Boid Example Continued, and Lists
Move to Centroid
Let’s start by implementing the centroid concept. The idea is fairly simple – each boid can see some distance away and wants to be close to the center of other boids. For simplicity, let’s make the visible distance of a boid a circle with the boid at the center (yes, this would mean it can see behind itself). For now, we’ll just make this a constant at the top of our form, where the constant represents the radius of a circle, specified in pixels, within which the boid can see: private const int BOID_VISION_RADIUS = 100; // Radius for a boid's vision
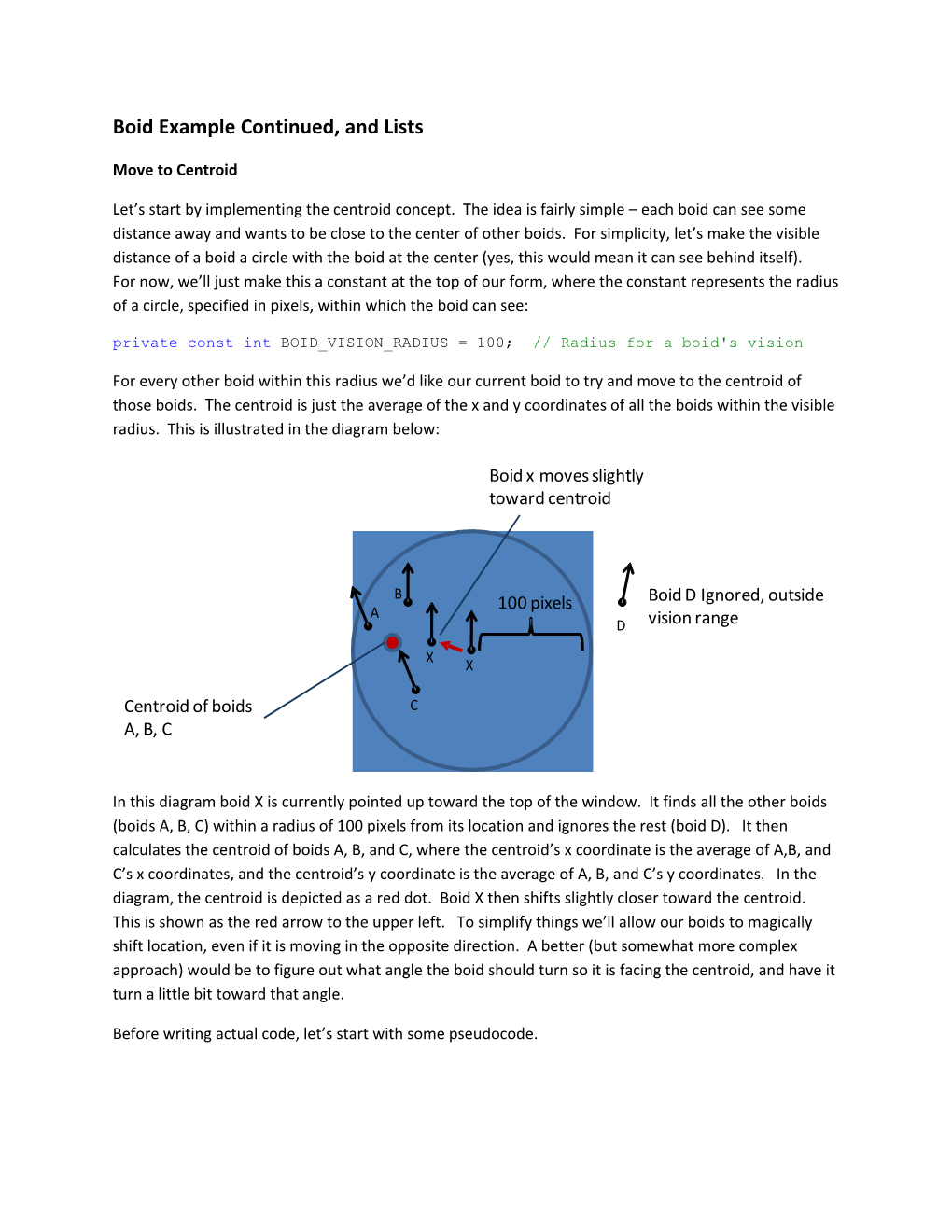
For every other boid within this radius we’d like our current boid to try and move to the centroid of those boids. The centroid is just the average of the x and y coordinates of all the boids within the visible radius. This is illustrated in the diagram below:
Boid x moves slightly toward centroid
B 100 pixels Boid D Ignored, outside A D vision range
X X
Centroid of boids C A, B, C
In this diagram boid X is currently pointed up toward the top of the window. It finds all the other boids (boids A, B, C) within a radius of 100 pixels from its location and ignores the rest (boid D). It then calculates the centroid of boids A, B, and C, where the centroid’s x coordinate is the average of A,B, and C’s x coordinates, and the centroid’s y coordinate is the average of A, B, and C’s y coordinates. In the diagram, the centroid is depicted as a red dot. Boid X then shifts slightly closer toward the centroid. This is shown as the red arrow to the upper left. To simplify things we’ll allow our boids to magically shift location, even if it is moving in the opposite direction. A better (but somewhat more complex approach) would be to figure out what angle the boid should turn so it is facing the centroid, and have it turn a little bit toward that angle.
Before writing actual code, let’s start with some pseudocode. To calculate the centroid for the boid b:
x1 = X coordinate of boid b y1 = Y coordinate of boid b
totalX = 0 totalY = 0 numCloseBoids = 0
For each boid i in the array of boids if (i != b) then x2 = X coordinate of boid i y2 = Y coordinate of boid i if the distance from (x1,y1) to (x2,y2) < BOID_VISION_RADIUS totalX = totalX + x2 totalY = totalY + y2 numCloseBoids++ End If End if Next centroidX = totalX / NumBoids centroidY = totalY / NumBoids
