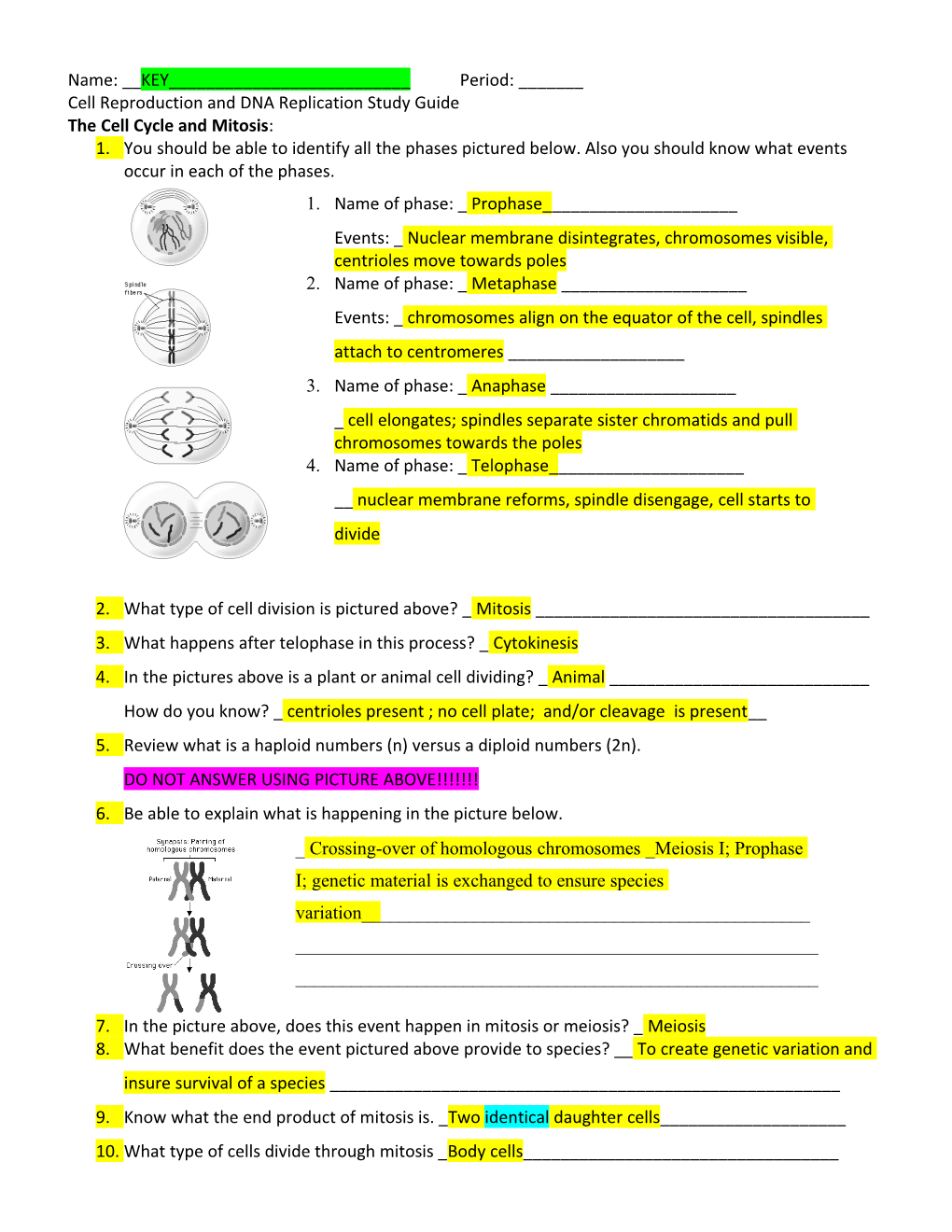
Name: __KEY______Period: ______Cell Reproduction and DNA Replication Study Guide The Cell Cycle and Mitosis: 1. You should be able to identify all the phases pictured below. Also you should know what events occur in each of the phases. 1. Name of phase: _ Prophase______Events: _ Nuclear membrane disintegrates, chromosomes visible, centrioles move towards poles 2. Name of phase: _ Metaphase ______Events: _ chromosomes align on the equator of the cell, spindles attach to centromeres ______3. Name of phase: _ Anaphase ______cell elongates; spindles separate sister chromatids and pull chromosomes towards the poles 4. Name of phase: _ Telophase______nuclear membrane reforms, spindle disengage, cell starts to divide
2. What type of cell division is pictured above? _ Mitosis ______3. What happens after telophase in this process? _ Cytokinesis 4. In the pictures above is a plant or animal cell dividing? _ Animal ______How do you know? _ centrioles present ; no cell plate; and/or cleavage is present__ 5. Review what is a haploid numbers (n) versus a diploid numbers (2n). DO NOT ANSWER USING PICTURE ABOVE!!!!!!! 6. Be able to explain what is happening in the picture below. _ Crossing-over of homologous chromosomes _Meiosis I; Prophase I; genetic material is exchanged to ensure species variation______7. In the picture above, does this event happen in mitosis or meiosis? _ Meiosis 8. What benefit does the event pictured above provide to species? __ To create genetic variation and insure survival of a species ______9. Know what the end product of mitosis is. _Two identical daughter cells______10. What type of cells divide through mitosis _Body cells______11. Know what the end product of meiosis is _ four gamete cells ______12. What type of cells divide through meiosis_sex cells______13. Know what A and B represent in the picture below.
_ B. ___ centromere_
A. __ sister chromatid ______14. Pictured below is the cell cycle. You should know the names of phases A, B, C, and D. Also what happens in each phase, especially the 5 sub-phases in phase D. Also know the name given to phases A, B, and C combined.
a. Name of each phase:
A: _ G1 phase ______C: _ G2 phase ______B: _ S phase ______D: _ M phase ______b. 5 sub-phases of phase D: 1. _ Prophase ______4. _ Telophase ______2. _ Metaphase ______5. _ Cytokinesis ______3. _ Anaphase ______c. Name given to phases A, B, and C combined: _ Interphase ______d. What type of cell division occurs during phase D of the cell cycle? _ Mitosis 15. Know the four phases of mitosis and briefly state the events of each phase. a. _ Prophase: Nuclear membrane disintegrates, chromosomes visible, centrioles move towards poles b. _ Metaphase: chromosomes align on the equator of the cell, spindles attach to centromeres c. _ Anaphase: cell elongates; spindles separate sister chromatids and pull chromosomes towards the poles d. _ Telophase: nuclear membrane reforms, spindle disengage, cell