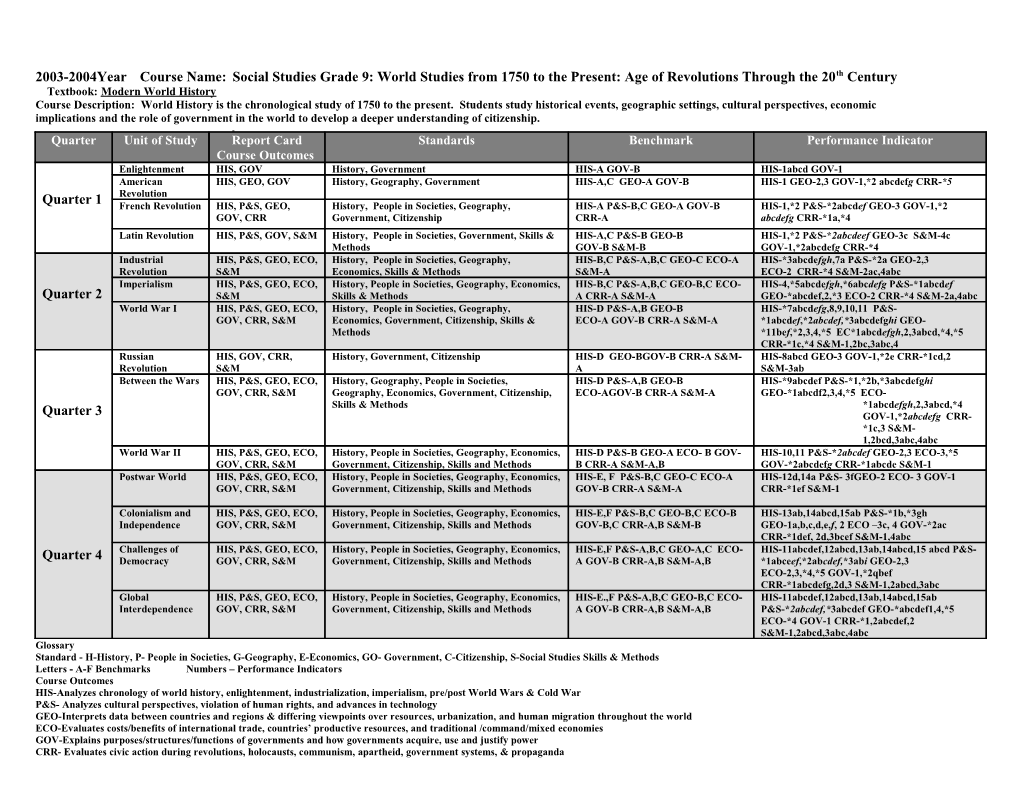
2003-2004Year Course Name: Social Studies Grade 9: World Studies from 1750 to the Present: Age of Revolutions Through the 20th Century Textbook: Modern World History Course Description: World History is the chronological study of 1750 to the present. Students study historical events, geographic settings, cultural perspectives, economic implications and the role of government in the world to develop a deeper understanding of citizenship.
