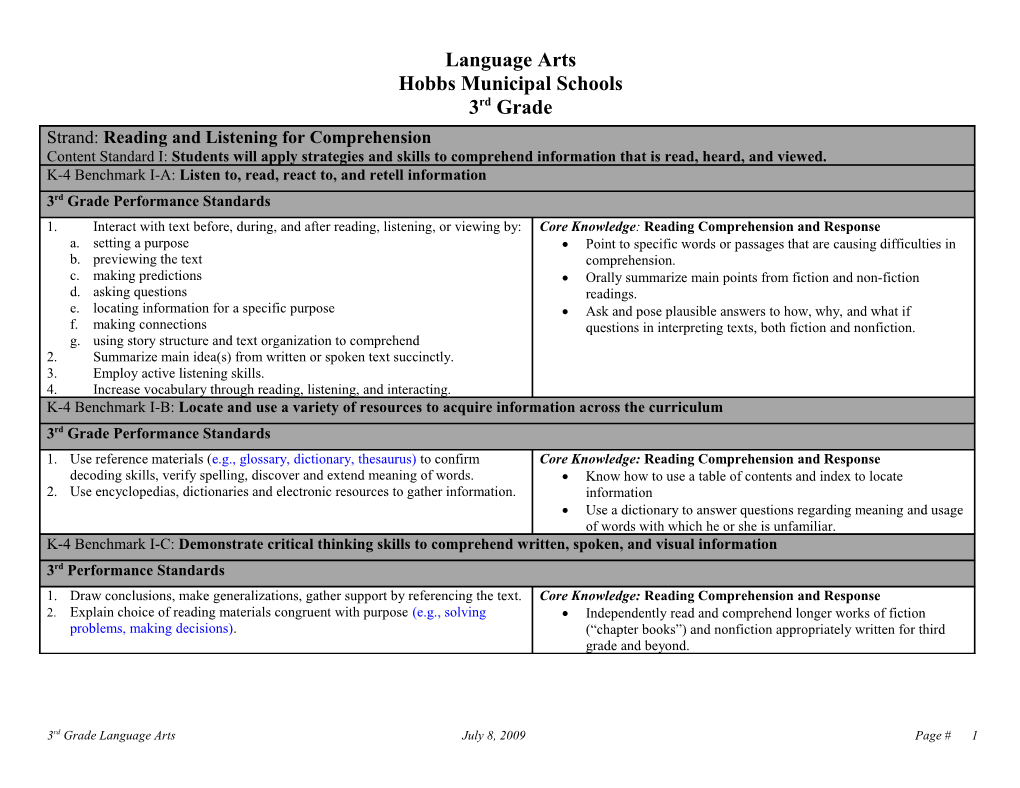
Language Arts Hobbs Municipal Schools 3rd Grade Strand: Reading and Listening for Comprehension Content Standard I: Students will apply strategies and skills to comprehend information that is read, heard, and viewed. K-4 Benchmark I-A: Listen to, read, react to, and retell information 3rd Grade Performance Standards 1. Interact with text before, during, and after reading, listening, or viewing by: Core Knowledge: Reading Comprehension and Response a. setting a purpose Point to specific words or passages that are causing difficulties in b. previewing the text comprehension. c. making predictions Orally summarize main points from fiction and non-fiction d. asking questions readings. e. locating information for a specific purpose Ask and pose plausible answers to how, why, and what if f. making connections questions in interpreting texts, both fiction and nonfiction. g. using story structure and text organization to comprehend 2. Summarize main idea(s) from written or spoken text succinctly. 3. Employ active listening skills. 4. Increase vocabulary through reading, listening, and interacting. K-4 Benchmark I-B: Locate and use a variety of resources to acquire information across the curriculum 3rd Grade Performance Standards 1. Use reference materials (e.g., glossary, dictionary, thesaurus) to confirm Core Knowledge: Reading Comprehension and Response decoding skills, verify spelling, discover and extend meaning of words. Know how to use a table of contents and index to locate 2. Use encyclopedias, dictionaries and electronic resources to gather information. information Use a dictionary to answer questions regarding meaning and usage of words with which he or she is unfamiliar. K-4 Benchmark I-C: Demonstrate critical thinking skills to comprehend written, spoken, and visual information 3rd Performance Standards 1. Draw conclusions, make generalizations, gather support by referencing the text. Core Knowledge: Reading Comprehension and Response 2. Explain choice of reading materials congruent with purpose (e.g., solving Independently read and comprehend longer works of fiction problems, making decisions). (“chapter books”) and nonfiction appropriately written for third grade and beyond.
