Men and Women’s Brain
October 20th, 2005
Mutsumi Kawasaki Emi Takahashi 1. Introduction
We can find many differences between man and woman in the way of thinking, feeling, and behaving. These differences come from the distinction of man and woman’s brain and the functions. We want to explain how those differences occur by looking at the functions of the brain.
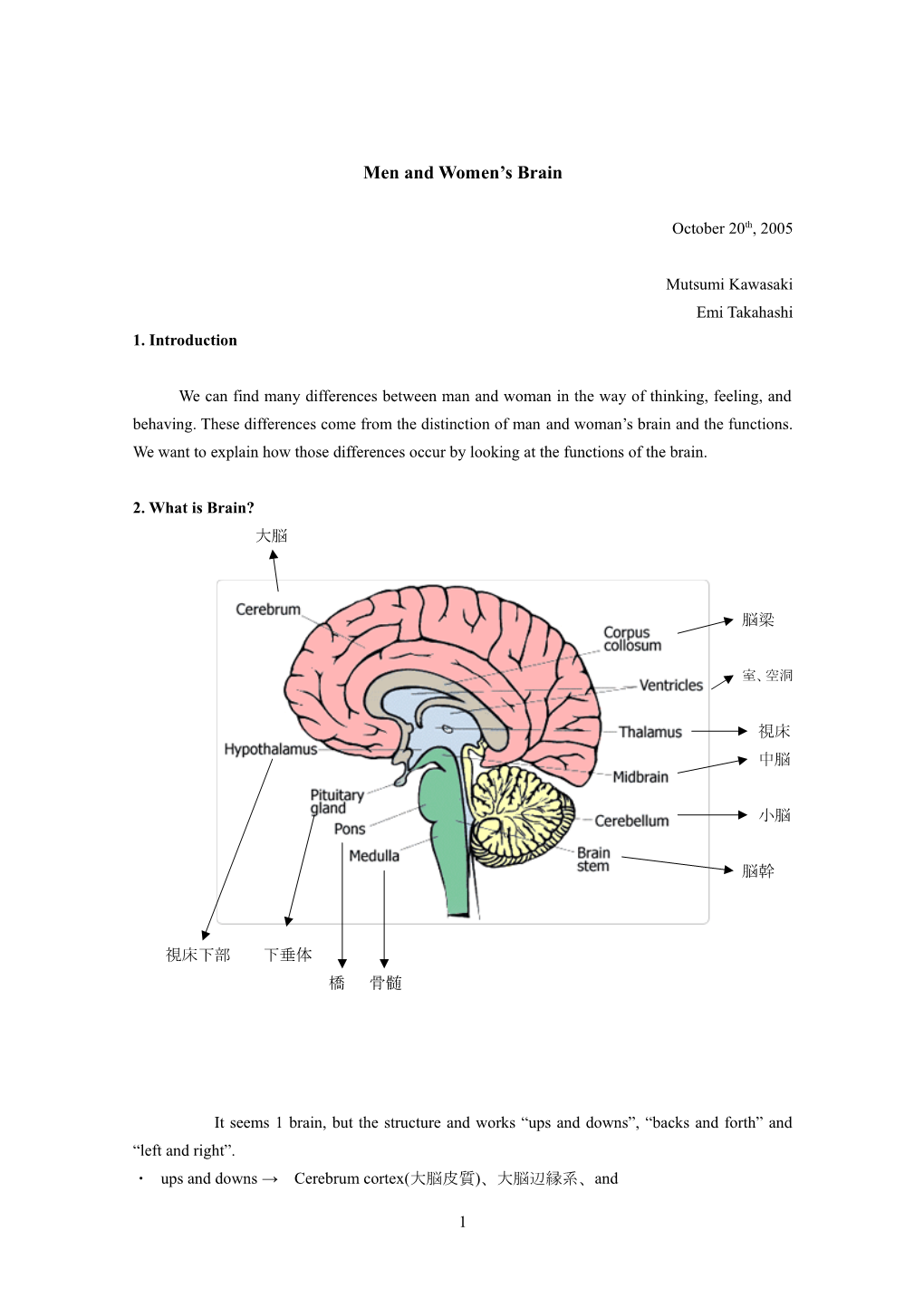
2. What is Brain? 大脳
脳梁
室、空洞
視床 中脳
小脳
脳幹
視床下部 下垂体 橋 骨髄
It seems 1 brain, but the structure and works “ups and downs”, “backs and forth” and “left and right”. ・ ups and downs → Cerebrum cortex(大脳皮質)、大脳辺縁系、and
1 Brainstem(脳幹) ・ backs and forth →Frontal lobe( 大 脳 皮 質 の 前 頭 葉 ) 、 Vertex lobe( 頭 頂 葉 ) ・ Temporal lobe(側頭葉)・後頭葉 ・ left and right →left hemispherical(左半球)、right hemispherical(右半球)
○ The division of backs and forth of brain, and the function ・ Frontal lobe works for “will, creation, thought and emotion” ・ Vertex lobe works “exercise and taste” ・ 後頭葉 works for “perception(知覚),knowledge, understanding and sight(視覚)” ・ Temporal lobe (側頭葉) works for “memory, judgment, hearing and language
○ The weight The weight of brain is about 2 % of weight and men’s is about 1350g and women’s is about 1200g.
