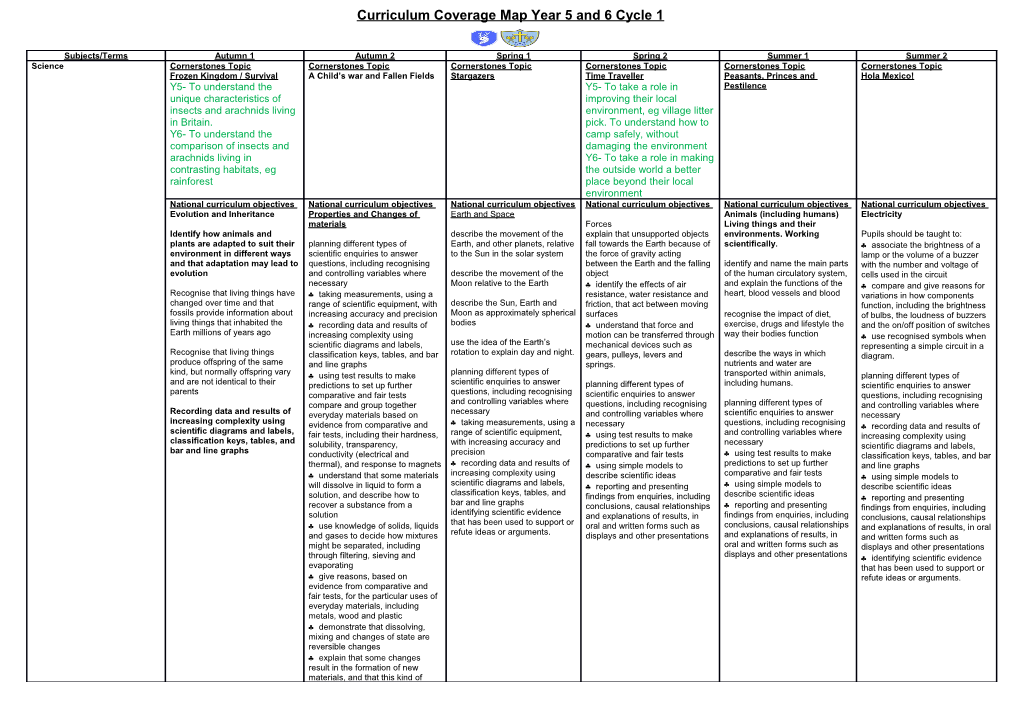
Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
Subjects/Terms Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2 Science Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Frozen Kingdom / Survival A Child’s war and Fallen Fields Stargazers Time Traveller Peasants, Princes and Hola Mexico! Y5- To understand the Y5- To take a role in Pestilence unique characteristics of improving their local insects and arachnids living environment, eg village litter in Britain. pick. To understand how to Y6- To understand the camp safely, without comparison of insects and damaging the environment arachnids living in Y6- To take a role in making contrasting habitats, eg the outside world a better rainforest place beyond their local environment National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives Evolution and Inheritance Properties and Changes of Earth and Space Animals (including humans) Electricity materials Forces Living things and their Identify how animals and describe the movement of the explain that unsupported objects environments. Working Pupils should be taught to: plants are adapted to suit their planning different types of Earth, and other planets, relative fall towards the Earth because of scientifically. . associate the brightness of a environment in different ways scientific enquiries to answer to the Sun in the solar system the force of gravity acting lamp or the volume of a buzzer and that adaptation may lead to questions, including recognising between the Earth and the falling identify and name the main parts with the number and voltage of evolution and controlling variables where describe the movement of the object of the human circulatory system, cells used in the circuit necessary Moon relative to the Earth . identify the effects of air and explain the functions of the . compare and give reasons for Recognise that living things have . taking measurements, using a resistance, water resistance and heart, blood vessels and blood variations in how components changed over time and that range of scientific equipment, with describe the Sun, Earth and friction, that act between moving function, including the brightness fossils provide information about increasing accuracy and precision Moon as approximately spherical surfaces recognise the impact of diet, of bulbs, the loudness of buzzers living things that inhabited the . recording data and results of bodies . understand that force and exercise, drugs and lifestyle the and the on/off position of switches Earth millions of years ago increasing complexity using motion can be transferred through way their bodies function . use recognised symbols when scientific diagrams and labels, use the idea of the Earth’s mechanical devices such as representing a simple circuit in a Recognise that living things classification keys, tables, and bar rotation to explain day and night. gears, pulleys, levers and describe the ways in which diagram. produce offspring of the same and line graphs springs. nutrients and water are kind, but normally offspring vary . using test results to make planning different types of transported within animals, planning different types of and are not identical to their predictions to set up further scientific enquiries to answer planning different types of including humans. scientific enquiries to answer parents comparative and fair tests questions, including recognising scientific enquiries to answer questions, including recognising compare and group together and controlling variables where questions, including recognising planning different types of and controlling variables where Recording data and results of everyday materials based on necessary and controlling variables where scientific enquiries to answer necessary increasing complexity using evidence from comparative and . taking measurements, using a necessary questions, including recognising . recording data and results of scientific diagrams and labels, fair tests, including their hardness, range of scientific equipment, . using test results to make and controlling variables where increasing complexity using classification keys, tables, and solubility, transparency, with increasing accuracy and predictions to set up further necessary scientific diagrams and labels, bar and line graphs conductivity (electrical and precision comparative and fair tests . using test results to make classification keys, tables, and bar thermal), and response to magnets . recording data and results of . using simple models to predictions to set up further and line graphs . understand that some materials increasing complexity using describe scientific ideas comparative and fair tests . using simple models to will dissolve in liquid to form a scientific diagrams and labels, . reporting and presenting . using simple models to describe scientific ideas classification keys, tables, and solution, and describe how to findings from enquiries, including describe scientific ideas . reporting and presenting bar and line graphs recover a substance from a conclusions, causal relationships . reporting and presenting findings from enquiries, including identifying scientific evidence solution and explanations of results, in findings from enquiries, including conclusions, causal relationships that has been used to support or . use knowledge of solids, liquids oral and written forms such as conclusions, causal relationships and explanations of results, in oral refute ideas or arguments. and gases to decide how mixtures displays and other presentations and explanations of results, in and written forms such as might be separated, including oral and written forms such as displays and other presentations through filtering, sieving and displays and other presentations . identifying scientific evidence evaporating that has been used to support or . give reasons, based on refute ideas or arguments. evidence from comparative and fair tests, for the particular uses of everyday materials, including metals, wood and plastic . demonstrate that dissolving, mixing and changes of state are reversible changes . explain that some changes result in the formation of new materials, and that this kind of Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
change is not usually reversible, including changes associated with burning and the action of acid on bicarbonate of soda.
Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage use the idea that light travels in Describe the differences in life compare and group together describe the movement of the recognise that living things have straight lines to explain that cycles of a mammal, an everyday materials on the basis of Earth, and other planets, relative changed over time and that associate the brightness of a objects are seen because they amphibian, an insect and a bird. their properties, including their to the Sun in the solar system fossils provide information about lamp or the volume of a buzzer give out or reflect light into the eye hardness, solubility, transparency, living things that inhabited the with the number and voltage of Describe the life process of conductivity (electrical and describe the movement of the Earth millions of years ago cells used in the circuit explain that we see things reproduction in some plants and thermal), and response to magnets Moon relative to the Earth recognise that living things because light travels from light animals. produce offspring of the same compare and give reasons for sources to our eyes or from light that some materials will dissolve in describe the Sun, Earth and kind, but normally offspring vary variations in how components sources to objects and then to our Describe the changes to humans liquid to form a solution, and Moon as approximately spherical and are not identical to their function, including the brightness eyes as they develop through to old describe how to recover a bodies parents of bulbs, the loudness of buzzers age. substance from a solution and the on/off position of use the idea that light travels in use the idea of the Earth’s identify how animals and plants switches straight lines to explain why Describe how living things are use knowledge of solids, liquids rotation to explain day and night are adapted to suit their shadows have the same shape as classified into broad groups and gases to decide how mixtures and the apparent movement of environment in different ways and use recognised symbols when the objects that cast them. according to common observable might be separated, including the sun across the sky. that adaptation may lead to representing a simple circuit in a characteristics and based on through filtering, sieving and evolution. diagram similarities and differences, evaporating including micro-organisms, plants and animals. give reasons, based on evidence from comparative and fair tests, for Give reasons for classifying the particular uses of everyday plants and animals based on materials, including metals, wood specific characteristics. and plastic
Identify and name the main parts demonstrate that dissolving, of the human circulatory system, mixing and changes of state are and describe the functions of the reversible changes heart, blood vessels and blood. Recognise the impact of diet, explain that some changes result exercise, drugs and lifestyle on in the formation of new materials, the way their bodies function. and that this kind of change is not usually reversible, including Describe the ways in which changes associated with burning nutrients and water are and the action of acid on transported within animals, bicarbonate of soda. including humans. Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
RE Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Frozen Kingdom / Survival A child’s War / Fallen Fields Stargazers Time Travellers Peasants Princes and Hola Mexico Pestilence
National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives Northern Saints Advent How the Bible supports Why the last supper is so The Muslim Religion How do the beliefs of Christians Christians throughout their lives. important to Christians influence their actions?
Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage
between questions, beliefs, • identify the influences on, and explain how selected features of • explain connections between • explain the reasons for, and • explain connections between values and practices in different distinguish between, different religious life and practice make a questions, beliefs, values and effects of, diversity within and questions, beliefs, values and belief systems viewpoints within religions and difference to the lives of practices in different belief between religions, beliefs and practices in different belief • recognise and explain the beliefs individuals and communities systems cultures. systems impact of beliefs and ultimate • interpret religions and beliefs • recognise and explain the • identify the influences on, and • recognise and explain the questions on individuals and from different perspectives impact of beliefs and ultimate distinguish between, different impact of beliefs and ultimate communities • interpret the significance and questions on individuals and viewpoints within religions and questions on individuals and • explain how and why impact of different forms of communities beliefs communities differences in belief are religious and spiritual expression • interpret religions and beliefs expressed. from different perspectives • interpret the significance and impact of different forms of religious and spiritual expression
History Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Frozen Kingdom / Survival A Child’s War / Fallen Fields Stargazers Time Traveller Peasants Princes and Hola Mexico Pestilence Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives
A study of an aspect of history or A significant turning point in British a study of an aspect or theme in a study of an aspect or theme in a study of an aspect or theme in a non-European society that a site dating from a period history, e.g. the Battle of Britain British history that extends British history that extends pupils’ British history that extends pupils’ provides contrasts with British beyond 1066 that is significant in pupils’ chronological knowledge chronological knowledge beyond chronological knowledge beyond history the locality. beyond 1066 1066 1066
Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Say where a period of history fits Say where a period of history fits Describe how different types of on a timeline on a timeline Use dates and historical language Describe features of historical .Summarise what Britain may evidence tell us about different in my work events and people from past have learnt from other countries things about the past and Place a specific event on a Place a specific event on a societies and periods they have and civilizations through time understand why contrasting timeline by decade timeline by decade studied gone by and more recently arguments and interpretations 2. Draw a timeline with different occur. Place features of historical events Place features of historical time periods outlined which show 5.Recognise and describe and people from past societies and events and people from past different information, such as, differences and similarities/ Place historical events or change periods in a chronological societies and periods in a periods of history, when famous changes and continuity between on a timeline independently, framework chronological framework people lived, etc. different periods of history remembering key facts from a Describe features of historical period of history studied. 4.Appreciate that significant events events and people from past in history have helped shape the societies and periods they have Follow independent lines of country we have today studied enquiry and make informed responses based on this. Recognise and describe differences and similarities/ Select, organise and record changes and continuity between relevant information, from a range different periods of history of sources, to produce well- structured narratives, descriptions and explanations.