Quarter Unit of Study Report Card Standards Benchmark Performance Indicator Course Outcomes Enlightenment HIS, GOV History, Government HIS-A GOV-B HIS-1abcd GOV-1 American HIS, GEO, GOV History, Geography, Government HIS-A,C GEO-A GOV-B HIS-1 GEO-2,3 GOV-1,*2 abcdefg CRR-*5 Revolution Quarter 1 French Revolution HIS, P&S, GEO, History, People in Societies, Geography, HIS-A P&S-B,C GEO-A GOV-B HIS-1,*2 P&S-*2abcdef GEO-3 GOV-1,*2 GOV, CRR Government, Citizenship CRR-A abcdefg CRR-*1a,*4 Latin Revolution HIS, P&S, GOV, S&M History, People in Societies, Government, Skills & HIS-A,C P&S-B GEO-B HIS-1,*2 P&S-*2abcdeef GEO-3c S&M-4c Methods GOV-B S&M-B GOV-1,*2abcdefg CRR-*4 Industrial HIS, P&S, GEO, ECO, History, People in Societies, Geography, HIS-B,C P&S-A,B,C GEO-C ECO-A HIS-*3abcdefgh,7a P&S-*2a GEO-2,3 Revolution S&M Economics, Skills & Methods S&M-A ECO-2 CRR-*4 S&M-2ac,4abc Imperialism HIS, P&S, GEO, ECO, History, People in Societies, Geography, Economics, HIS-B,C P&S-A,B,C GEO-B,C ECO- HIS-4,*5abcdefgh,*6abcdefg P&S-*1abcdef Quarter 2 S&M Skills & Methods A CRR-A S&M-A GEO-*abcdef,2,*3 ECO-2 CRR-*4 S&M-2a,4abc World War I HIS, P&S, GEO, ECO, History, People in Societies, Geography, HIS-D P&S-A,B GEO-B HIS-*7abcdefg,8,9,10,11 P&S- GOV, CRR, S&M Economics, Government, Citizenship, Skills & ECO-A GOV-B CRR-A S&M-A *1abcdef,*2abcdef,*3abcdefghi GEO- Methods *11bef,*2,3,4,*5 EC*1abcdefgh,2,3abcd,*4,*5 CRR-*1c,*4 S&M-1,2bc,3abc,4 Russian HIS, GOV, CRR, History, Government, Citizenship HIS-D GEO-BGOV-B CRR-A S&M- HIS-8abcd GEO-3 GOV-1,*2e CRR-*1cd,2 Revolution S&M A S&M-3ab Between the Wars HIS, P&S, GEO, ECO, History, Geography, People in Societies, HIS-D P&S-A,B GEO-B HIS-*9abcdef P&S-*1,*2b,*3abcdefghi GOV, CRR, S&M Geography, Economics, Government, Citizenship, ECO-AGOV-B CRR-A S&M-A GEO-*1abcdf2,3,4,*5 ECO- Skills & Methods *1abcdefgh,2,3abcd,*4 Quarter 3 GOV-1,*2abcdefg CRR- *1c,3 S&M- 1,2bcd,3abc,4abc World War II HIS, P&S, GEO, ECO, History, People in Societies, Geography, Economics, HIS-D P&S-B GEO-A ECO- B GOV- HIS-10,11 P&S-*2abcdef GEO-2,3 ECO-3,*5 GOV, CRR, S&M Government, Citizenship, Skills and Methods B CRR-A S&M-A,B GOV-*2abcdefg CRR-*1abcde S&M-1 Postwar World HIS, P&S, GEO, ECO, History, People in Societies, Geography, Economics, HIS-E, F P&S-B,C GEO-C ECO-A HIS-12d,14a P&S- 3fGEO-2 ECO- 3 GOV-1 GOV, CRR, S&M Government, Citizenship, Skills and Methods GOV-B CRR-A S&M-A CRR-*1ef S&M-1
Colonialism and HIS, P&S, GEO, ECO, History, People in Societies, Geography, Economics, HIS-E,F P&S-B,C GEO-B,C ECO-B HIS-13ab,14abcd,15ab P&S-*1b,*3gh Independence GOV, CRR, S&M Government, Citizenship, Skills and Methods GOV-B,C CRR-A,B S&M-B GEO-1a,b,c,d,e,f, 2 ECO –3c, 4 GOV-*2ac CRR-*1def, 2d,3bcef S&M-1,4abc Challenges of HIS, P&S, GEO, ECO, History, People in Societies, Geography, Economics, HIS-E,F P&S-A,B,C GEO-A,C ECO- HIS-11abcdef,12abcd,13ab,14abcd,15 abcd P&S- Quarter 4 Democracy GOV, CRR, S&M Government, Citizenship, Skills and Methods A GOV-B CRR-A,B S&M-A,B *1abceef,*2abcdef,*3abi GEO-2,3 ECO-2,3,*4,*5 GOV-1,*2qbef CRR-*1abcdefg,2d,3 S&M-1,2abcd,3abc Global HIS, P&S, GEO, ECO, History, People in Societies, Geography, Economics, HIS-E.,F P&S-A,B,C GEO-B,C ECO- HIS-11abcdef,12abcd,13ab,14abcd,15ab Interdependence GOV, CRR, S&M Government, Citizenship, Skills and Methods A GOV-B CRR-A,B S&M-A,B P&S-*2abcdef,*3abcdef GEO-*abcdef1,4,*5 ECO-*4 GOV-1 CRR-*1,2abcdef,2 S&M-1,2abcd,3abc,4abc Glossary Standard - H-History, P- People in Societies, G-Geography, E-Economics, GO- Government, C-Citizenship, S-Social Studies Skills & Methods Letters - A-F Benchmarks Numbers – Performance Indicators Course Outcomes HIS-Analyzes chronology of world history, enlightenment, industrialization, imperialism, pre/post World Wars & Cold War P&S- Analyzes cultural perspectives, violation of human rights, and advances in technology GEO-Interprets data between countries and regions & differing viewpoints over resources, urbanization, and human migration throughout the world ECO-Evaluates costs/benefits of international trade, countries’ productive resources, and traditional /command/mixed economies GOV-Explains purposes/structures/functions of governments and how governments acquire, use and justify power CRR- Evaluates civic action during revolutions, holocausts, communism, apartheid, government systems, & propaganda S&M- Evaluates primary/other sources of information & presents a research project *CMSD grade level indicators integrated with ODE grade level indicators (See CMSD Addendum)
