ME3251 Flow of Compressible Fluids Spring 2013 Dr. T. J. Barber
Problem 19: airfoil force coefficients
Using shock-expansion theory, calculate the lift and drag (coefficient) on a symmetrical diamond airfoil of semiangle = 15 at an angle of attack to the free stream of 5 when the upstream Mach number and pressure are 2.0 and 2116 lb/ft2, respectively. The maximum thickness of the airfoil is t = 0.5 ft. Assume a unit length of 1 ft in the span direction (perpendicular to the page).
Problem 20: supersonic airfoil trailing edge
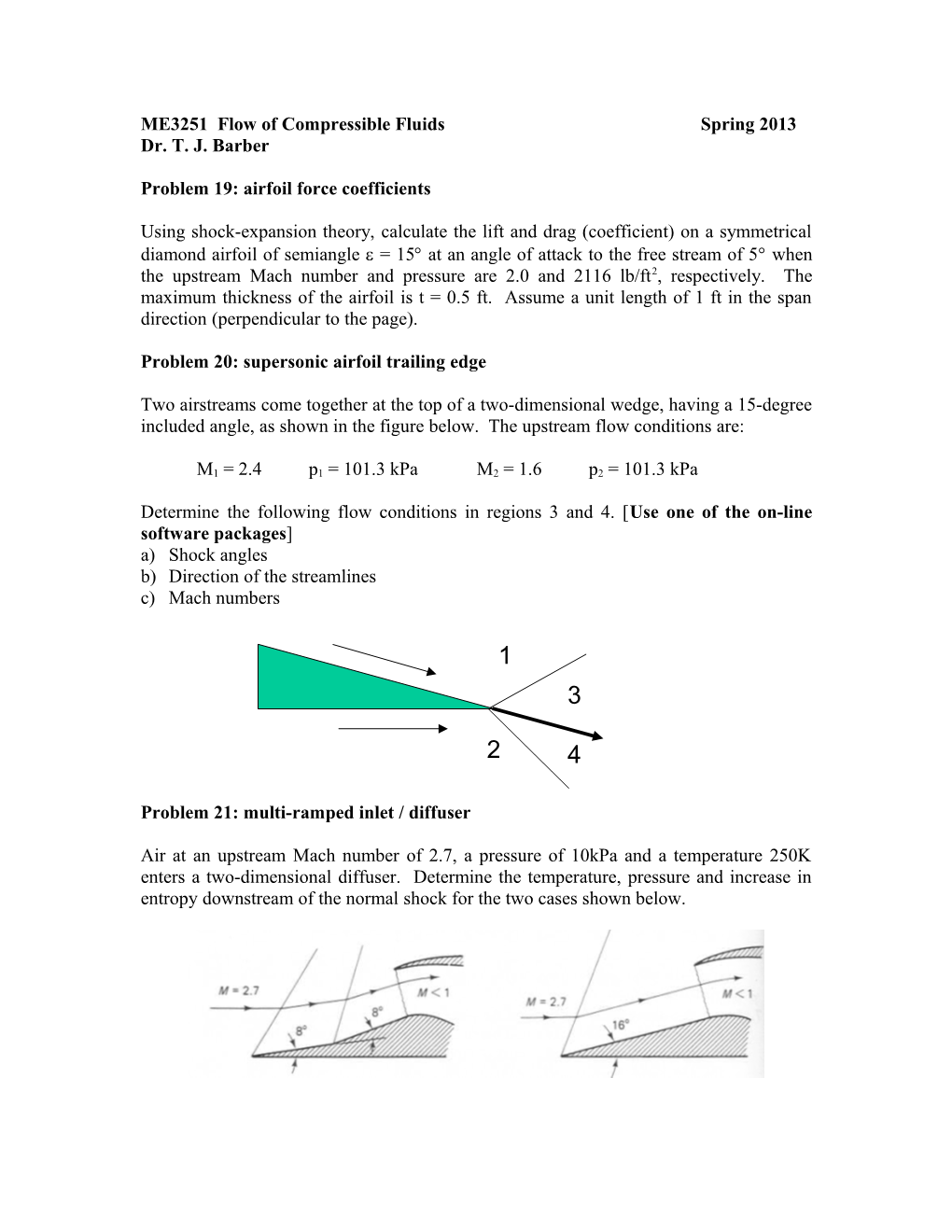
Two airstreams come together at the top of a two-dimensional wedge, having a 15-degree included angle, as shown in the figure below. The upstream flow conditions are:
M1 = 2.4 p1 = 101.3 kPa M2 = 1.6 p2 = 101.3 kPa
Determine the following flow conditions in regions 3 and 4. [Use one of the on-line software packages] a) Shock angles b) Direction of the streamlines c) Mach numbers
1 3
2 4
Problem 21: multi-ramped inlet / diffuser
Air at an upstream Mach number of 2.7, a pressure of 10kPa and a temperature 250K enters a two-dimensional diffuser. Determine the temperature, pressure and increase in entropy downstream of the normal shock for the two cases shown below.