To calculate the distance from (x,y) to (x2,y2) we can make a function that returns:
2 x x22 y y2
Here it is in actual code:
// A helper function to calculate the distance between two points private double distance(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) { return Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(x1-x2,2) + Math.Pow(y1-y2,2)); }
// Calculate the centroid of other boids close to boid b private void Centroid(int b) { int x1, y1, x2, y2; // x1,y1 = coordinate of boid b // x2,y2 = coordinate of target boid in array int totalX = 0, totalY = 0; // Total of coordinates for centroid
x1 = Xs[b]; // Set to coordinates of boid b y1 = Ys[b]; // Loop through every boid's coordinates // to calculate centroid int boidsSeen = 0; for (int i = 0; i < NUMBOIDS; i++) { // Don't include boid b in centroid calculations if (i != b) { x2 = Xs[i]; y2 = Ys[i]; // Check if target boid is visible if (distance(x1, y1, x2, y2) < BOID_VISION_RADIUS) { totalX += x2; totalY += y2; boidsSeen++; } } } // Do nothing if no boids in sight if (boidsSeen == 0) { return; }
// Calculate coordinates of the centroid int centroidX = totalX / boidsSeen; int centroidY = totalY / boidsSeen;
// Do nothing if we're already at the centroid if ((centroidX == x1) && (centroidY == y1)) { return; }
// More code will go here to move the boid }
This code calculates the centroid’s X and Y coordinate, so now we need to move the boid toward that location. As mentioned earlier, ideally we’d change the boid’s heading so it would be going toward the centroid, but to keep things simple we’ll just “transport” the boid a few pixels so that its closer to the centroid:
// Move 2% of the way toward centroid, // or not at all if within 50 pixels of the centroid double deltaX = (centroidX - x1) / 50.0; double deltaY = (centroidY - y1) / 50.0; Xs[b] += Convert.ToInt32(deltaX); Ys[b] += Convert.ToInt32(deltaY);
This code would be placed at the end of the Centroid() method. It computes the X and Y distance away from the centroid, then moves it 1/50th of the way, or 2%, of the way there. I’ve used a small number so the boid doesn’t look like it suddenly jumps to a new location in space. Note that there is no change if the centroid is within 50 pixels of the boid, due to the integer conversion.
