Coaching Roles
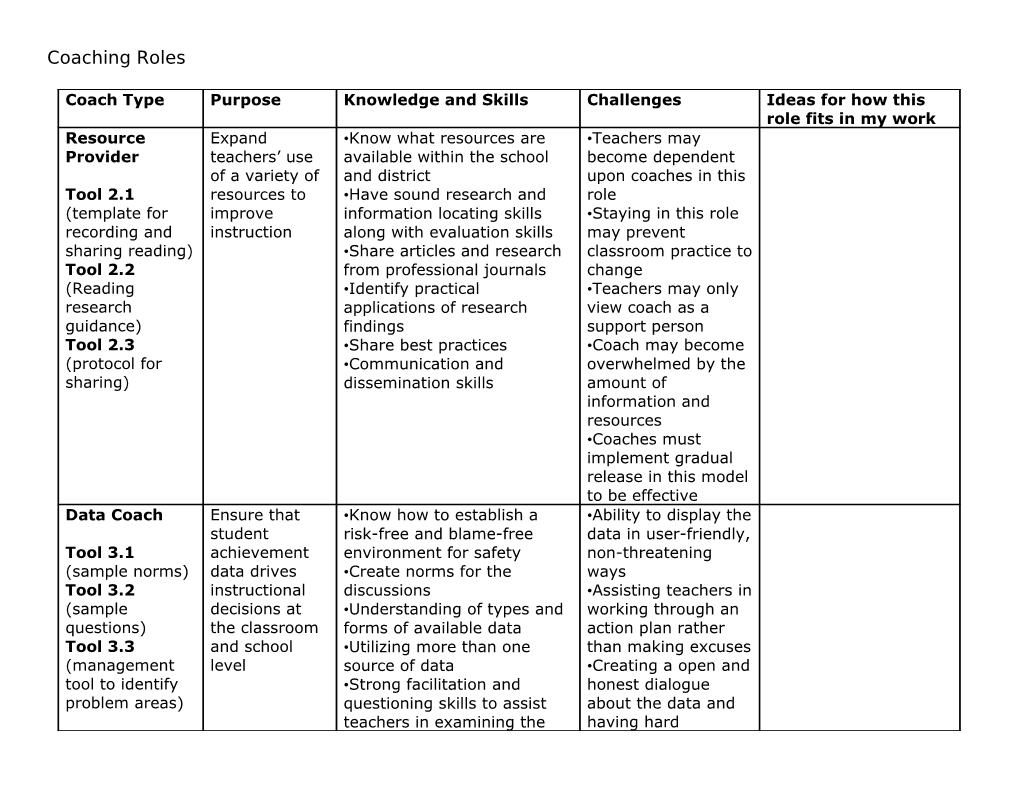
Coach Type Purpose Knowledge and Skills Challenges Ideas for how this role fits in my work Resource Expand •Know what resources are •Teachers may Provider teachers’ use available within the school become dependent of a variety of and district upon coaches in this Tool 2.1 resources to •Have sound research and role (template for improve information locating skills •Staying in this role recording and instruction along with evaluation skills may prevent sharing reading) •Share articles and research classroom practice to Tool 2.2 from professional journals change (Reading •Identify practical •Teachers may only research applications of research view coach as a guidance) findings support person Tool 2.3 •Share best practices •Coach may become (protocol for •Communication and overwhelmed by the sharing) dissemination skills amount of information and resources •Coaches must implement gradual release in this model to be effective Data Coach Ensure that •Know how to establish a •Ability to display the student risk-free and blame-free data in user-friendly, Tool 3.1 achievement environment for safety non-threatening (sample norms) data drives •Create norms for the ways Tool 3.2 instructional discussions •Assisting teachers in (sample decisions at •Understanding of types and working through an questions) the classroom forms of available data action plan rather Tool 3.3 and school •Utilizing more than one than making excuses (management level source of data •Creating a open and tool to identify •Strong facilitation and honest dialogue problem areas) questioning skills to assist about the data and teachers in examining the having hard data conversations to •Assist teachers in creating a ensure that all plan of action based on the inequities in the data data are addressed •Be knowledgeable about actions to take to address learning issues •Organizational and Coaching skills to lead these discussions Curriculum To ensure •A deep understanding of •Having adequate Specialist implementatio standards and curriculum understanding of all n of adopted •How to break a standard the curriculum areas Tool 4.1 curriculum down into essential •Establishing (standards knowledge and skills credibility based unit •How to plan pacing guides •Understanding how planner) •Understanding of the skills are assessed Tool 4.2 developmental needs of the and presented on (Standards students high stakes tests based weekly •Ability to communicate how planning the concept appears later in template) the scope and sequence of Tool 4.3 the curriculum (unpacking a •Ability to assist in designing standard tool) assessments that accurately Tool 4.4 measure the expected (planning for outcome assessment •Know how to read and use a tool) curriculum guide Instructional To align •Understanding of the •Requires a large Specialist instruction research on effective amount of with instructional strategies knowledge about a Tool 5.1 curriculum to •Ability to align instruction variety of strategies (Marzano met the needs with content •Being a continuous summary) of all students •Ability to model effective learner in Tool 5.2 instruction researching, (Question tool •Understanding of standards practicing and to assess based planning introducing new needed •Assist teachers in looking at strategies instructional the big picture first then plan •Be willing to critique strategy) instructional and assessment their own practices Tool 5.4 strategies as a model for all (differentiation •Understanding of how to teachers strategies) integrate a variety of content areas •Facilitation skills to assist teacher sin thinking through the process of planning •Understanding that the learning for teachers is in the process not just the outcome of the unit planning •Ability to do think alouds of their own