: external or human feeling and/or reference in one work to words cacophany work protagonist internal – we generally capacity to something in another work or to a divide this into 3 types nature historical person or event conflict pathetic fallacy allusion is the use of hints or clues is putting two is the indirect comparison is the repetition of initial is an outcome of events to suggest what will contradictory words of two unlike things using sounds in neighbouring contrary to what was, or happen later in literature together (the “living “like” or “as” words might have been, foreshadowing dead”) oxymoron simile alliteration expected irony is a word that imitates the is giving human qualities is a person or force which is an account or is action that interrupts to sound it represents to inanimate objects opposes the protagonist in representation of a show an event that onomatopoeia personification a literary work subject which is happened at an earlier antagonist presented as fact time non-fiction flashback
Literary Devices: Euphony Symbolism Rising Action Setting Oxymoron Cacophony Antagonist Climax Genre Conflict Pathetic Fallacy Protagonist Figurative Language Fiction Omniscient Narrator Simile Alliteration Falling Action Non-fiction Theme Metaphor Foreshadowing Allegory Personification Onomatopoeia Allusion Flashback Irony Hyperbole Imagery