Lastly, we should update the heading toward the centroid for every boid before we draw it. This can be done by simply adding a call to Centroid in the timer:
// When the timer goes off, update the location of each boid private void timer1_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e) { for (int i = 0; i < NUMBOIDS; i++) { // Centroid rule New Centroid(i); Code // Set the location of the boid to a new spot moving at // speed BOID_VELOCITY Xs[i] += Convert.ToInt32(Math.Cos(Dirs[i]) * BOID_VELOCITY); Ys[i] += Convert.ToInt32(Math.Sin(Dirs[i]) * BOID_VELOCITY); // Check for going off the edge of the screen // and wrap around to the other side if (Xs[i] > pboxWorld.Width) { Xs[i] = Xs[i] - pboxWorld.Width; } if (Xs[i] < 0) { Xs[i] = pboxWorld.Width + Xs[i]; } if (Ys[i] > pboxWorld.Height) { Ys[i] = Ys[i] - pboxWorld.Height; } if (Ys[i] < 0) { Ys[i] = pboxWorld.Height + Ys[i]; } }
// Invalidate the picturebox so it calls the paint subroutine // and re-draws the boid in the new location pboxWorld.Invalidate(); }
Upon running the program the boids that are going in close to the same direction should now be somewhat aligned as the centroid draws them closer to each other. Note that at this point the boids can’t change direction, so we only see grouping for the boids going the same direction. Move away from neighbor that’s too close
Whew, we’ve written a fair bit of code, but the good news is that we can reuse a lot of it to implement the final two rules. To counteract the rule of moving toward the centroid, we can add a new rule that we don’t like to be too close to another boid. It might result in a collision (although we don’t detect one) and invades a boid’s personal space.
Let’s add a simple rule that we find the distance to the closest boid. If that distance is less than some threshold, say 30 pixels, then the boid should move a short distance in the OPPOSITE direction. To do this we need to find the coordinates of the closest boid. Here is pseudocode to find the boid closest to boid b:
x1 = X coordinate of boid b y1 = Y coordinate of boid b
closestDistanceOtherBoid = Some big number
For each boid i in the array of boids if (i != b) then x2 = X coordinate of boid i y2 = Y coordinate of boid i if the distance from (x1,y1) to (x2,y2) < closestDistanceOtherBoid then closestX = x2 closestY = y2 closestDistanceOtherBoid = distance from (x1, y1) to (x2, y2) End If End if Next
Return if (closestX = x1 and closestY = y1) // If closest is on top of you, do nothing
// closestX and closestY are the coordinates of the closest boid so now check if // it’s within the repel distance
if (closestDistanceOtherBoid < BOID_REPEL_DISTANCE) move away from (closestX, closestY) You might recognize that the code is fairly similar to calculating the centroid, but instead we remember the coordinates and distance of the closest boid (as long as it’s at least within the boid’s vision). Here is working code. First let’s define another constant, BOID_REPEL_DISTANCE, set to 30:
private const int BOID_REPEL_DISTANCE = 30; // Move away if closer
The method to find the closest boid’s coordinates is below:
// Find the closest boid to boid b and move away if it's too close private void Repel(int b) { int x1, y1, x2, y2; // x1,y1 = coordinate of boid b // x2,y2 = coordinate of target boid in array int closestX = -1, closestY = -1; // Coords of closest boid, // -1 initially for no boid int closestDistance = 99999; // Initially, nothing is close
x1 = Xs[b]; // Set to coordinates of boid b y1 = Ys[b]; // Loop through every boid's coordinates // to find closest for (int i = 0; i < NUMBOIDS; i++) { // Don't include boid b if (i != b) { x2 = Xs[i]; y2 = Ys[i]; // Check if target boid is visible if (distance(x1, y1, x2, y2) < closestDistance) { // Remember distance and coordinates of closest one closestDistance = Convert.ToInt32(distance(x1, y1, x2, y2)); closestX = x2; closestY = y2; } } } // Do nothing if closest boid is on top of you, // we'll be moving off in some direction anyway if ((closestX == x1) && (closestY == y1)) { return; }
// Move away from closest if it's too close if (closestDistance <= BOID_REPEL_DISTANCE) { // Move 10% away from the too-close boid double deltaX = (x1 - closestX) / 10.0; double deltaY = (y1 - closestY) / 10.0; Xs[b] += Convert.ToInt32(deltaX); Ys[b] += Convert.ToInt32(deltaY); } }
Note that we compute (x1 – closestX) and (y1 – closestY) whereas with the centroid we calculated (centroidX – x1) and (centroidY - y1). This time we’re reversing the subtraction so we add on a value that moves us away from (closestX, closestY). The last step is to add a call to Repel(i) into the timer:
for (int i = 0; i < NUMBOIDS; i++) { // Centroid rule Centroid(i); // Repulse rule Repel(i);
Running the new version will make the boids scatter when they get too close.
