Scope and Sequence TEXARKANA INDEPENDENT SCHOOL DISTRICT
I = Introduced P = Practiced M= Mastered
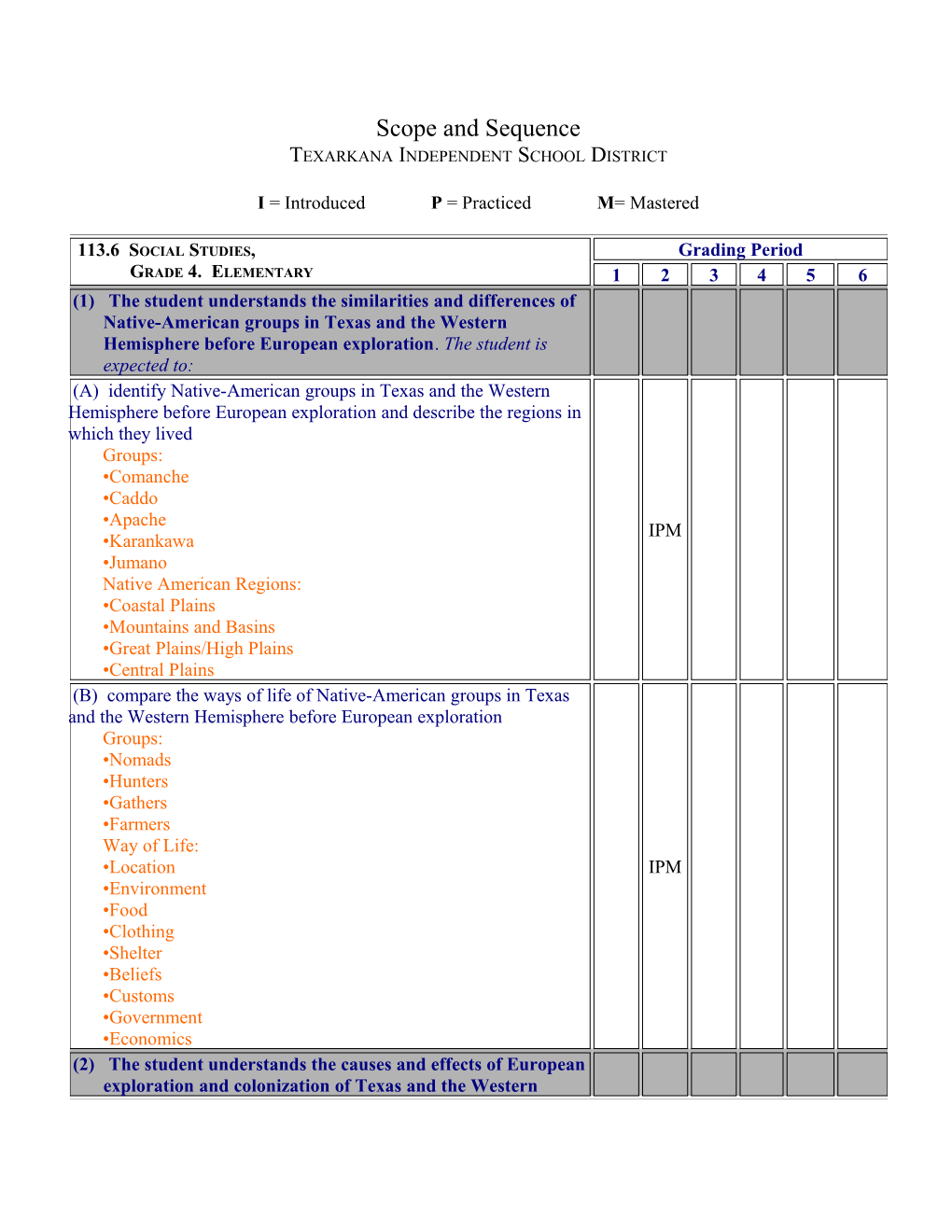
113.6 SOCIAL STUDIES, Grading Period GRADE 4. ELEMENTARY 1 2 3 4 5 6 (1) The student understands the similarities and differences of Native-American groups in Texas and the Western
Hemisphere before European exploration. The student is expected to: (A) identify Native-American groups in Texas and the Western Hemisphere before European exploration and describe the regions in which they lived Groups: •Comanche •Caddo •Apache IPM •Karankawa •Jumano Native American Regions: •Coastal Plains •Mountains and Basins •Great Plains/High Plains •Central Plains (B) compare the ways of life of Native-American groups in Texas and the Western Hemisphere before European exploration Groups: •Nomads •Hunters •Gathers •Farmers Way of Life: •Location IPM •Environment •Food •Clothing •Shelter •Beliefs •Customs •Government •Economics (2) The student understands the causes and effects of European exploration and colonization of Texas and the Western Hemisphere. The student is expected to: (A) summarize reasons for European exploration and settlement of Texas and the Western Hemisphere The 3 G’s – I PM •God – spread Catholicism •Gold – seeking wealth •Glory – claims for European countries (B) identify the accomplishments of significant explorers such as Cabeza de Vaca; Christopher Columbus; Francisco Coronado; and Rene-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de la Salle and explain their impact on the settlement of Texas Including: •Christopher Columbus- launched the European exploration and colonization of America •Cabeza de Vaca- explored Texas, met Native Americans, and I PM reported about Texas in his book Relación •Francisco Coronado- explored the Southwest for Spain looking for riches and the seven cities of Cibola and Quivira; reported that the area north of Mexico had little value for Spain •René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle- explore the length of the Mississippi river and secured Louisiana for France, built Fort St. Louis at Matagorda Bay for the French; threatened Spain’s domination of the area which led to mission system in Texas (C) explain when, where, and why the Spanish established Catholic missions in Texas •When: Late 1600’s to mid 1700’s •Where: East Texas (Nacogdoches), South Central Texas, West IPM Texas (El Paso) •Why: growth of the Catholic church, protection of Spanish territory (D) identify the accomplishments of significant empresarios IPM including Moses Austin, Stephen F. Austin, and Martin de Leon explain their impact on the settlement of Texas Including: •Moses Austin: made an agreement with the Spanish to start the first Anglo colony in Texas • Stephen F. Austin: known as the “Father of Texas,” first empresario who took over Texas land grant after his father died. He selected an ideal spot for his colony, successfully brought 1200 families to Texas, effectively enforced rules as empresario, and served as liaison between colonists and Mexican government, settled “Old 300” •Martin De Leon: the only Mexican empresario; rancher who settled around 200 Mexican families near the Texas coast; founded the town of Victoria and encouraged the development of the cattle industry in Texas (E) identify the impact of Mexico's independence from Spain on the events in Texas IPM •allowing Austin to settle and more U. S. immigrants to settle Texas (3) The student understands the causes and effects of the Texas Revolution, the Republic of Texas, and the annexation of Texas to the United States. The student is expected to: (A) analyze the causes, major events, and effects of the Texas Revolution, including the battles of the Alamo and San Jacinto Including: Causes : •Colonial Conflicts with Mexican government 0 o Religious differences 1 o Language problems 2 o Slavery 3 o Mexican Citizenship •Law of April 6, 1830 •Arrest of