3rd Grade Language Arts July 8, 2009 Page # 1 K-4 Benchmark I-D: Acquire reading strategies 3rd Grade Performance Standards 1. Apply phonics and structural analysis to decode words (e.g., less common Core Knowledge: Reading Comprehension and Response vowel patterns, syllable breaks). Use a dictionary to answer questions regarding meaning and usage 2. Apply context clues to decode unknown words. of words with which he or she is unfamiliar. 3. Use reference materials (e.g., glossary, dictionary, thesaurus) to confirm decoding skills, verify spelling and discover and extend meaning of words. 4. Use a variety of strategies to comprehend text (e.g., re-read, read ahead, ask for help, adjust reading speed, question, paraphrase, retell). 5. Read aloud with fluency, accuracy and comprehension when presented with a grade level passage of connected text. 6. Increase vocabulary through reading, listening and interacting. Strand: Writing and Speaking for Expression Content Standard II: Students will communicate effectively through speaking and writing. K-4 Benchmark II-A: Demonstrate competence in speaking to convey information 3rd Grade Performance Standards 1. Present information in a logical manner with a clear main point. 2. Sustain conversation on a topic. 3. Answer open-ended questions. 4. Explain own learning. 5. Read aloud with fluency and comprehension grade-level text.
3rd Grade Language Arts July 8, 2009 Page # 2 K-4 Benchmarks II-B: Apply grammatical and language conventions to communicate 3rd Grade Performance Standards 1. Use correct subject and verb agreement. Core Knowledge: Spelling, Grammar, and Usage 2. Use correct capitalization and punctuation. Spell most words correctly or with a high probable spelling, and use a 3. Use a variety of complete sentences (declarative, imperative, interrogative and dictionary to check and correct spellings about which he/she is uncertain. exclamatory) in writing and speaking. Use capital letters correctly 4. Compose two or more paragraphs with: topic sentences, supporting details, Understand what a complete sentence is, and identify subject and appropriate, logical sequence and sufficient elaboration. predicate in single-clause sentences, distinguish complete sentences from 5. Use strategies for spelling (e.g., sound patterns, visual patterns, silent letters). fragments. Identify and use different sentence types: declarative, interrogative, 6. Proofread one’s own writing for spelling and edit (with assistance) for language imperative, and exclamatory conventions and format. Know the following parts of speech and how they are used: nouns (for 7. Create readable documents with legible handwriting. concrete nouns), pronouns (singular and plural), verbs (action and helping 8. Write compositions that have few significant errors in use of pronouns, verbs), adjectives (including articles) and adverbs adjectives, adverbial forms and coordinating conjunctions. Know how to use end punctuation: period, question mark, or exclamation 9. Create and deliver recitations and presentations about familiar experiences or point interests that are organized around a coherent statement. Know how to use comma: between day and year, between city and state, 10. Demonstrate a command of standard English when speaking. in a series, after yes and no Know how to use an apostrophe: in contractions; in singular and plural possessive nouns Recognize and avoid the double negative Core Knowledge: Vocabulary Know what prefixes and suffixes are and how the following affect word meaning: o Prefixes re meaning “again”(as in reuse); un meaning “not” (as in unfriendly); dis meaning “not” (as in dishonest); un meaning “opposite of” or “reversing an action” (as in untie); dis meaning “opposite of” or “reversing an action” (as in disappear) o Suffixes er and or (as in singer, painter, actor); less (as in careless); ly (as in quickly) Know what homophones are (for example, by, buy; hole, whole) and correct usage of homophones that commonly cause problems: their, there, they’re your, you’re its, it’s here, hear to, too, two Recognize common abbreviations (for example, St., Rd., Mr., Mrs., Ms., Dr., U.S.A., ft., in, lb.)
