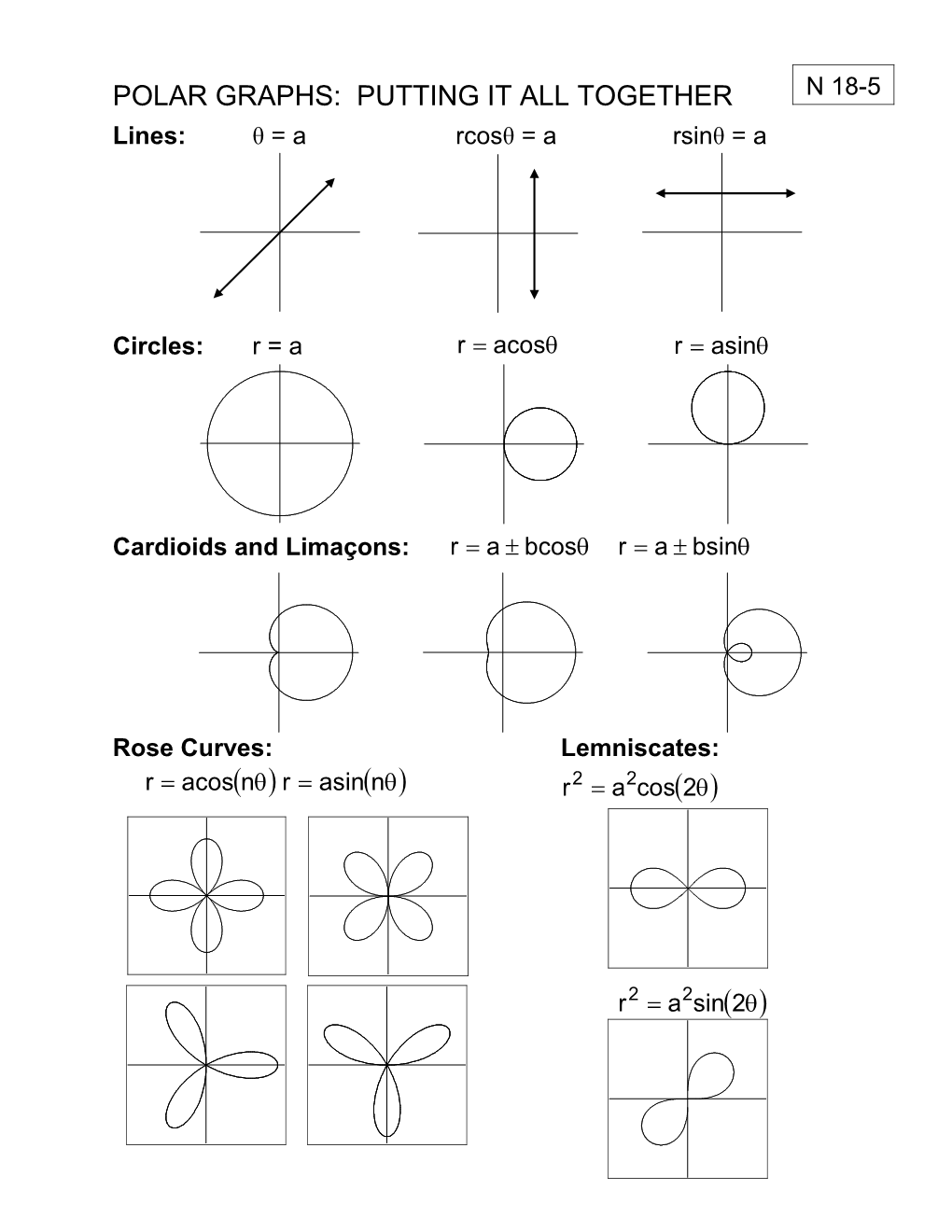
POLAR GRAPHS: PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER N 18-5 Lines: θ = a rcosθ = a rsinθ = a
Circles: r = a r acos r asin
Cardioids and Limaçons: r a bcos r a bsin
Rose Curves: Lemniscates: r acosn r asinn r2 a2cos2
r2 a2sin2 N 18-5 1. When are polar graphs functions? For rectangular equations: Function: A relation in which ______. No x-value can be used twice with different y-values. Graph will pass the ______Test. X is the ______(input) Y is the ______(output)
For polar equations: Function: A relation in which ______. ___ is the ______(input) ___ is the ______(output)
2. Are the graphs on page 1 functions?
3. Do polar functions pass the Vertical Line Test?
4. Advantages of polar graphs over rectangular graphs:
Write the equation for each graph. 5. ______6. ______N 18-5 7. ______8. ______
9. The Spiral of Archimedes: r = aθ Make a table and graph: r =
r θ r θ 0 5 2 2 3π π 7 3 2 2 4π 2π
What happens to r as θ increases?
Graph r = on your calculator.