Stephen F. Austin •Santa Anna becomes dictator Major Events: IPM •Battle of Gonzales •Battle of Goliad •Battle of San Antonio •Convention of 1836 0 o Declaration of Independence – March 2, 1836 •Battle of the Alamo – March 6, 1836 •Runaway Scrape •Goliad Massacre •Battle of San Jacinto – April 21, 1836 •Treaty of Velasco Effects: •Establishment of a new republic (B) describe the successes and problems of the Republic of Texas Problems: debt, border wars, disputes with Native Americans Successes: development of an education system, set up new IPM government – a democratic republic, land grants, the creation of the Texas Rangers (C) explain the events that led to the annexation of Texas to the IPM United States •Debate in U. S. Congress •Sam Houston’s views •Vote by people •Mexico still a threat, •Texas in debt •U.S. westward expansion
(D) explain the impact of the Mexican War on Texas No more border disputes, land lost by Texas, U.S. will pay off IPM debt (E) identify leaders important to the founding of Texas as a republic and state, including Sam Houston, Mirabeau Lamar, and Anson Jones Including: •Sam Houston: first and third president of Texas; favored annexation; tried to protect Native Americans •Mirabeau B. Lamar: second president of Texas; opposed IPM annexation; called the “Father of Education” in Texas; wanted Texas to expand westward; reversed policy on treatment of Native Americans; relocated capital from Houston to Austin •Anson Jones: last elected president of the Republic of Texas; handed over power to new governor of Texas when Texas became a state (4) The student understands the political, economic, and social changes in Texas during the last half of the 19th century. The student is expected to: (A) describe the impact of the Civil War and Reconstruction on Texas •Slavery in Texas •Texas joins the Confederacy •Amendment 13( the ending of slavery) •Amendment 14 (the grant of citizenship) IPM •Amendment 15 (the right to vote for every male citizen ) •How Abraham Lincoln treated Anglos and African Americans Juneteenth – June 19, 1865 - the day the Emancipation Proclamation was heard by slaves in Texas and were freed Last battle of Civil War fought in Texas (Brownsville) (B) explain the growth and development of the cattle and oil industries IPM Demand for beef in the North, cattle drives, use of barbed wire, railroad, development of automobile, trains for oil, Spindletop (C) identify the impact of railroads on life in Texas, including IPM changes to cities and major industries Positive and negative changes to cities and major industries Develop cities where trains stopped (junctions) (D) describe the effects of political, economic, and social changes on Native Americans in Texas Effects: Native Americans forced to relocate, slaughter of buffalo, loss of culture/way of life, many years of warfare between Native Americans and Anglo Texans, war, disease, and IP P PM starvation took many Native American lives, Native Americans forced to live on reservations
(5) The student understands important issues, events, and individuals of the 20th century in Texas. The student is expected to: (A) identify the impact of various issues and events on life in Texas such as urbanization, increased use of oil and gas, and the growth of aerospace and other technology industries Including: Urbanization – growth of Houston (oil and gas and aerospace), Austin (seat of government and expansion of technology), urban sprawl (Houston, I-35, San Antonio, Dallas) IP PM Increased use of oil and gas – plastics, roads and interstate system Aerospace - NASA Other technology – computers, telecommunications •Texas Instruments ,Dell; •Southwestern Bell (B) identify the accomplishments of notable individuals such as Henry Cisneros, Miriam A. Ferguson, Audie Murphy, Cleto Rodriguez, and John Tower