3rd Grade Language Arts July 8, 2009 Page # 3 K-4 Benchmarks II-C: Demonstrate competence in the skills and strategies of the writing process 3rd Grade Performance Standards 1. Compose a draft that conveys major ideas and maintains focus on the topic by Core Knowledge: Writing using preliminary plans. Produce a variety of types of writing – such as stories, reports, poems, 2. Compose a variety of fiction, nonfiction, poetry, and drama selections using letters, descriptions – and make reasonable judgments about what to self-selected topics and multimedia forms (e.g., poems, simple narratives, short include in his/her own written words based on the purpose and type of reports, learning logs, letters, notes, directions, instructions). composition. 3. Suggest and implement reflection and revision (with assistance) on target Know how to gather information from basic print sources, and write a short report presenting the information in his/her own words. elements by: Know how to use established conventions when writing a friendly letter, a. clarifying ideas, adding descriptive words and phrases, heading, salutation (greeting), closing, and signature. b. sequencing events and ideas, Produce written work with a beginning, middle, and end c. combining short, related sentences, and Organize material in paragraphs and understand: how to use a topic d. strengthening word choice. sentence, how to develop a paragraph with examples and details, and that 4. Begin to incorporate literary words and language patterns in writing (e.g., each new paragraph is indented elaborate descriptions, use figurative wording). In some writings, proceed with guidance through a process of gathering 5. Combine information from multiple sources, using technology as a tool in information, organizing thoughts, composing a draft, revising to clarify writing reports and stories. and refine his/her meaning, proofreading with attention to spelling, 6. Write stories and essays that show an awareness of an intended audience and mechanics, and presentation of a final draft. purpose. Strand: Literature and Media Content Standard III: Students will use literature and media to develop an understanding of people, societies, and the self. K-4 Benchmarks III-A: Use language, literature, and media to gain and demonstrate awareness of cultures around the world 3rd Grade Performance Standards 1. Use language and media to make connections between own experiences and the Core Knowledge: Sayings and Phrases experiences of others (e.g., local stories, stories about local culture and history). Actions speak louder than words 2. Create and participate in responses to a variety of literature and media (e.g., His bark is worse than his bite. dramatizations, presentations, fantasy plays). Beat around the bush 3. Identify and discuss similarities and differences in events and characters across Beggars can’t be choosers. examples of literature and media. Clean bill of health 4. Make informed judgments about the purpose of media productions. Cold shoulder A feather in your cap Last straw Let bygones be bygones One rotten apple spoils the whole barrel. On its last legs Rule the roost The show must go on. Touch and go When in Rome do as the Romans do. 3rd Grade Language Arts July 8, 2009 Page # 4 K-4 Benchmarks III-B: Identify and use the types of literature according to their purpose and function 3rd Grade Performance Standards 1. Read and create a variety of texts, including: fiction (short stories, novels, Core Knowledge: Literary Terms fantasies, fairy tales and fables), non-fiction (biographies, letters, articles, biography and autobiography essays), poetry and drama (skits and plays). fiction and nonfiction 2. Respond to fiction, non-fiction, poetry and drama using interpretive, critical and Core Knowledge: Poetry evaluative processes by: Adventures of Isabel (Ogden Nash) a. considering the differences among genres, The Bee (Isaac Watts) b. relating plots, settings and characters to one’s own experiences and ideas, By Myself (Eloise Greenfield) c. considering the main character’s point of view; participating in creative Catch a Little Rhyme (Eve Merriam) interpretations; and The Crocodile (Lewis Carroll) d. making inferences and drawing conclusions about characters and events. Dream Variation (Langston Hughes) Eletelephony (Laura Richards) Father William (Lewis Carroll) First Thanksgiving of All (Nancy Byrd Turner) For want of a nail, the shoe was lost …(traditional) Jimmy Jet and His TV Set (Shel Silverstein) Knoxville, Tennessee (Nikki Giovanni) Trees (Sergeant Joyce Kilmer) Core Knowledge: Fiction Alice in Wonderland (Lewis Carroll) from The Arabian Nights: Aladdin and the Wonderful Lamp and Ali Baba and the Forty Thieves The Hunting of the Great Bear (an Iroquois legend about the origin of the Big Dipper) The Husband Who Was to Mind the House (a Norse/English folk tale, also known as “Gone is Gone”) The Little Match Girl (Hans Christian Anderson) The People Who Could Fly (An African American folk tale) Three Words of Wisdom (a folk tale from Mexico) William Tell Selections from The Wind in the Willows: “The River Bank” and “The Open Road” (Kenneth Grahame) Core Knowledge: Myths and Mythical Characters Norse Mythology: Asgard (home of the gods), Valhalla, Hel (underworld), Odin, Thor, trolls, Norse gods and English names for the days of the week: Tyr, Odin (Wodin), Thor, Freya Core Knowledge: More Myths and Legends of Ancient Greece and Rome Jason and the Golden Fleece; Perseus and Medusa; Cupid and Psyche; The Sword of Damocles; Damon and Pythias; Androcles and the Lion; Horatius at the Bridge
3rd Grade Language Arts July 8, 2009 Page # 5