2 3. What decides the difference between a man and woman’s brain?
There are three types of factors which show the sex of the brain: different ways of using right and left brain, works of a male hormone, and a size of corpus callosum(脳梁).
3.1 Right and Left Brain
There are some differences between man and woman’s brain through the two sides of the brain. These control the different ways of thinking.
Left Right Logical (論理的な) Random Sequential Intuitive(直感の) Rational(理性的な) Holistic(全体論の) Analytical Synthesizing(総合的な) Objective(客観的な) Subjective(主観的な) Fact-based Feeling-based
Most people have a distinct preference for one of these two styles of thinking (though some equally are adept at using both sides of the brain). Left-brain people are good at logical thinking, analysis, and accuracy. On the other hand, right-brain people are good at aesthetics ( 美 的 な),feelings and creativity.
3.2 a male hormone(男性ホルモン), ‘testosterone’
In fact, there are no differences that distinguish between man and woman in fetus ( 胎 児)body until two months of pregnancy. The fetus body is programmed to be a woman’s one if any specific instructions are not given. In other words, woman is the basic form of the human body. In the case that the fetus has a male gene, a number of male hormones which are called ‘testosterone’ are made in the body. Then, the work of the male hormones make a sex organ of a male instead of a female one. Moreover, the more male hormones are made, the more male the brain becomes, so it is possible that there is a man who has a female brain. If a male fetus do not get enough testosterone during pregnancy, he might be a gay later. Most of homosexual are men because
3 a male fetus lacks testosterone. Homosexually is determined before birth. The testosterone also influences the restraint of the left brain development. The left brain is the part which controls a language ability and count ability. Therefore, the development of a boy’s left brain will be later than a girl’s. However, the boy’s right brain that controls a power of recognition of space and figure processing ability will be more developed instead. Because of the work of the testosterone, a man is good at dealing with right-brain activities.
female testosterone male
3.3 Corpus callosum(脳梁)
The corpus callosum is the bunch of nerves(神経) that connect the right brain and left brain. Generally speaking, woman brain has a bigger corpus callosum than man’s, so two sides of the brain in woman brain are contact with each other better. In the case of women, various types of abilities such as language ability tend to spread over the whole brain while the abilities tend to be unevenly distributed in right or left brain. Therefore, if some part of the brain is injured, language ability might be lost at a burst in the male brain, but it might not in the female brain.
4. Multiple Intelligences (MI)
4.1 Howard Gardner
4 There are a lot of different types of methods that measure intelligence, and the most famous one is I.Q. (‘Intelligence Quotient’) tests. However, they do not tell us anything about the real abilities of the people, such as the ability to understand the others’ feelings. The theory of multiple intelligences (MI) was developed in 1983 by Howard Gardner, professor of education at Harvard University. He pointed out that I.Q. test cannot measure the value of one’s ability because a high I.Q. does not equate to intelligence. Gardner defined that an intelligence is a potential ability to process a certain type of information for example, information about sounds, meanings, rhythms of a word. He suggests that each individual has several intelligences, but each person has a unique combinations or profiles. In other words, one person might be more intelligent in one way and another might be more intelligent in another. We are also able to improve each of the intelligences, but some will improve more easily in one intelligence area than in others. These intelligences can be nurtured and strengthened. They are located in different areas of the brain and either work independently or together.