Including: Henry Cisneros – mayor of San Antonio, Secretary of Department of Housing and Urban Development IP PM Miriam A. Ferguson – first female governor of Texas Audie Murphy – most decorated soldier in WWII, actor Cleto Rodriguez – the 5th Mexican-American to receive the Congressional Medal of Honor during WWII John Tower – influential Republican senator from Texas 1961- 1985 (6) The student uses geographic tools to collect, analyze, and
interpret data. The student is expected to: (A) apply geographic tools, including grid systems, legends, IP P P P P M symbols, scales, and compass roses, to construct and interpret maps Including: •grid systems, legends, symbols, scales, and compass roses •student use these to create hand-made maps (B) translate geographic data into a variety of formats such as raw data to graphs and maps IP P P P P M • raw data to graphs and maps (7) The student understands the concept of regions. The student
is expected to: (A) describe a variety of regions in Texas and the Western Hemisphere such as political, population, and economic regions that result from patterns of human activity Including: Political population and economic regions Four Physical Regions: Coastal Plains, North Central Plains, Great Plains, Mountains and Basins IP P P P PM Republic of Texas Capitals of Texas Spindletop Major cattle trails- Chisholm and Goodnight-Loving Rivers- Rio Grande, Red River, Sabine, Colorado, Brazos Major Towns and Metropolitan Areas (B) describe a variety of regions in Texas and the Western Hemisphere such as landform, climate, and vegetation regions that result from physical characteristics Including: IP PM •Landform regions – coastal plain, hills, high plains, desert, •Climate regions – humid coastal regions, dry desert regions, include discussion of “northers” •Vegetation – piney woods, cotton (C) compare the regions of Texas with regions of the United States IP PM and other parts of the world Including: •Coastal Plains •Mountains and Basins •Central Plains •Great Plains/High Plains Physical Characteristics: Climate, topography, vegetation/wildlife, water sources Human Characteristics: Population, land use, immigration, agriculture, industry, cities, transportation, wealth, cultures (8) The student understands the location and patterns of settlement and the geographic factors that influence where people live. The student is expected to: (A) identify clusters of settlement in Texas and explain their distribution •Along coast, ports (Galveston) earlier •Near rivers (Austin, San Antonio, Waco) I P P P P M •Other major transportation centers (rail line in Fort Worth and cattle industry) •Today’s growth near local highway intersections (B) explain patterns of settlement at different time periods in Texas •Immigration to Texas from U.S. (migration) •Mexico I P P P P M •Central America •Europe •Asia (C) describe the location of cities in Texas and explain their distribution, past and present •Midland-Odessa •Galveston •El Paso •Houston I P P P P M •Austin •San Antonio •Dallas •Fort Worth •Brownsville •Texarkana (D) explain the geographic factors that influence patterns of I P P P M settlement and the distribution of population in Texas, past and present Including rivers, the coast, and fertile land, natural resources such as oil •Caddo •Karankawa •Jumano •Comanche •Apache (9) The student understands how people adapt to and modify their environment. The student is expected to: (A) describe ways people have adapted to and modified their environment in Texas, past and present Locate Native Americans on a map in relationship to the geography of Texas Examples of adaptations and modifications: •Texans dam rivers to control flooding/generate electricity/promote tourism •Farmers establish systems of irrigation/windmill and erosion prevention IP PM •All native tribes of Texas adapted to their environment •Barbed wire fencing closed open range and changed cattle ranching •Mining/drilling for natural resources •Highway system •Railroad system