starts to divide 16. What happens during cytokinesis? __ Division of the cytoplasm; cell divides______17. Know the similarities and differences between mitosis and meiosis. Similarities: __Phases called PMAT; Cells and cytoplasm divide through cytokinesis Differences: _ Mitosis:_ one diploid cell becomes two diploid cells; cell divides once; body cells ___Meiosis: one diploid cell becomes four haploid cells; cell divides twice; sex cells______18. Know all the phases of Meiosis I and Meiosis II in order, begin with Interphase and end with Cytokinesis. Know the events that occur in each phase. a. Interphase: _Cell grows; DNA replicates; cell prepares to divide; organelles divide______b. Prophase I: Chromosome condense; Nuclear envelop breaks down; Centrioles move to opposite poles; _ Spindle begins to form ; Homologous chromosomes pair up (unique to prophase I)- process called synapsis; Sections of the chromosomes are exchanged or go through crossing-over c. Metaphase I: Spindle fibers attach to the paired homologous chromosomes ; Paired homologous chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell______d. Anaphase I: Spindle fibers shorten ; Chromosomes of each homologous pair start to separate from each other; Chromosomes move to opposite poles e. Telophase I: _ Spindle breaks down; New nuclear membranes form f. _Cytokinesis I: Cytoplasm divides, and two haploid daughter cells result in four haploid cells; Each cell has a unique combination of chromosomes ; Daughter cells go on to meiosis II ______g. _Prophase II: Nuclear envelope breaks down ; Spindle begins to form in each haploid daughter cell from meiosis I ; Centrioles also start to separate h. _Metaphase II: _ Spindle fibers line up the sister chromatids; Each chromosome along the equator of the cell.______i. _Anaphase II: Sister chromatids separate ; _ Move to opposite poles j. _Telophase II: Spindles break down;_New nuclear membranes forms______k. Cytokinesis II: _ Division of the cytoplasm; cell divides Four haploid cells result; Each cell has a unique combination of chromosomes 19. When cells lose their ability to control their growth rate what condition/disease could possibly develop? _cancer______20. What regulates cell division? _ protein cyclins ______Cell Reproduction and DNA Replication: 1. The Structure of DNA a. What three parts make up a nucleotide? Phosphate group; 5-C sugar (deoxyribose); and a nitrogenous base (A,T,C, G)_ b. How many nitrogenous bases are there? What are they called? _Four : Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine _ c. What is the backbone of DNA composed of?_Phosphate group and 5-C sugar_ d. What types of bonds hold together the nitrogenous bases? _Hydrogen bonds______e. What types of bonds hold together the backbone to the bases? _Covalent bonds____
2. Which nitrogenous bases have two-rings and what are they called? _Adenine and Guanine; purines______3. Which have one-ring and what are they called? _Thymine and Cytosine; pyrimidines_____