Explain why people acted as they did.
Describe how a significant individual or movement has influenced the UK or wider world.
Geography Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Frozen Kingdom / Survival Darwin’s Delights Stargazers Time Traveller Peasants Princes and Hola Mexico Y5- Use wider range of Y5- To have a good Y5- Use wider range of Pestilence Y5- Use wider range of Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1 atlases e.g. Google Earth to understanding of the atlases e.g. Google Earth Y5- To understand the atlases e.g. Google Earth to identify countries in the behaviours of birds local to to identify countries in the different roles on a farm, identify countries in the world To understand what a the environment, eg bird world To understand what including sheepdogs and world To understand what a scale means on a map calls, nesting habits (eg the a scale means on a map different equipment used, scale means on a map Y6- Understand the swallows that nest under the Y6- Understand the eg combine harvester. Y6- Understand the principles behind basic school eaves) principles behind basic Y6- To understand which principles behind basic contour maps To calculate Y6- To be able to describe contour maps To calculate farms are in our local contour maps To calculate distances on a map using and identify the behaviours distances on a map using environment, what they distances on a map using scale of birds in the local scale farm and how the farms scale environment and beyond to work. contrast National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives Location knowledge Identify the position and name and locate counties and use maps, atlases, globes and name and locate counties and use maps, atlases, globes and locate the world’s countries, using significance of latitude, longitude, cities of the United Kingdom, digital/computer mapping to cities of the United Kingdom, digital/computer mapping to maps to focus on Europe Equator, Northern Hemisphere, geographical regions and their locate countries and describe geographical regions and their locate countries and describe (including the location of Russia) Southern Hemisphere, the identifying human and physical features studied identifying human and physical features studied and North and South America, Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, characteristics, key topographical . use the eight points of a characteristics, key topographical name and locate counties and concentrating on their Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the features (including hills, compass, four and six-figure grid features (including hills, cities of the United Kingdom, environmental regions, key Prime/Greenwich Meridian and mountains, coasts and rivers), and references, symbols and key mountains, coasts and rivers), geographical regions and their physical and human time zones (including day and land-use patterns; and understand (including the use of Ordnance and land-use patterns; and identifying human and physical characteristics, countries, and night) how some of these aspects have Survey maps) to build their understand how some of these characteristics, key topographical major cities changed over time. knowledge of the United aspects have changed over time features (including hills, Use maps, atlases, globes and Kingdom and the wider world mountains, coasts and rivers), understand geographical digital/computer mapping to Describe and understand key and land-use patterns; and similarities and differences locate countries and describe aspects of; human geography, understand how some of these through the study of human and features studied including: types of settlement and aspects have changed over time physical geography of a region of land use, economic activity the United Kingdom, a region in a including trade links, and the European country, and a region Human and physical distribution of natural resources within North or South America Understand geographical including energy, food, minerals similarities and differences and water use maps, atlases, globes and through the study of human and digital/computer mapping to locate physical geography of a region of countries and describe features the United Kingdom, a region in a studied European country, and a region within North or South America
Describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water.
Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Use the eight points of a Use the eight points of a Understand geographical Use the eight points of a Understand geographical compass, four and six-figure grid Describe and understand key compass to describe locations similarities and differences compass to describe locations similarities and differences references, symbols and key aspects of human geography and routes: on maps of the through the study of human and and routes: on maps of the through the study of human and (including the use of Ordnance including: economic activity and United Kingdom and the wider physical geography of a region of United Kingdom and the wider physical geography of a region of Survey maps) to build their settlements linked to the world; and, in fieldwork. the United Kingdom and a region world; and, in fieldwork. the United Kingdom and a region knowledge of the United Kingdom distribution of fossil fuels (natural within North America. within South America. and the wider world resources – energy). Use six figure grid references Use six figure grid references and symbols to describe Name and locate countries within and symbols to describe Describe and understand key Compare land use and locations and routes on an North and South America locations and routes on an aspects of physical geography geographical features on different Ordnance Survey map. Apply (Canada, USA, Mexico, Brazil Ordnance Survey map. Apply including: mountains, rivers and types of maps. during fieldwork. and Argentina) and their capital during fieldwork. the water cycle. Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
cities. Explain how things change by Explain the relative degrees of Describe the environmental Explain the relative degrees of referring to the physical and accuracy of four/ six figure grid regions, key physical and human accuracy of four/ six figure grid human features of the landscape. referencing. characteristics and major cities of referencing. Brazil, Canada and USA. Recognise and describe the Read a range of aerial Read a range of aerial physical and human features of photographs and maps (e.g. Identify the position and photographs and maps (e.g. places and appreciate the Google Maps, Mapstart, significance of tropics of Cancer Google Maps, Mapstart, importance of wider geographical Ordnance Survey, Google Earth) and Capricorn. Ordnance Survey, Google Earth) location in understanding places. using a range of symbols/ keys using a range of symbols/ keys (e.g. general features, tourist Name and locate counties (e.g. general features, tourist and and leisure, different types of (Gwynedd, Merseyside and leisure, different types of footpaths, roads and Greater Manchester) and cities footpaths, roads and boundaries). (Liverpool, Manchester, Bangor) ) boundaries). of the UK and relate to the To use map scales to convert geographical regions (North To use map scales to convert units of measurement on the West, Wales) units of measurement on the map map into units of measurement into units of measurement in real in real life. life.