Course Description: Grade 9 Modern World History Quarter: 1 Unit of Study: Enlightenment, American Revolution, French Revolution, Latin Revolution Unit of Study Standard Course Benchmark Performance Topic/Concept Vocabulary Instructional Assessment Outcome Indicator Strategies History History A 1 John Locke Enlightenment, Social Debate Research Paper contract Venn Diagram
Enlightenment Government Government B 1 Systems of Natural rights, Philosopher Historical Analysis Persuasive Government Separation of powers letter Personal freedoms Neoclassical, Enlightened despot History History A,C 1,2 Declaration Geography Geography A 2,3 Seven Years War American Government Government B 1,2b King Georges III Checks and balances, federal Revolution system Bill of rights representation History History A 1,2 Old Regime Regime, estate Role Play Write a poem Louis XVI Estates-general, national Debate – 3 levels of Estates-General assembly Estates National Assembly People in People in B 2 Tennis Court Oath Compare and Societies Societies Great Fear Declaration contrast Declaration Rights Declaration of of Man Rights of Man French with other bill Revolution of rights. Geography Geography A 3 Legislative Legislature Assembly Emigres Sans-culottes Government Government B 1,2a Maximilien Guillotine Robespierre Citizenship Citizenship A 1a Committee of Public safety Rights & Rights & Public Safety Responsibilities Responsibilities Reign of Terror History History A,C 1,2 Simon Bolivar Peninsulares, Creoles Socratic Seminar Form a thesis Jose de San Mulattos Character statement Martin examination Miguel Hildago Latin People in People in B 2 Jose Morelos Venn Diagram Revolution Societies Societies George Washington Skills & Skills & B 4c Methods Methods
Course Description: Grade 9 Modern World History Quarter: 2 Unit of Study: Industrial Revolution Unit of Study Standard Course Benchmark Performance Topic/Concept Vocabulary Instructional Assessment Outcome Indicator Strategies History History B-C 3 Origins of the Industrial Timelines, Quizzes, 7a Industrial Revolution, Mobiles, Tests, Revolution, enclosure, crop Posters, Charts, Culminating Spread of rotation Songs, Projects, Industrializatio Collective n bargaining, Pamphlets, Oral strike Maps, Defense People in A-C 2a Spread of Industrializatio Layered See above Societies Industrializatio n, factors of Curriculum, n, Age of production Student Internet Reform Research, Geography C 2-3 Political Reform Factory, Graphic See above and Activism entrepreneur Organizers, Industrializat urbanization Distance ion Learning Economics A 2 Self-Rule for Middle class, See above See above British corporation, Colonies laissez-faire Skills & A 2, 4 Imperialist Adam Smith, See above See above Methods Divide Africa, capitalism, Muslim Lands utilitarianism Fall to Karl Marx, Imperialism communism, British union Imperialism in India The West Divides Asia