(B) identify reasons why people have adapted to and modified their environment in Texas, past and present, such as the use of natural resources to meet basic needs •Use and over use of irrigation IP PM •Urbanization-immigrants built homes of materials readily available •Transportation (C) analyze the consequences of human modification of the environment in Texas, past and present •the building of dams on the Brazos and the Colorado IP P P P PM •water use of the Rio Grande •road systems •fencing (10) The student understands the basic economic patterns of early societies in Texas and the Western Hemisphere. The student is expected to: (A) explain the economic patterns of various early Native-American groups in Texas and the Western Hemisphere IPM •Trade between Native Americans including barter (B) explain the economic patterns of early European immigrants to Texas and the Western Hemisphere Including: •Agriculture: cattle and ranching, farming IPM •The exchange of goods and products: •Livestock including horses •Plants including maize, corn, tomatoes •Cultural implements including guns, swords (11) The student understands the reasons for exploration and colonization. The student is expected to: (A) identify the economic motivations for European exploration and settlement in Texas and the Western Hemisphere IP M •Gold and land (B) identify the economic motivations for Anglo-American colonization in Texas Including : •Stephen F. Austin’s colony IPM •Land acquisition •Agriculture •Escape debt •Escape low socio-economic status (12) The student understands the characteristics and benefits of the free enterprise system in Texas. The student is expected to: (A) describe the development of the free enterprise system in Texas Definition of free enterprise including supply and demand •What to produce? •How to produce? IP M •How much to produce? •For whom to produce? Trading posts, cities and railroad junctions are affected by free enterprise (B) describe how the free enterprise system works in Texas IP M (C) give examples of the benefits of the free enterprise system in IP M Texas •Economic freedom •Voluntary exchange •Private property •Profit motive (13) The student understands patterns of work and economic
activities in Texas. The student is expected to: explain how people in different regions of Texas earn their living, past and present (A)•Ranching including vaqueros •Farming •Petrochemical industries I P P P P M •Computers/technology industries •Service industries including medical •Military installations •Aerospace industries
(B) explain how geographic factors have influenced the location of economic activities in Texas •Landforms •Bodies and sources of water I P P P M •Vegetation •Climate and weather patterns •Animal life (C) analyze the effects of immigration, migration, and limited I P P P P M resources on the economic development and growth of Texas Define: •Immigration-process of people moving to a new place to stay permanently or at least for a long time. •Migration-process of moving from one place to another intending to stay permanently or at least for a long period of time. •Limited resource- when there is a fixed supply of a resource; any non-renewable resource Effects: •Growth of existing towns •New towns formed •New businesses established •Changes in taxes and community services (D) describe the impact of mass production, specialization, and division of labor on the economic growth of Texas •Mass production means making many of the same thing. It can cause an economy to grow. It can lead to a decline in the number of things made by hand by craftspeople. It can increase pollution and can reduce variation in society. •Specialization concentrates research, design, and production on IP M a particular good or service. •Division of labor means dividing work so that each worker does only part of a larger job, as in an assembly line. This contributes to efficiency in mass production but does not result in a highly skilled job force.