Record discrete and continuous Record discrete and continuous data from observations and data from observations and measurements of the human measurements of the human and and physical features of the local physical features of the local area. Present this data in bar/ area. Present this data in bar/ line charts. line charts.
Use basic tools and layers on Use basic tools and layers on Google Earth to describe Google Earth to describe features studied. features studied. Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
Computing Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Frozen Kingdom / Survival Frozen Kingdom / Survival Stargazer Time Travellers Peasants Princes and Hola Mexico Pestilence National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives Select, use and combine a variety Use sequence, selection, and Use search technologies . use search technologies . use search technologies of software (including internet Use search technologies repetition in programs; work with effectively, appreciate how results effectively, appreciate how effectively, appreciate how results services) on a range of digital effectively. Appreciate how results variables and various forms of are selected and ranked, and be results are selected and ranked, are selected and ranked, and be devices to accomplish given are selected and ranked and be input and output discerning in evaluating digital and be discerning in evaluating discerning in evaluating digital goals, including collecting, discerning in evaluating digital . use search technologies content digital content content analysing, evaluating and content effectively, appreciate how Select, use and combine a variety . select, use and combine a . select, use and combine a presenting data and information. results are selected and ranked, of software (including internet variety of software (including variety of software (including Select use and combine a variety and be discerning in evaluating services) on a range of digital internet services) on a range of internet services) on a range of of software on a range of digital digital content devices to accomplish given digital devices to accomplish digital devices to accomplish devices to design and create a . select, use and combine a goals, including collecting, given goals, including collecting, given goals, including collecting, range of programs, systems and variety of software (including analysing, evaluating and analysing, evaluating and analysing, evaluating and content that accomplish given internet services) on a range of presenting data and information. presenting data and information. presenting data and information. goals, including collecting, digital devices to accomplish analysing, evaluating and given goals, including collecting, presenting data and information. analysing, evaluating and presenting data and information. Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Understand computer networks Understand computer networks Understand computer networks Understand computer networks including the internet; how they Understands the terms upload and Identify the 2 key design including the internet; how they including the internet; how they including the internet; how they can provide multiple services, download and how that applies to principles of a spreadsheet (no can provide multiple services, can provide multiple services, can provide multiple services, such as the world-wide web; and the internet. values in a formula, blank line such as the world-wide web; and such as the world-wide web; and such as the world-wide web; and the opportunities they offer for Can include various media in a before a total). the opportunities they offer for the opportunities they offer for the opportunities they offer for communication and collaboration presentation. communication and collaboration communication and collaboration communication and collaboration Sort a given set of files by name, Use tools in Word to create own by date, by type or by size PDF document. effectively, appreciate how results Delete one file. Delete one file. effectively, appreciate how results effectively, appreciate how effectively, appreciate how results are selected and ranked, and be Find a lost file on a given set of Insert a film to an on-screen are selected and ranked, and be results are selected and ranked, are selected and ranked, and be discerning in evaluating digital criteria using one method. presentation. discerning in evaluating digital and be discerning in evaluating discerning in evaluating digital content Re-name, move, delete and content digital content content copy at least one sheet (Pages Presentation and recording of at bottom). Presentation and recording of Presentation and recording of Presentation and recording of findings from research. Creation findings from research. Creation findings from research. Creation findings from research. Creation of display and factsheets. of display and factsheets. of display and factsheets. of display and factsheets. Free rotate a shape. Use tools in Word to create own Re-name, move, delete and copy PDF document. at least one sheet (Pages at Email pdf document. bottom). Sort a given set of files by name, by date, by type or by size Delete one file. Find a lost file on a given set of criteria using one method. Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
PE Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Animal Kingdom / Survival Frozen Kingdom / Survival Y5- Plan and organise a simple orienteering trail usIng a variety of map reading and compass skills Y6- Plan and navigate a variety of orienteering challenges using map reading and compass skills in unfamiliar settings National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives Pupils should continue to implement and develop a broader Dance Gymnastics Team Games Target games Athletics range of skills, learning how to use them in different ways and to Pupils should continue to Pupils should continue to Pupils should continue to Pupils should continue to Pupils should continue to link them to make actions and implement and develop a broader implement and develop a implement and develop a broader implement and develop a broader implement and develop a broader sequences of movement. range of skills, learning how to use broader range of skills, learning range of skills, learning how to range of skills, learning how to range of skills, learning how to They should enjoy them in different ways and to link how to use them in different use them in different ways and to use them in different ways and to use them in different ways and to communicating, collaborating and them to make actions and ways and to link them to make link them to make actions and link them to make actions and link them to make actions and competing with each other. sequences of movement. actions and sequences of sequences of movement. sequences of movement. sequences of movement. They should develop an They should enjoy communicating, movement. They should enjoy They should enjoy They should enjoy understanding of how to succeed collaborating and competing with They should enjoy communicating, collaborating and communicating, collaborating and communicating, collaborating and in different activities and sports each other. communicating, collaborating competing with each other. competing with each other. competing with each other. and learn how to evaluate and They should develop an and competing with each other. They should develop an They should develop an They should develop an recognise their own success. understanding of how to succeed They should develop an understanding of how to succeed understanding of how to succeed understanding of how to succeed in different activities and sports understanding of how to in different activities and sports in different activities and sports in different activities and sports and learn how to evaluate and succeed in different activities and learn how to evaluate and and learn how to evaluate and and learn how to evaluate and recognise their own success. and sports and learn how to recognise their own success. recognise their own success. recognise their own success. evaluate and recognise their own success.
Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage • Link skills together appropriately • Link skills together Show an understanding of Show an understanding of As last term AND • Link skills together in PE activities appropriately in PE activities compositional elements and the compositional elements and the appropriately in PE activities • Link actions and ideas together • Link actions and ideas use use • Explain and use basic safety • Link actions and ideas together and use them accurately and together and use them of speed, level and direction in of speed, level and direction in rules in preparing for PE activities and use them accurately and appropriately in PE activities accurately and creative PE activities by starting creative PE activities by starting • Describe what effect PE appropriately in PE activities • Perform PE skills precisely, appropriately in PE activities to vary how you respond to vary how you respond activities have on your body Perform PE skills precisely, showing control and fluency • Perform PE skills precisely, • Show an understanding of • Show an understanding of • Know and describe how PE showing control and fluency • Combine skills, techniques and showing control and fluency tactics in team games by varying tactics in team games by varying activities are valuable to your Show an understanding of ideas consistently showing • Combine skills, techniques how how fitness and health compositional elements and the precision, control and fluency and ideas consistently showing you respond you respond • Warm up and cool down in use of speed, level and direction precision, control and fluency • Select and apply skills, • Select and apply skills, ways that suit the activity and in creative PE activities by techniques and ideas accurately techniques and ideas accurately explain how the body reacts starting to vary how you respond and and during different types of exercise. Show an understanding of tactics appropriately in all areas of PE appropriately in all areas of PE in team games by varying how • Perform in all areas of PE, • Perform in all areas of PE, you respond drawing on knowledge of drawing on knowledge of • Select and apply skills, strategy, strategy, techniques and ideas accurately tactics and composition tactics and composition and appropriately in all areas of • Compare and comment on • Compare and comment on PE skills, techniques and ideas used skills, techniques and ideas used • Perform in all areas of PE, in in drawing on knowledge of their own and others’ work their own and others’ work strategy, tactics and composition • Use this understanding to • Use this understanding to • Compare and comment on improve their own performance improve their own performance skills, techniques and ideas used • Analyse and comment on skills • Analyse and comment on skills Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
in their own and others’ work and techniques and how these and techniques and how these • Use this understanding to are applied in their own and are applied in their own and improve their own performance others’ work others’ work • Analyse and comment on skills • Modify and refine skills and • Modify and refine skills and and techniques and how these techniques to improve their techniques to improve their are applied in their own and Performance. Performance. others’ work • Modify and refine skills and techniques to improve their performance
Music Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Animal Kingdom / Survival National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives Recorders Recorders Ukulele Ukulele Ukulele Ukulele Classical music appreciation Classical Music Appreciation Classical Music Appreciation Classical Music Appreciation play tuned and untuned play tuned and untuned play tuned and untuned play tuned and untuned play tuned and untuned play tuned and untuned instruments musically instruments musically instruments musically instruments musically instruments musically instruments musically
listen with concentration and listen with concentration and listen with concentration and listen with concentration and listen with concentration and listen with concentration and understanding to a range of high- understanding to a range of high- understanding to a range of understanding to a range of high- understanding to a range of high- understanding to a range of high- quality live and recorded music quality live and recorded music high-quality live and recorded quality live and recorded music quality live and recorded music quality live and recorded music music
Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Hand-eye coordination Hand-eye coordination Hand-eye coordination Hand-eye coordination Hand-eye coordination Hand-eye coordination Note making Note making Note making Note making Note making Note making Breathing technique Breathing technique Breathing technique Breathing technique Breathing technique Breathing technique Reading simple notation Reading simple notation Reading simple notation Reading simple notation Reading simple notation Reading simple notation Rythym, beat,timing, ce Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
Art Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Animal Kingdom / Survival A Child’s War / Fallen Fields Stargazers Time Travellers Paupers, Princes and Hola Mexico Pestilence National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives produce creative work, exploring produce creative work, exploring produce creative work, exploring DT focus their ideas and recording their DT focus their ideas and recording their their ideas and recording their experiences experiences experiences Engage- sculpture? become proficient in drawing, . become proficient in drawing, DT focus . about great artists, architects painting, sculpture and other art, painting, sculpture and other art, and designers in history craft and design techniques craft and design techniques evaluate and analyse creative . evaluate and analyse creative works using the language of art, works using the language of art, craft and design craft and design To know about great artists, Artist- Salvador Dahli architects and designers in history Artist- Focus- drawing Focus- painting Artist- stimulus- Aztec materials and design / suns. Focus- textiles- sewing/weaving
Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Create a simple design and Paint to show some techniques: Work in a sustained and create with batik. e.g. colour wash, independent way to create different brush strokes, different detailed drawings. Apply decoration using needle textures Develop a key element of their and thread: buttons, sequins. colour mixing – tint, tone, shade. work: line, tone, pattern, texture. Use sketchbooks to collect and Begin to use different techniques Become confident in applying record visual information from for different purposes e.g. colour with printing, tie dye or different sources as well as shading, shadows, hatching batik. planning, trying out ideas, plan within their own work. colours and collect source material Use sketchbooks to collect and Use sketchbooks to collect and for future works. Annotate. record visual information from record visual information from Recognise the art of key artists different sources as well as different sources as well as and begin to place them in key planning and colleting source planning and colleting source movements or historical events. material for future works. material. Discuss and review own and Annotate sketches to explain others work, expressing thoughts ideas. Adapt their work according to their and feelings, and identify Begin to use tonal contrast, e... views and describe how they modifications/ changes and see how light and dark things look. might develop iit further. how they can be developed further. Be able to Identify and talk about Identify artists who have worked in printmakers in history. a similar way to their own work. Design and Technology Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Frozen Kingdom / Survival A Child’s War / Fallen fields Stargazers Time Travellers Peasants, Princes and Hola Mexico WEST VIEW- y5To know Pestilence how to cook 2 courses outdoors on a stove WEST VIEW- y6To know how to survive overnight outdoors Y5- Be responsible for own safety and remind others of safety in more challenging environments Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