planning practices for modeling purposes Classroom To increase the •Understanding the Theory of •Finding time to Supporter quality and Gradual Release debrief the lesson in Tool 6.1 (model effectiveness •Knowing when to provide a a meaningful for planning a of classroom model lesson – being dialogue demonstration instruction intentional about what •Getting stuck in the lesson) outcomes they want to deomonstration end Tool 6.2 achieve of the continuum (template for •Being specific about the •Ability to co-teach teacher to use data the teacher should be lessons while observing collecting during the •Balancing positive lesson) observation and constructive Tool 6.4 •Skills in conducting a feedback that points (preobservation reflection conference with out areas for tool to discuss teachers to provide feedback improvement lesson to be and observations without reflected on) •Structuring a productive overwhelming the Tool 6.5 feedback session focused on teacher (Reflective the area the teacher •Knowing when and feedback requested for information how to move the protocol) •Observation, data collection, teacher along the analysis, giving feedback, gradual release promoting metacognition, continuum reflection and building trusting relationship skills Mentor To increase •Building trusting •Ability to move instructional relationships teachers from Page 62 skills of the •Understanding the stages of dependence to (Stages of novice teacher teacher development independence as a teacher and support •Ability to identify and match teacher development) schoolwide support with teacher needs •Balancing directive Tool 7.1 induction •Using cognitive coaching to coaching with more (identifying a activities assist teachers in analyzing reflective and teachers their own practice, how to metacognitive struggle collect, analyze and share coaching protocol) data, how to provide specific •Implementing the and corrective feedback and gradual release how to provide a range of model alternatives •Balancing time •Deep understanding of spent with novice knowledge and skills related teachers to curriculum, planning, effective instruction, assessment, and classroom management Learning To design •Deep understanding of high •Ability to align the Facilitator collaborative, quality professional learning with teacher job-embedded, development needs and school Tool 8.2 standards- •Understanding of the NSDC goals (identifying based standards •Create a appropriate PD professional •Utilize research on change collaborative designs) learning •Ability to plan, deliver, learning Tool 8.3 coordinate, implement and environment (identifying evaluate PD •Understanding that ways to find •Couple the roles of learning follow up is key time for PD) facilitator with classroom factor in influencing Tool 8.4 (lesson supporter to provide ongoing change in the study tool) support for the learning teacher practice Page 70 (12 •Identify the expected principles for outcomes and evidence of effective adult success, understands the learning) learner, identifies how the Tool 8.5 interaction will occur and (template to determines the sequence of focus learning) interaction Tool 8.6 •Follows this procedure… (planning Considers what the intended template for PD) learning should be, how to structure the learning experience, how to guide the learning, how to assess the learning School Leader To work •Must act with the intention •Providing collaboratively of making a positive differentiated Page 78 with the difference services and (stages of school’s formal •Strong understanding of the resources to concern leadership to theory of change and accommodate the Tool 9.2 design, designs for interventions various stages of (planning an implement, •Commitment to the school concern effective and assess vision and be sure that •Fine line between meeting) school