4.2 Nine types of intelligences
Current research shows that there are at least nine types of intelligences: linguistic intelligence, logical-mathematical intelligence, spatial intelligence, body-kinesthetic ( 運 動 感 覚 ) intelligence, musical intelligence, interpersonal intelligence, intrapersonal ( 心 の 内 部 の)intelligence, naturalist intelligence, and existential intelligence. According to Gardner, learning and teaching in the theory of multiple intelligences should be focused on the particular intelligences of each individual. For instant, if someone has strong musical intelligence, he/she should be emphasized on developing this ability.
5
Intelligence Area Definitions and Abilities Learns best through:
Linguistic well-developed verbal skills and reading, hearing and seeing sensitivity to the sounds, meaning and words, speaking, writing, rhythms of words discussing and debating. (reading, writing, telling stories, memorizing dates, thinking in words)
Logical- ability to think conceptually(概念的 working with patterns and mathematical に) and abstractly, and capacity to relationships, classifying, distinguish logical or numerical patterns categorizing, working with the (math, reasoning, logic, problem-solving, abstract. patterns)
Spatial capacity to think in images and pictures, working with pictures and to visualize accurately and abstractly colors, visualizing, drawing. (reading maps, charts, drawing, mazes, puzzles, imaging things, visualization)
Bodily- ability to control one's body movements touching, moving, processing Kinesthetic and to handle objects skillfully knowledge through bodily (athletics, dancing, acting, crafts, using sensations. tools)
Musical ability to produce and appreciate rhythm, rhythm, melody, singing, pitch and timber listening to music and melodies. singing, picking up sounds, remembering melodies, rhythms.
Interpersonal capacity to detect and respond sharing, comparing, relating, appropriately to the moods, motivations interviewing, cooperating. and desires of others (understanding people, leading, organizing, communicating, resolving conflicts, selling)
Intrapersonal capacity to be self-aware and in tune with working alone, doing self-paced
6 inner feelings, values, beliefs and projects, having space, thinking processes reflecting. (understanding self, recognizing strengths and weaknesses, setting goals)
Naturalist ability to recognize and categorize plants, working in nature, exploring animals and other objects in nature things, learning about plants and (understanding nature, making natural events. distinctions, identifying flora(植物相) and fauna(動物相))
Existential sensitivity and capacity to tackle deep Religious expression, questions about human existence, such as the meaning of life, why do we die, and how did we get here Spiritual and philosophical
5. Nature versus Nurture(Genetic versus Environment)in Intelligence
We just looked at a various types of intelligences and the issue that we need to focus on is what causes individual differences in the intelligences. A relation of genetics and environment is the major issue. Both genes and the environment decide the difference of intelligences that each people have. In addition, social factors also influence intelligences. It is difficult to define which decides the types of intelligences that relate to the individuals’ abilities nature or nurture. People may have tendencies at birth, but the possibility of directions that they can take is limitless.
5. Conclusion
We understood that the difference and ability of brain are decided before birth, and we learned
7 the functions of brain between man and woman’s brain, but we know the environment to grow up is important too. Human has various intelligences, so we should grow our each intelligence as well as we can. Nowadays, the theory that shows the differences of intelligences through the structure and function, such as right and left brain is a bit old. The most recent theory is multiple intelligences. It is limited to measure the individuals’ intelligences with I.Q. tests. Therefore, we need to focus on a various types of intelligence more.
References
Author unknown 2001.diagnosis of man & woman brain http:// www. chaoo. net/sindan/
Author unknown 2005.home science investigation http://www.kasoken.com/archires/02child/brain.php
Author unknown 2005.Seeing by brain http://www14.pll.or.jp/CMDT1Ww/nou00html
Author unknown.2005,right brain and left brain http://www.funderstanding.com/right_brain_brain.cfm
Kathryn Phillips. Date unknown. Why can’t a man be more like a woman…and versa http://www.genderweb.org/general/whycant.phtml
David Paul. 2003. Teaching English to Children in Asia. Longman
8