Move in the same direction as our neighbors
It’s sometimes good to go with the flow, so our final rule is to influence each boid to move in the same direction as its neighbors. To implement this we just calculate the average direction of all other boids within the vision radius, then make our boid move a little bit toward that average direction.
Pseudocode for boid i:
x1 = X coordinate of boid b y1 = Y coordinate of boid b
totalDir = 0 numCloseBoids = 0
For each boid i in the array of boids if (i != b) then x2 = X coordinate of boid i y2 = Y coordinate of boid i if the distance from (x1,y1) to (x2,y2) < BOID_VISION_RADIUS totalDir += Direction of Boid i numCloseBoids++ End If End if Next If numCloseBoids = 0 return ' No nearby boids averageDir = totalDir / numCloseBoids Here is the corresponding code to calculate the average direction for the boids in sight:
// Align boid b in the same direction as nearby boids private void Alignment(int b) { int x1, y1, x2, y2; // x1,y1 = coordinate of boid b // x2,y2 = coordinate of target boid in array double totalDir = 0; // total of dir's for nearby boids double aveDir;
x1 = Xs[b]; // Set to coordinates of boid b y1 = Ys[b]; // Loop through every boid int boidsSeen = 0; for (int i = 0; i < NUMBOIDS; i++) { // Don't include boid b in alignment calculations if (i != b) { x2 = Xs[i]; y2 = Ys[i]; // Check if target boid is visible if (distance(x1, y1, x2, y2) < BOID_VISION_RADIUS) { totalDir += Dirs[i]; boidsSeen++; } } } // Do nothing if no boids in sight if (boidsSeen == 0) { return; } // Calculate average aveDir = totalDir / boidsSeen;
// Will add more code here to change // directions toward the average direction }
Now that we have an angle representing the average direction, we have to figure out which way our boid should turn, toward the left (subtract) or to the right (add). We should turn in a direction that gets us to the centroid more quickly. Unfortunately, it’s not as simple as adding if the average direction is bigger, and subtracting if the average angle is smaller. Here are two scenarios: Average heading, 7/4 or 315 degrees
Θ1 = |7/4 - /4| = 6/4 = 3/2
Θ2 = 2 - Θ1
Our heading, /4 or 45 degrees
We should subtract from our heading to move closer to the average since Θ2 is smaller than Θ1
Rule:
If our heading is smaller than the target heading then if Θ1 < Θ2 then subtract else add
Our heading, 7/4 or 315 degrees
Θ1 = |7/4 - /4| = 6/4 = 3/2
Θ2 = 2 - Θ1
Average heading, /4 or 45 degrees
We should add to our heading to move closer to the average since Θ2 is smaller than Θ1
Rule:
If our heading is greater than the target heading then if Θ1 > Θ2 then add else subtract Here are the rules combined together:
If our heading <= target heading theta1 = target heading – our heading theta2 = 2*PI - theta1 if theta1 > theta2 then Subtract from our heading Else Add to our heading Else // Our heading > target heading theta1 = target heading – our heading theta2 = 2*PI – theta1 if theta1 > theta2 then Add to our heading Else Subtract from our heading