Course Description: Grade 9 Modern World History Quarter: 2 Unit of Study: Imperialism Unit of Study Standard Course Benchmark Performance Topic/Concept Vocabulary Instructional Assessment Outcome Indicator Strategies History History B-C 4-5 China’s Response to Suffrage Chartist 7a Western Pressure movement sepoy, Mutiny Raj, annexation Sphere of influence, Open Door Policy Doctrine, assembly line People In People In A-C 1 Japan Modernizes Queen Victory Third Societies Societies Republic, Darwinism Paternalism, Assimilation Imperialism Geography Geography B-C 2-3 U.S. Economic Dreyfus affair anti- 5 Imperialism in Latin Semitism America Geopolitics Pacific Rim Panama Canal Economics Economics A 2 Zionism, dominion, Maori Citizenship Citizenship A 2c Aborigine, penal colony, Rights Rights home rule Social Studies Social A 2 Manifest Destiny, Skills Studies 4 emancipation proclamation Skills segregation, History History D 7,8,9,10,11 World War I Alliance, entente, allies, Layered Triple Alliance trench warfare Curriculum Triple Entente Armistice Reading Central Powers treaty guides 14 Points Distance Treaty of Versailles learning League of Nations People in People in A,B 1,2,31bcdefg World War I Societies Societies Geography Geograph B 1,2,3,4,5 y Economy Economy A 1,2,3,4 Government Governme B 1,2 nt Citizenship Citizenshi A 1c,3 p Skills & Skills & A 1,2,3,4 Methods Methods
Course Description: Grade 9 Modern World History Quarter: 3 Unit of Study: Russian Revolution Unit of Study Standard Course Benchmark Performance Topic/Concept Vocabulary Instructional Assessment Outcome Indicator Strategies
Russian Revolution Standard Course Benchmark Organizer Performance Topic/Concept Vocabulary Instructional Assessment Outcome Indicator Strategies Imperialism, racism, Social
Berlin Conference, Shaka, Boer Great Trek, Boer War, paternalism Assimilation, Menelik II, geopolitics Crimean War, Suez Canal, sepoy Jewel in the crown, Sepoy Mutiny, Raj Pacific Rim, King Monghut Standard Course Benchmark Organizer Performance Topic/Concept Vocabulary Instructional Assessment Outcome Indicator Strategies Emilio Aguinaldo, annexation
Queen Liliokalani, Opium War Extraterritorial Rights, Taiping Rebellion Sphere of influence, Open Door Policy Boxer Rebellion, Treaty of Kanagawa Meiji Era, Russo- Japanese War
Annexation, caudillo, Monroe Doctrine Standard Course Benchmark Organizer Performance Topic/Concept Vocabulary Instructional Assessment Outcome Indicator Strategies Jose Marti, Spanish- American War Panama Canal, Roosevelt Corollary Course Name: Textbook:
Quarter: 2003-2004Year
Standard Course Outcome Benchmark Performance Quarter 1 Quarter 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4 Indicator
Cleveland Municipal School District Social Studies Department
Writing Prompt Extended Response
Directions: Answer the question.
Explain the relationship among the rise of industrialization, large scale rural to urban migration, and massive immigration from Southern and Eastern Europe. ______
Rubric Score
4 Appraise the effect of industrialization on living and working conditions, including the treatment of working conditions and food safety in Upton Sinclair’s The Jungle Judge the changing landscape, including the growth of cities linked by industry and trade; the development of cities divided according to race, ethnicity, and class Rate the effect of the Americanization movement Argue the effect of urban political machines and responses by immigrants and middle-class reformers Assess corporate mergers that produced trusts and cartels and the economic and political policies of industrial leaders Appraise the economic development of the U.S. and its emergence as a major industrial power, including the gains from trade and advantages of its physical geography Compare the similarities and differences between the ideologies of Social Darwinism and Social Gospel (e.g. biographies of William Graham Sumner, Billy Sunday, Dwight L. Moody) Evaluate the effect of political programs and activities of Populists Rate the effect of political programs and activities of the Progressives (e.g. federal regulation of railroad transport, Children’s Bureau, the 16th Amendment, Theodore Roosevelt) World War I Cleveland Municipal School District Social Studies Department
Writing Prompt Extended Response
Directions: Answer the question. Four Point Response
Explain the causes and major events during World War I.