4. What did Edwin Chargaff discover? _ concentration of adenine was always about the same as the concentration of thymine; concentrations of guanine and cytosine always about the same.______5. What did this discovery lead to the establishment of? _ Chargaff’s rules; A pairs with T and G pairs with C. ______
6. Who discovered the shape of a DNA molecule? _ James Watson and Francis Crick ______7. In what year did they make their discovery? _ April, 1953______8. What is the process called that allows DNA to duplicate itself? _ DNA Replication_____ 9. Why does replication need to occur? _ So that each new cell gets a copy of all the instructions that it needs to carry out life processes__ 10. What are the results at the end of DNA replication? _ two daughter molecules that contain one strand from the parent molecule and one new complementary strand; two daughter molecules identical (mirror images) to the parent molecule. ______
11. Where does DNA replicate itself in prokaryotes? And how does it happen? _In the cytoplasm; starts at on spot and continues in two direction until the entire molecule is replicated______12. Where does DNA replicate itself in eukaryotes? And how does it happen? _In the nucleus; happens at hundreds of places at the same time because molecule is so large and continues until entire molecule is replicated______13. Explain what happens when DNA replicates, be sure to include the enzymes used and the type of bonds that are broken. DNA helicase unwinds & unzips the DNA molecule; DNA polymerase copies the bases from each original strand of the DNA that acts as a template until the entire molecule is replicated; then the molecule is rewound and you have two new molecules each with one original strand and one new strand______Meiosis and Cell Reproduction: 1. What major advantage does sexual reproduction give an organism over asexual reproduction? provides genetic diversity 2. What happens if non-disjunction occurs? Some gametes may have an extra copy of some genes. 3. Explain how cytokinesis is different between animal and plant cells.
In animal cells, the plasma membrane of the parent cell pinches inward along the cell’s equator until two daughter cells form. In plant cells, a cell plate forms along the equator of the parent cell. Then, a new plasma membrane and cell wall form along each side of the cell plate. 4. Know what happens to chromosome numbers in all the phases of meiosis. A. Begins with Four chromosomes B. Four original with replicated chromatids =8 chromatids C. Same as ‘B’ D. Now two in each cell with their replicated chromatids= 4 chromatids E. Same as ‘D’ F. Sister chromatids splitting G. Two chromatids in each cell
5. A laboratory technique called polymerase chain reaction (PCR) produces millions of copies of a DNA molecule in only a few hours. PCR is most similar to which of the following cellular processes? A. mitosis B. replication C. transcription D. translocation