For now, let’s just say that a boid is able to change directions at a rate of /64 (set in the constant BOID_TURN_RADIUS) so we’ll add or subtract that much every time. For example, it wouldn’t be very realistic to allow a boid to suddenly change directions by , or 180 degrees. private const double BOID_TURN_RADIUS = Math.PI / 64; // Max Turn Amount
Here is the pseudocode turned into a method:
// Return how many radians we should turn to get closer // to the target heading private double calcTurnAmount(double curHeading, double targetHeading) { double theta1, theta2; double turnAmount;
if (curHeading <= targetHeading) { theta1 = targetHeading - curHeading; theta2 = 2 * Math.PI - theta1; if (theta1 > theta2) { turnAmount = -1 * BOID_TURN_RADIUS; } else { turnAmount = BOID_TURN_RADIUS; } } else { theta1 = curHeading - targetHeading; theta2 = 2 * Math.PI - theta1; if (theta1 > theta2) { turnAmount = BOID_TURN_RADIUS; } else { turnAmount = -1 * BOID_TURN_RADIUS; } } return turnAmount; }
Now we should invoke our calcTurnAmount method from the Alignment method:
// Calculate average aveDir = totalDir / boidsSeen;
// Move toward the average double myHeading = Dirs[b]; // Current heading of b myHeading += calcTurnAmount(myHeading, aveDir);
// Save new direction back into array, // ensure range no more than 2PI Dirs[b] = myHeading % (2 * Math.PI); }
And finally, invoke Alignment from the Timer Tick:
for (int i = 0; i < NUMBOIDS; i++) { // Centroid rule Centroid(i); // Repulse rule Repel(i); // Alignment rule Alignment(i);
We now get nicely aligned flocks/schools of boids! We can experiment a little by varying some of the constants. For example, a smaller vision radius of 30 and a larger turn radius of /16 gives us more insect-like swarms.
We can increase the turn radius, but if we increase it too much we get un-natural turning because the boids will overshoot the target. For example, if the boid only wants to turn /32 degrees, but BOID_TURN_RADIUS is set to /8 degrees, then it is always forced to turn /8 degrees. We can correct this by allowing the boid to move to the exact heading if it’s within the turning radius:
// Returns the minimum of two numbers passed in private double min(double num1, double num2) { if (num1 < num2) { return num1; } else { return num2; } }
private double calcTurnAmount(double curHeading, double targetHeading) { double theta1, theta2; double turnAmount;
if (curHeading <= targetHeading) { theta1 = targetHeading - curHeading; theta2 = 2 * Math.PI - theta1; if (theta1 > theta2) { turnAmount = -1 * min(BOID_TURN_RADIUS, theta2); } else { turnAmount = min(BOID_TURN_RADIUS, theta1); } } else { theta1 = curHeading - targetHeading; theta2 = 2 * Math.PI - theta1; if (theta1 > theta2) { turnAmount = min(BOID_TURN_RADIUS, theta2); } else { turnAmount = -1 * min(BOID_TURN_RADIUS, theta1); } } return turnAmount; }
Running the program now results in much smoother behavior as boids fall in line behind one another. In fact it gets a little boring quickly as all the boids eventually adopt the same alignment as everyone else. We could throw in some random factors or obstacles to shake things up.
There’s one last enhancement to make, and that is to add buttons to start/stop the animation, and trackbar controls to change the constants we added for the Boid’s VISION_RADIUS, TURN_RADIUS, and REPEL_DISTANCE.