Y6- Work with others to risk assess and identify potential hazards in school outdoor areas and on visits to other outdoor areas
National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives select from and use a wider range select from and use a wider select from and use a wider of materials and components, range of materials and range of materials and including construction materials, components, including components, including textiles and ingredients, construction materials, textiles construction materials, textiles according to their functional and ingredients, according to and ingredients, according to properties and aesthetic qualities their functional properties and their functional properties and investigate and analyse a range aesthetic qualities aesthetic qualities of existing products investigate and analyse a range prepare and cook a variety of . evaluate their ideas and of existing products predominantly savoury dishes products against their own design . evaluate their ideas and using a range of cooking criteria and consider the views of products against their own techniques others to improve their work design criteria and consider the apply their understanding of how views of others to improve their to strengthen, stiffen and work reinforce more complex apply their understanding of how structures to strengthen, stiffen and reinforce more complex structures
Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Begin to consider the influence -Use an extensive range of Measures, marks out, cuts and Know how to prepare Know how to prepare Describe in detail, the purpose of of a range of lifestyle factors and materials and components e.g. shapes materials and and cook a variety of and cook a variety of their products. consumer choices when designing textiles, mechanical, components with accuracy. savoury and some savoury and some Begin to consider the influence of products. construction sweet dishes safely and sweet dishes safely and a range of lifestyle factors and Gather information about the kits, electrical and food -Accurately assembles, joins and hygienically, including hygienically, including consumer choices when needs and wants of particular ingredients. combines most materials. the use of a heat source. the use of a heat source. designing products. individuals and groups. Indicate design features of their Share and clarify ideas -Measures,marks out, cuts and Accurately apply a range of Know how to use a wide Know how to use a wide products that will appeal to confidently, through shapes materials and finishing techniques, including range of techniques such range of techniques such intended users. discussion. components with accuracy. those from art and design. as peeling, chopping, as peeling, chopping, Gather information about the Produce appropriate lists of tools, slicing, grating, mixing, slicing, grating, mixing, needs and wants of particular equipment and materials that they -Accurately assembles, joins and -Use techniques that involve a spreading, kneading and spreading, kneading and individuals and groups. will need combines most materials. number of steps. baking. baking. Develop their own design criteria and use this to inform their ideas. -Use resourcefulness and Know that a Know that a resilience when tackling healthy diet is made up healthy diet is made up practical problems. of a variety and balance of a variety and balance of different foods and of different foods and drinks, as depicted on drinks, as depicted on ‘The Eatwell Plate.’ ‘The Eatwell Plate.’
Know that to be active and Know that to be active and healthy, food is needed to healthy, food is needed to provide provide energy for the body. energy for the body. Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
MFL Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Frozen Kingdom / Survival A Child’s War Fallen Fields Stargazers Time Travellers Peasants, Princes and Hola Mexico! Pestilence National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives Naming animals French colours Numbers and letters Introduction to Italian Introduction to Spanish listen attentively to spoken listen attentively to spoken language and show listen attentively to spoken listen attentively to spoken listen attentively to spoken listen attentively to spoken language and show understanding by joining in and language and show language and show understanding language and show language and show understanding by joining in and responding understanding by joining in and by joining in and responding understanding by joining in and understanding by joining in and responding . explore the patterns and responding . explore the patterns and sounds responding responding . explore the patterns and sounds of language through . explore the patterns and of language through songs and . explore the patterns and . explore the patterns and sounds of language through songs and rhymes and link the sounds of language through rhymes and link the spelling, sounds of language through sounds of language through songs and rhymes and link the spelling, sound and meaning of songs and rhymes and link the sound and meaning of words songs and rhymes and link the songs and rhymes and link the spelling, sound and meaning of words spelling, sound and meaning of . engage in conversations; ask spelling, sound and meaning of spelling, sound and meaning of words . engage in conversations; ask words and answer questions; express words words . engage in conversations; ask and answer questions; express . engage in conversations; ask opinions and respond to those of . engage in conversations; ask . engage in conversations; ask and answer questions; express opinions and respond to those of and answer questions; express others; seek clarification and help* and answer questions; express and answer questions; express opinions and respond to those of others; seek clarification and help* Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
opinions and respond to those of . speak in sentences, using opinions and respond to those of opinions and respond to those of others; seek clarification and . speak in sentences, using others; seek clarification and familiar vocabulary, phrases and others; seek clarification and others; seek clarification and help* familiar vocabulary, phrases and help* basic language structures help* help* . speak in sentences, using basic language structures . speak in sentences, using . develop accurate pronunciation . speak in sentences, using . speak in sentences, using familiar vocabulary, phrases and . develop accurate pronunciation familiar vocabulary, phrases and and intonation so that others familiar vocabulary, phrases and familiar vocabulary, phrases and basic language structures and intonation so that others basic language structures understand when they are reading basic language structures basic language structures . develop accurate understand when they are reading . develop accurate pronunciation aloud or using familiar words and . develop accurate . develop accurate pronunciation pronunciation and intonation so aloud or using familiar words and and intonation so that others phrases* pronunciation and intonation so and intonation so that others that others understand when they phrases* understand when they are . present ideas and information that others understand when understand when they are are reading aloud or using . present ideas and information