change attitudes, behaviors and supporting Tool 9.3 initiatives to commitments align with the administrator change (Norms for ensure vision and maintaining a meetings) alighnment •Utilize informal relationship with the Tool 9.4 and focus on conversations champions the teachers (consensus intended school and teacher successes •Going slow to go decision results •Assesses barriers to change, fast making) listens to understand causes •Protecting teachers Tool 9.5 of resistance and provides from unnecessary (resolving information about the work or distractions conflict benefits of initiatives •Keeping the focus strategies) •Ability to create a plan to on student learning Tool 9.6 moved from current state to •identifying (communication desired state, an action plan implementation skills) model for implementing issues and assisting Tool 9.7 change the administration in (creating teams) •Leadership skills to build addressing them and assess the •Ability to make implementation of a vision, connections between monitoring the progress of a different initiatives goal, reporting progress and assist others in •Strong facilitation skills seeing the alignment Catalyst for To create •Ability to question current •Maintaining the Change disequilibrium practice, challenge current balance between with the mental models status quo and Tool 10.1 current state •Ability to evaluate critically assisting others in (critical inquiry as an impetus and analyze what is and is being confident and process) to explore not working competent in their Tool 10.2 and alternatives to •Must model continuous work 10.3 (Gap current improvement in your work – •Being ready to act analysis practice Make practice public, seek whenever the framework) feedback, examine and opportunity arises Tool 10.4 refine practices, learn •Balance between (evaluation continuously from others in initiating the change think process) same role, read and conduct and planting the Tool 10.5 action research seeds to allow others (school vision) •Understanding of change, to perceive the need Tool 10.6 leadership, reform and adult to change (assessing development •Fostering ownership school culture) •Use creative and critical in others for Tool 10.6 problem solving skills and initiating, (keeping your thinking skills implementing and spirit alive) •State observations factually sustaining the •Strong communication and change relationship skills •Assist others in viewing the change through a new lens Learner To model •Modeling the lead learner to •Time to learn continuous influence others •Making it a habit to Hayes Mizell learning, to •Understand how it is you reflect on your work suggests that keep current learn – strengths and •Consider impact on this is the most and to be a weaknesses, awareness of both people and important role thought leader biases and assumptions environment in for coaches! in the school •Focus their learning on which you work themselves, their work and •Ability to Tool 11.1 the field of education acknowledge one’s (critical events •Model attitudes and ignorance analysis) behaviors teachers need to •Struggle between Tool 11.2 11.3 be successful (desire to being right and (dialogue learn, knowing how to learn, being open to journal) and know how to apply understand different Tool 11.4 learning) points of view (assumptions •Ability to acknowledge one’s •Knowing your that underlie ignorance publicly beliefs or mental work) •Take charge of your own models and how Tool 11.5 11.6 learning they impact your (feedback •Utilize networks and decisions protocol) learning communities •Having your actions •”Learning without applying be congruent with is meaningless.” your espoused •Utilize reflection as a beliefs process to support your learning •Has reading, action research, reflecting, analyzing, dialoguing, journaling and synthesizing skills