(E) explain how developments in transportation and communication have influenced economic activities in Texas •Transportation including railroad, automobile industries, oil IP M industries, and aerospace industries •Communication- technology including computers/Internet, cell phones, satellites (F) explain the impact of American ideas about progress and equality of opportunity on the economic development and growth of Texas IP M •Plantation system and spread of slavery •Civil Rights Act of 1965 (14) The student understands how Texas, the United States, and other parts of the world are economically interdependent. The student is expected to: (A) identify ways in which technological changes have resulted in increased interdependence among Texas, the United States, and the world IP M •Internet/computers (B) identify oil and gas, agricultural, and technological products of Texas that are purchased to meet needs in the United States and around the world •Oil and gas – gasoline, jet fuel, heating oil, plastics, IP M •Agricultural products – food (vegetables, fruits, nuts), cotton, milo, sugarcane, rice, beef (cattle), seafood •Technology products – silicon chips, computers, software, medical products, satellites (C) explain how Texans meet some of their needs through the purchase of products from the United States and the rest of the IPM world (15) The student understands how people organized governments in different ways during the early development of Texas. The student is expected to: (A) compare how selected Native-American groups governed themselves •Caddo-confederacy IP P PM •Karankawa-village chief •Jumano-village governments •Comanche-band leaders (B) identify characteristics of Spanish and Mexican colonial governments and their influence on inhabitants of Texas •Catholic IP P PM •Anti-slavery •Trade allowed only with Spain/Mexico (16) The student understands important ideas in historic
documents of Texas. The student is expected to: (A) identify the purposes and explain the importance of the Texas Declaration of Independence, the Texas Constitution, and the Treaty of Velasco Texas Declaration of Independence – unanimously declared independence from Mexico on March 2, 1836 •Freedom of religion •Right to trial by jury •Public school system •Right to petition the government Texas Constitution – set up government and laws of Texas IPM •US Constitution used as a model •Three branches of government •Included a Bill of Rights Treaty of Velasco – written after Santa Anna was captured during the Battle of San Jacinto •Stopped fighting the Texans •Recognized the independence of Texas •Agreed to withdraw all Mexican troops from Texas •Never ratified in Mexico (B) identify and explain the basic functions of the three branches of IPM state government •Executive – execute laws •Judicial – judge laws according to Constitution •Legislative – legislate or make laws (17) The student understands important customs, symbols, and celebrations of Texas. The student is expected to: (A) explain the meaning of selected patriotic symbols and landmarks of Texas, including the six flags over Texas, San Jose Mission, and the San Jacinto Monument Including: •Six flags over Texas IPM •San Jose Mission –“Queen of Missions”- largest and one of the best examples of the Spanish missions in Texas; still in operation •San Jacinto Monument •Alamo (B) sing or recite Texas, Our Texas IPM Texas, Our Texas (C) recite and explain the meaning of the Pledge to the Texas Flag IPM The meaning of the Pledge to the Texas Flag (D) describe the origins and significance of state celebrations such as Texas Independence Day and Juneteenth Including: •Texas Independence Day – March 2, 1836 – Texas declared IPM independence from Mexico at Washington-on-the-Brazos •Juneteenth – June 19, 1865- Date Emancipation Proclamation first read in Galveston, Texas freeing 250,000 slaves in Texas. (18) The student understands the importance of voluntary individual participation in the democratic process. The student is expected to: (A) explain how individuals can participate voluntarily in civic affairs at state and local levels •Voting •Serving on jury IPM •Obeying the law, •Knowledge of the law •Public service •Paying taxes (B) explain the role of the individual in state and local elections IPM •Voting (C) identify the importance of historical figures such as Sam IPM Houston, Barbara Jordan, and Lorenzo de Zavala who modeled active participation in the democratic process Including: Sam Houston •President of the Republic •US Senator •Texas Governor •Hero of the Battle of the San Jacinto •Opposed secession from the union and left the governor’s office