reading aloud or using familiar orally to a range of audiences* they are reading aloud or using reading aloud or using familiar familiar words and phrases* orally to a range of audiences* words and phrases* . read carefully and show familiar words and phrases* words and phrases* . present ideas and information . read carefully and show . present ideas and information understanding of words, phrases . present ideas and information . present ideas and information orally to a range of audiences* understanding of words, phrases orally to a range of audiences* and simple writing orally to a range of audiences* orally to a range of audiences* . read carefully and show and simple writing . read carefully and show . appreciate stories, songs, . read carefully and show . read carefully and show understanding of words, phrases . appreciate stories, songs, understanding of words, phrases poems and rhymes in the understanding of words, phrases understanding of words, phrases and simple writing poems and rhymes in the and simple writing language and simple writing and simple writing . appreciate stories, songs, language . appreciate stories, songs, . appreciate stories, songs, . appreciate stories, songs, poems and rhymes in the broaden their vocabulary and poems and rhymes in the poems and rhymes in the poems and rhymes in the language develop their ability to understand language language language broaden their vocabulary and new words that are introduced develop their ability to into familiar written material, understand new words that are including through using a introduced into familiar written dictionary material, including through using . write phrases from memory, a dictionary and adapt these to create new . write phrases from memory, sentences, to express ideas and adapt these to create new clearly sentences, to express ideas clearly Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Understands the main point(s) Understand the main points from a Understand the main points from Understand the main points from Understand the main points from Understand the main points from from a short written text – e.g. spoken passage made up of a spoken passage made up of a spoken passage made up of a spoken passage made up of a spoken passage made up of simple messages on a familiar language – e.g. familiar language – e.g. familiar language – e.g. familiar language – e.g. familiar language – e.g. postcard/in an email • short rhyme or song • short rhyme or song • short rhyme or song • short rhyme or song • short rhyme or song • basic telephone message • basic telephone • basic telephone message • basic telephone • basic telephone message • weather forecast message • weather forecast message • weather forecast Ask and answer simple questions– • weather forecast Ask and answer simple • weather forecast Ask and answer simple Ask and answer simple questions– Know how to Ask and answer simple questions– Know how to questions– pronounce some letter strings. questions– pronounce some letter strings. Know how to pronounce some Know how to pronounce some letter strings. letter strings. PHSE Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Cornerstones Topic Frozen Kingdom / Survival Fallen Fields / A Child’s War Stargazers Time Travellers Peasants, Princes and Hola Mexico CRUCIAL CREW Y5- Be Pestilence Y5- To take a role in responsible for own safety improving their local and remind others of safety environment, eg village litter in more challenging pick. To understand how to environments. camp safely, without CRUCIAL CREW Y6- Work damaging the environment with others to risk assess Y6- To take a role in making and identify potential the outside world a better hazards in school outdoor place beyond their local areas and on visits to other environment outdoor areas. National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives National curriculum objectives New Beginnings-SEAL Getting on and falling out- SEAL Going for Goals-SEAL Good To Be Me- SEAL SRE – Seal Health 1a) to recognise their worth as 2a) to research, discuss and 1b) to recognise their worth as 1b) to recognise their worth as 1a) to recognise their worth as 2a) to research, discuss and individuals, by identifying positive debate topical issues, problems individuals, by identifying individuals, by identifying positive individuals, by identifying positive debate topical issues, problems things about themselves and their and events; positive things about themselves things about themselves and their things about themselves and and events. achievements, seeing their 2c) to realise the consequences of and their achievements, seeing achievements, seeing their their achievements, seeing their 2b)why and how rules and laws mistakes, making amends and antisocial and aggressive their mistakes, making amends mistakes, making amends and mistakes, making amends and are made and enforced, why setting personal goals; behaviours, such as bullying and and setting personal goals; setting personal goals; setting personal goals;1c) to face different rules are needed in Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
1b) to face new challenges racism, on individuals and 1c) to face new challenges 2e) to reflect on spiritual, moral, new challenges positively by different situations and how to positively by collecting communities; positively by collecting social and cultural issues, using collecting information, looking for take part in making and changing information, looking for help, 2e) to reflect on spiritual, moral information, looking for help, imagination to understand other help, making responsible choices rules. making responsible choices and social and cultural issues, using making responsible choices and people’s experiences; and taking action; 2e) to reflect on spiritual, moral, taking action; imagination to understand other taking action; 3f) that pressure to behave in an 3b) to be aware of different types social and cultural issues, using 2a) why and how rules and laws people’s experiences; 4a) that their actions affect unacceptable or risky way can of relationships, including imagination to understand other are made and enforced, why 2f) to resolve differences by themselves and others, to care come from a variety of sources, marriage and those between people’s experiences; different rules are needed in looking at alternatives, making about other people’s feelings including people they know and friends and families, and to 2f) to resolve differences by different situations and how to decisions and explaining choices; and to try to see things from their how to ask for help, and use develop the skills to be effective looking at alternatives, making take part in making and changing 4a) that their actions affect points of view. basic techniques for resisting in relationships; decisions and explaining choices; rules; themselves and others, to care Speaking and Listening- T2 63. pressure to do wrong; 3c) about how the body changes 3a) that their actions affect 2b) that there are different kinds about other people’s feelings and To consider examples of conflict 4a) that their actions affect as they approach puberty themselves and others, to care of responsibilities, rights and to try to see things from their and resolution, exploring the themselves and others, to care about other people’s feelings and duties at home, at school and in points of view; language used. about other people’s feelings and to try to see things from their the community, and that these 4c) to be aware of different types to try to see things from their points of view; can sometimes conflict with each of relationship, including marriage point of view. 3d)which commonly available other; and those between friends and 4c) to be aware of different types substances and drugs are legal 2c) to reflect on spiritual, moral, families, and to develop the skills of relationships, including and illegal and what the effects