The Level of analysis Problem in International Relations - J. David Singer Appearing as chapter 3 in International Politics and forgein Policy edited by J.N.Rosenau
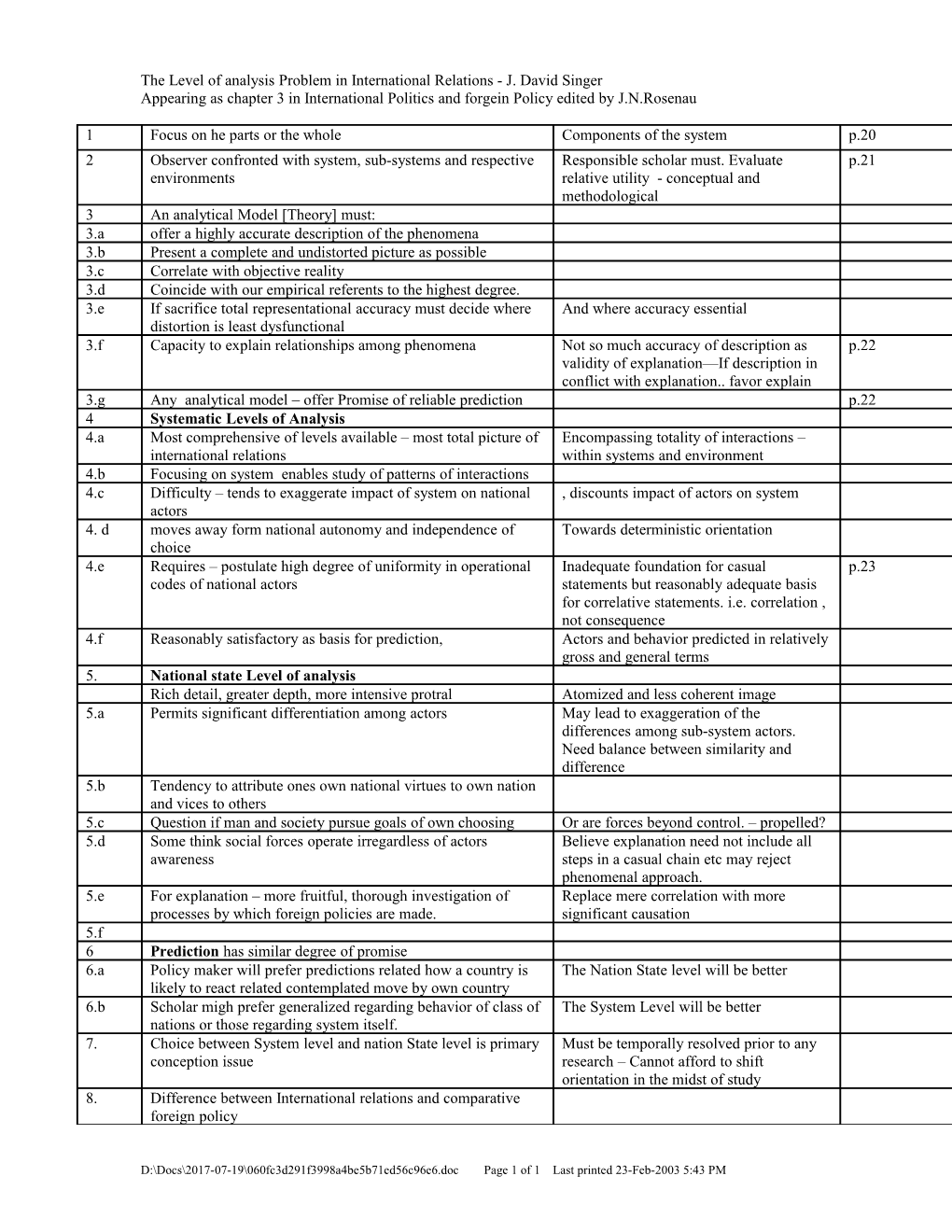
1 Focus on he parts or the whole Components of the system p.20 2 Observer confronted with system, sub-systems and respective Responsible scholar must. Evaluate p.21 environments relative utility - conceptual and methodological 3 An analytical Model [Theory] must: 3.a offer a highly accurate description of the phenomena 3.b Present a complete and undistorted picture as possible 3.c Correlate with objective reality 3.d Coincide with our empirical referents to the highest degree. 3.e If sacrifice total representational accuracy must decide where And where accuracy essential distortion is least dysfunctional 3.f Capacity to explain relationships among phenomena Not so much accuracy of description as p.22 validity of explanation—If description in conflict with explanation.. favor explain 3.g Any analytical model – offer Promise of reliable prediction p.22 4 Systematic Levels of Analysis 4.a Most comprehensive of levels available – most total picture of Encompassing totality of interactions – international relations within systems and environment 4.b Focusing on system enables study of patterns of interactions 4.c Difficulty – tends to exaggerate impact of system on national , discounts impact of actors on system actors 4. d moves away form national autonomy and independence of Towards deterministic orientation choice 4.e Requires – postulate high degree of uniformity in operational Inadequate foundation for casual p.23 codes of national actors statements but reasonably adequate basis for correlative statements. i.e. correlation , not consequence 4.f Reasonably satisfactory as basis for prediction, Actors and behavior predicted in relatively gross and general terms 5. National state Level of analysis Rich detail, greater depth, more intensive protral Atomized and less coherent image 5.a Permits significant differentiation among actors May lead to exaggeration of the differences among sub-system actors. Need balance between similarity and difference 5.b Tendency to attribute ones own national virtues to own nation and vices to others 5.c Question if man and society pursue goals of own choosing Or are forces beyond control. – propelled? 5.d Some think social forces operate irregardless of actors Believe explanation need not include all awareness steps in a casual chain etc may reject phenomenal approach. 5.e For explanation – more fruitful, thorough investigation of Replace mere correlation with more processes by which foreign policies are made. significant causation 5.f 6 Prediction has similar degree of promise 6.a Policy maker will prefer predictions related how a country is The Nation State level will be better likely to react related contemplated move by own country 6.b Scholar migh prefer generalized regarding behavior of class of The System Level will be better nations or those regarding system itself. 7. Choice between System level and nation State level is primary Must be temporally resolved prior to any conception issue research – Cannot afford to shift orientation in the midst of study 8. Difference between International relations and comparative foreign policy
D:\Docs\2017-07-19\060fc3d291f3998a4be5b71ed56c96e6.doc Page 1 of 1 Last printed 23-Feb-2003 5:43 PM