______
Rubric Score 4 Evaluate the arguments for entering into war presented by leaders from all sides of the Great War and the role of political and economic rivalries, ethnic and ideological conflicts, domestic discontent and disorder, and propaganda and nationalism in mobilizing civilian population in support of "total war" Appraise the principal theaters of battle, major turning points and the importance of geographic factors in military decisions and outcomes (e.g., topography, waterways, distance, climate) Judge how the Russian Revolution and the entry of the United States affected the course and outcome of the war Assess the nature of the war, the human costs (military and civilian) on all sides of the conflict, including how colonial peoples contributed to the war effort Appraise human rights and genocide, including the Ottoman government’s actions against Armenian citizens
Cleveland Municipal School District Social Studies Department
Writing Prompt Extended Response
Directions: Explain the rise of totalitarian governments after World War I.
______Rubric Score 4 Judge the causes and consequences of the Russian Revolution, including Lenin's use of totalitarian means to seize and maintain control (e.g., the Gulag) Appraise Stalin's rise to power in the Soviet Union and the connection between economic policies, political policies, the absence of a free press, and systematic violations of human rights (e.g., the Terror Famine in Ukraine) Compare the rise, aggression, and human costs of totalitarian regimes (Fascist and Communist) in Germany, Italy, and the Soviet Union noting their common and dissimilar traits Cleveland Municipal School District Social Studies Department
Writing Prompt Extended Response
Directions: Answer the question. Four point response.
Explain the international developments in the post-World War II world.
______Rubric Score 4 Evaluate the economic and military power shifts caused by the war, including the Yalta Pact, the development of nuclear weapons, Soviet control over Eastern European nations, and the economic recovery of Germany and Japan Appraise the causes of the Cold War, with the free world on one side and Soviet client states on the other, including competition for influence in such places as Egypt, the Congo, Vietnam, and Chile Estimate the importance of the Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan which established the pattern for the postwar American policy of supplying economic and military aid to prevent the spread of communism and the resulting economic and political competition in arenas such as Southeast Asia (i.e., Korean War, Vietnam War), Cuba, and Africa Assess the Chinese Civil War, the rise of Mao Tse-tung, and the subsequent political and economic upheavals in China (e.g., the Great Leap Forward, the Cultural Revolution, and the Tiananmen Square uprising) Evaluate uprisings in Poland (1952), Hungary (1956), and Czechoslovakia (1968) and their resurgence in the 1970's and 1980's as people in Soviet satellites sought freedom from Soviet control Appraise how the forces of nationalism developed in the Middle East, how the Holocaust affected world opinion regarding the need for a Jewish state, the significance and effects of the location and establishment of Israel on world affairs Formulate the reasons for the collapse of the Soviet Union, including the weakness of the command economy, burdens of military commitments, and growing resistance to Soviet rule by dissidents in satellite states and the non-Russian Soviet republics Compare the establishment and work of the United Nations, the Warsaw Pact, SEATO, and NATO, Organization of American States and their purposes and functions
Cleveland Municipal School District Social Studies Department Writing Prompt
Extended Response
Directions: Answer the prompt. Four point response.
Explain how nation building occurred in China.
Rubric Score 4 Evaluate challenges in the region (e.g., geopolitical, cultural, military, economic and international relationship) Compare the recent history of the region (e.g., political divisions and systems, key leaders, religious issues, natural features, resources, and population patterns) Appraise the important trends in the region today and whether they appear to serve the cause of individual freedom and democracy