social and cultural issues, using to be effective in relationships. marriage, and those between and risks are. imagination to understand other 4d) to realise the nature and friends and families, and to 3e) to recognise the different risks people’s experiences; consequences of racism, teasing, develop the skills to be effective in different situations and then 3a) that their actions affect bullying and aggressive in relationships. decide how to behave themselves and others, to care behaviours and how to respond to Speaking and Listening-T2 63. To responsibly; about other people’s feelings and them and ask for help; consider examples of conflict and 3f) that pressure to behave in an to try to see things from their 4e) to recognise and challenge resolution, exploring the language unacceptable or risky way can points of view; stereotypes; used. come from a variety of sources, 3b) to be aware of different types 4f) that differences and similarities including people they know, and of relationships, including between people arise from a how to ask for help and use basic marriage and those between number of factors, including techniques for resisting pressure friends and families, and to cultural, ethnic, racial and religious to do wrong; develop the skills to be effective diversity, gender and disability. 3g) school rules about health and in relationships; Speaking and Listening- T1 60. To safety, basic emergency aid 4a) to realise the nature and understand and use a variety of procedures and where to get help; consequences of racism, teasing, ways to criticise constructively and 4g) where individuals, families bullying and aggressive respond to criticism. and groups can get help and behaviours, and how to respond ANTI-BULLYING WEEK: support to them and ask for help. Say No to Bullying- SEAL Speaking and Listening- T1 60- 1b) to recognise their worth as To understand and use a variety f individuals, by identifying positive ways to criticise constructively things about themselves and their and respond to criticism. achievements, seeing their mistakes, making amends and setting personal goals; 1c) to face new challenges positively by collecting information, looking for help, making responsible choices and taking action; 2c) to realise the consequences of anti-social and aggressive behaviours, such as bullying and racism, on individuals and communities; 2e) to reflect on spiritual, moral, social and cultural issues, using imagination to understand other people’s experiences; 2f) to resolve differences by looking at alternatives, making decisions and explaining choices; 3e) to recognise the different risks in different situations and then decide how to behave responsibly; 3f) that pressure to behave in an Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
unacceptable or risky way can come from a variety of sources, including people they know, and how to ask for help and use basic techniques for resisting pressure to do wrong; 3g) school rules about health and safety, basic emergency aid procedures and where to get help; 4a) that their actions affect themselves and others, to care about other people’s feelings and to try to see things from their points of view; 4d) to realise the nature and consequences of racism, teasing, bullying, and aggressive behaviours and how to respond to them and ask for help; 4e) to recognise and challenge stereotypes; 4f) that differences and similarities between people arise from a number of factors, including cultural, ethnic, racial and religious diversity, gender and disability; 4g) where individuals, families and groups can get help and support. Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Skill coverage Demonstrate that they recognise .Demonstrate that they recognise .Demonstrate that they .Demonstrate that they recognise Express their views confidently their own worth and that of others their own worth and that of others recognise their own worth and their own worth and that of others 3. Express their views confidently Identify positive ways to face new that of others 4. Listen to and show respect for challenges 2. Identify positive ways to face 2. Identify positive ways to face 4. Listen to and show respect for the views of others Express their views confidently new challenges 2. Identify positive ways to face new challenges the views of others Listen to and show respect for the new challenges 12. Make judgements and views of others 3. Express their views confidently 3. Express their views confidently 5. Discuss some bodily and decisions and list some ways of Show how their views can 3. Express their views emotional changes at puberty resisting negative peer pressure develop in the light of listening to 4. Listen to and show respect for confidently 4. Listen to and show respect for around issues affecting their others the views of others the views of others 6. Demonstrate dealing with health and wellbeing Explain their interests and how 4. Listen to and show respect for these changes in a positive way they will develop skills to work in 16. Identify different types of the views of others 11. Identify some factors that 13. List the commonly available the future relationships affect emotional health and 10. Make choices about how to substances and drugs that are Demonstrate some ways of wellbeing develop a healthy lifestyle legal and illegal dealing with these in a positive 17. Show ways of maintaining 10. Make choices about how to way good relationships develop a healthy lifestyle 12. Make judgements and 11. Identify some factors that 14. Describe some of the effects 18. Describe the nature and decisions and list some ways of affect emotional health and and risks consequences of bullying 11. Identify some factors that resisting negative peer pressure wellbeing affect emotional health and around issues affecting their 15. Explain how to manage the 19. Express ways of responding to wellbeing health and wellbeing 12. Make judgements and risks in different familiar situations it decisions and list some ways of 25. Take part in making and 16. Identify different types of resisting negative peer pressure 20. Respond to, or challenge 20. Respond to, or challenge changing rules relationships around issues affecting their negative behaviours such as negative behaviours such as health and wellbeing stereotyping and aggression stereotyping and aggression 26. Demonstrate respect and 17. Show ways of maintaining tolerance towards others good relationships 13. List the commonly available 21. Realise the consequences of 23. Understand why and how rules 18. Describe the nature and substances and drugs that are anti-social behaviours such as are made and enforced consequences of bullying legal and illegal bullying and racism on individuals 24. Understand why different rules and communities are needed in different situations 19. Express ways of responding 14. Describe some of the effects to it and risks 25. Take part in making and 33. Explore how the media changing rules 20. Respond to, or challenge 15. Explain how to manage the present information negative behaviours such as risks in different familiar 26. Demonstrate respect and stereotyping and aggression situations Curriculum Coverage Map Year 5 and 6 Cycle 1
tolerance towards others 21. Realise the consequences of 16. Identify different types of 27. Resolve differences by looking anti-social behaviours such as relationships at alternatives, making decisions bullying and racism on individuals and explaining choices and communities 17. Show ways of maintaining good relationships 22. Research, discuss and debate topical issues, problems and events
26. Demonstrate respect and tolerance towards others
27. Resolve differences by looking at alternatives, making decisions and explaining choices
30. Appreciate the range of national, regional, religious and ethnic identities in the UK
31. Describe some of the different beliefs and values in society