Here are the controls on the form:
Here are the control’s initial values: tbRepelDistance: Minimum = 1 Maximum = 100 TickFrequency = 10 Value = 30 tbTurnRadius: Minimum = 1 Maximum = 64 TickFrequency = 10 Value = 16 tbVisionRadius Minimum = 1 Maximum = 400 TickFrequency = 20 Value = 150 For the buttons we just enable or disable the timer:
private void btnGo_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { timer1.Enabled = true; }
private void btnStop_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { timer1.Enabled = false; }
We don’t need to add any events for the sliders, but we should use their values in place of the constants. In calcTurnAmount we (Math.Pi / tbTurnRadius.Value) instead of the constant BOID_TURN_RADIUS:
private double calcTurnAmount(double curHeading, double targetHeading) { double theta1, theta2; double turnAmount;
if (curHeading <= targetHeading) { theta1 = targetHeading - curHeading; theta2 = 2 * Math.PI - theta1; if (theta1 > theta2) { turnAmount = -1 * min(Math.PI / tbTurnRadius.Value, theta2); } else { turnAmount = min(Math.PI / tbTurnRadius.Value, theta1); } } else { theta1 = curHeading - targetHeading; theta2 = 2 * Math.PI - theta1; if (theta1 > theta2) { turnAmount = min(Math.PI / tbTurnRadius.Value, theta2); } else { turnAmount = -1 * min(Math.PI / tbTurnRadius.Value, theta1); } } return turnAmount; }
In Alignment and Centroid, replace BOID_VISION_RADIUS with tbVisionRadius.Value: if (distance(x1, y1, x2, y2) < tbVisionRadius.Value)
In Repel, replace BOID_REPEL_DISTANCE with tbRepelDistance.Value:
if (closestDistance <= tbRepelDistance.Value)
We can now fiddle with these parameters and watch the results unfold! It is also easy to change the number of boids by recompiling with a different number for NUMBOIDS. Too many boids will make the program to slower, though (there are however many ways to make it run faster).
There are a lot of other enhancements we could make. Just a couple are listed here:
Rewrite as an object-oriented program, with objects for boids, object for the world
Add variable velocities instead of constant velocity
Add collision detection, physical obstacles
Action of wind or current
Tendency to a particular place, e.g. nest or food
Perching
Predator and scattering of prey
Lists
The List object behaves like a dynamic array. We can add and remove from it at will, and also delete items at specific locations. This can be useful when you don’t know how many items will be processed in your array and you can then use a List instead. The textbook doesn’t discuss Lists, but it does discuss an older (and similar) object called the ArrayList. The List object is pretty straightforward to use if you understand arrays. Lists are just a simpler version of a Collection (The collection allows you to index values with different keys, while the list forces you to index values with a key identical to the value).
The following code sample illustrates the usage:
List
stringList.Add("foo"); stringList.Add("bar"); stringList.Add("zot"); stringList.Add("bah");
Console.WriteLine("Size of List: " + stringList.Count); Console.WriteLine("Contents:"); for (int i = 0; i < stringList.Count; i++) { Console.WriteLine("At index " + i + " Value=" + stringList[i]); } stringList.Remove("bar"); Console.WriteLine("Contents after remove bar:"); for (int i = 0; i < stringList.Count; i++) { Console.WriteLine("At index " + i + " Value=" + stringList[i]); } stringList.RemoveAt(0); Console.WriteLine("Contents after remove:"); for (int i = 0; i < stringList.Count; i++) { Console.WriteLine("At index " + i + " Value=" + stringList[i]); }
Output:
Size of List: 4 Contents: At index 0 Value=foo At index 1 Value=bar At index 2 Value=zot At index 3 Value=bah
Contents after remove bar: At index 0 Value=foo At index 1 Value=zot At index 2 Value=bah
Contents after remove: At index 0 Value=zot At index 1 Value=bah
As you can see, the List is convenient because we don’t need to declare the size up front like an array, and we are able to delete (or insert) items at specific places in the List. Both of these operations are not allowed with normal arrays.
One last operation that you may find useful is the IndexOf function. It tells you the position of a matching item, and -1 if there is no match. For example:
stringList.Add("foo"); stringList.Add("bar"); stringList.Add("zot"); stringList.Add("bah"); Console.WriteLine(stringList.IndexOf("foo")); Console.WriteLine(stringList.IndexOf("zot")); Console.WriteLine(stringList.IndexOf("moo"));
This code outputs:
0 2 -1
The string “foo” is found at position 0, and “zot” at position 2. , and “moo” gives us -1 because it does not exist in the List.
Exercise: Convert the Trivia program to use Lists instead of arrays.