after Texans voted overwhelmingly to secede in January of 1861 Barbara Jordan •First African-American congresswoman from the south Lorenzo de Zavala •Empresario •Served on Mexican congress •Governor of the state of Mexico •Vice President of temporary government established during Texas Revolution •Designed the first flag of the Republic of Texas (D) explain how to contact elected and appointed leaders in state and local governments IPM Letter, email, phone (19) The student understands the importance of effective leadership in a democratic society. The student is expected to: (A) identify leaders in state and local governments, including the governor, selected members of the Texas Legislature, and Texans who have been President of the United States, and their political parties •State: the governor, lieutenant governor, attorney general, chief justice, speaker of the House of Representatives, selected IPM members of the Texas Legislature •Local: mayor, county judge, police chief •Presidents: Texans who have been president of the United States (Dwight Eisenhower, LBJ, George H.W. Bush, George W. Bush) (B) identify leadership qualities of state and local leaders, past and IPM present ((20) The student understands the contributions of people of various racial, ethnic, and religious groups to Texas. The student is expected to: (A) identify the similarities and differences within and among IP P P P M selected racial, ethnic, and religious groups in Texas •Spanish/Mexican •German •Native American •African American (B) identify customs, celebrations, and traditions of various culture groups in Texas •Spanish/Mexican IP P P P M •German •Native American •African American (C) summarize the contributions of people of various racial, ethnic, and religious groups in the development of Texas •Spanish/Mexican IP P P P M •German •Native American •African American (21) The student understands the impact of science and technology on life in Texas. The student is expected to: (A) identify famous inventors and scientists such as Gail Borden, Joseph Glidden, and Patillo Higgins and their contributions Including IPM •Gail Borden (condensed milk) •Joseph Glidden (barbed wire) •Patillo Higgins (Spindletop) (B) describe how scientific discoveries and technological innovations have benefited individuals, businesses, and society in Texas •cotton gin •steamboat •windmills •barbed wire IPM •telegraph •railroads •oil and gas •microchip technology •aerospace technology (C) predict how future scientific discoveries and technological IPM innovations might affect life in Texas Include Medicine Science Technology Energy (22) The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of sources including electronic technology. The student is expected to: (A) differentiate between, locate, and use primary and secondary sources such as computer software; interviews; biographies; oral, I P P P P M print, and visual material; and artifacts to acquire information about the United States and Texas (B) analyze information by sequencing, categorizing, identifying cause-and-effect relationships, comparing, contrasting, finding I P P P P M the main idea, summarizing, making generalizations and predictions, and drawing inferences and conclusions (C) organize and interpret information in outlines, reports, databases, and visuals including graphs, charts, timelines, and I P P P P M maps (D) identify different points of view about an issue or topic I P P P P M (E) identify the elements of frame of reference that influenced the I P P P P M participants in an event (F) use appropriate mathematical skills to interpret social studies I P P P P M information such as maps and graphs (23) The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to: (A) use social studies terminology correctly I P P P P M (B) incorporate main and supporting ideas in verbal and written I P P P P M communication (C) express ideas orally based on research and experiences I P P P P M (D) create written and visual material such as journal entries, I P P P P M reports, graphic organizers, outlines, and bibliographies (E) use standard grammar, spelling, sentence structure, and I P P P P M punctuation (24) The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others, in a variety of settings. The student is expected to: (A) use a problem-solving process to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and I P P P P M disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution (B) use a decision-making process to identify a situation that requires a decision, gather information, identify options, predict I P P P P M consequences, and take action to implement a decision