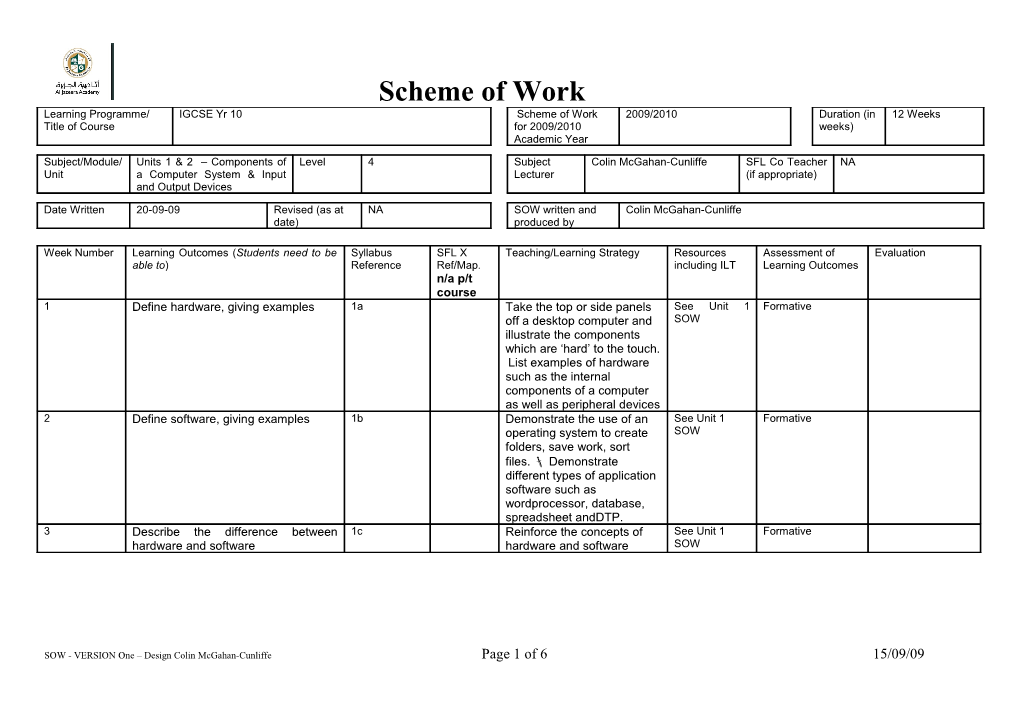
Scheme of Work Learning Programme/ IGCSE Yr 10 Scheme of Work 2009/2010 Duration (in 12 Weeks Title of Course for 2009/2010 weeks) Academic Year
Subject/Module/ Units 1 & 2 – Components of Level 4 Subject Colin McGahan-Cunliffe SFL Co Teacher NA Unit a Computer System & Input Lecturer (if appropriate) and Output Devices
Date Written 20-09-09 Revised (as at NA SOW written and Colin McGahan-Cunliffe date) produced by
Week Number Learning Outcomes (Students need to be Syllabus SFL X Teaching/Learning Strategy Resources Assessment of Evaluation able to) Reference Ref/Map. including ILT Learning Outcomes n/a p/t course 1 Define hardware, giving examples 1a Take the top or side panels See Unit 1 Formative off a desktop computer and SOW illustrate the components which are ‘hard’ to the touch. List examples of hardware such as the internal components of a computer as well as peripheral devices 2 Define software, giving examples 1b Demonstrate the use of an See Unit 1 Formative operating system to create SOW folders, save work, sort files. Demonstrate different types of application software such as wordprocessor, database, spreadsheet andDTP. 3 Describe the difference between 1c Reinforce the concepts of See Unit 1 Formative hardware and software hardware and software SOW
SOW - VERSION One – Design Colin McGahan-Cunliffe Page 1 of 6 15/09/09 Scheme of Work Week Number Learning Outcomes (Students need to be Syllabus SFL X Teaching/Learning Strategy Resources Assessment of Evaluation able to) Reference Ref/Map. including ILT Learning Outcomes n/a p/t course 4 Identify the main components of a 1d Take the top or side panels See Unit 1 Formative general purpose computer: central off a desktop computer and SOW processing unit,main/internal memory illustrate the components (including ROM and RAM), input including the floppy and hard devices, output devices and disc drives. Highlight the secondary/backing storage. differences between input and output devices 5 Identify operating systems, including 1e Demonstrate the use of a See Unit 1 Formative Graphic User Interface, command line ‘Windows’ type operating SOW interface system using point and click to copy a file from a floppy disc to a folder in ‘My Documents’.Show how complicated it is to repeat this exercise using a command lineinterface.
SOW - VERSION One – Design Colin McGahan-Cunliffe Page 2 of 6 15/09/09 Scheme of Work Week Number Learning Outcomes (Students need to be Syllabus SFL X Teaching/Learning Strategy Resources Assessment of Evaluation able to) Reference Ref/Map. including ILT Learning Outcomes n/a p/t course Identify input devices 2a Wherever possible teachers See Unit 2 Formative 6 should obtain the devices SOW assessment listed below and demonstrate how they are used. Where this is more difficult such as MICR, OMR and OCR, for example, typical media such as bank cheques (MICR), multi choice examination stationery (OMR) and utility bills (OCR) should be used as examples Keyboard, mouse, touchpad, tracker ball, video digitizer et al – see Unit 2 for details
identify suitable uses of the input 2b Keyboard See Unit 2 Formative 7 devices stating the advantages and Describe suitable uses of SOW assessment disadvantages the keyboard such as entering text into a word processing document. Keyboards are used where text concerned is original and is created rather than copied. Examples are letters, manuals, business documents etc et al see Unit 2 Identify output devices 2c CRT Monitors et al see Unit See Unit 2 Formative 8 2 SOW assessment
SOW - VERSION One – Design Colin McGahan-Cunliffe Page 3 of 6 15/09/09 Scheme of Work Week Number Learning Outcomes (Students need to be Syllabus SFL X Teaching/Learning Strategy Resources Assessment of Evaluation able to) Reference Ref/Map. including ILT Learning Outcomes n/a p/t course Identify suitable uses of the output 1d CRT monitor See Unit 2 Formative 9 devices stating the advantages and Explain that these are used SOW assessment disadvantages in applications where space is not a problem. They are used when more than one user may need to view the screen simultaneously such as in design use, e.g. when several designers may need to offer suggestions on a prototype. See Unit 1 for more
Describe common backing storage NA Show the students a backup Use internet for Formative 10 media tape and explain how the information assessment tape is impregnated with magnetic spots representing binary data. See Unit 2 for more
SOW - VERSION One – Design Colin McGahan-Cunliffe Page 4 of 6 15/09/09 Scheme of Work Week Number Learning Outcomes (Students need to be Syllabus SFL X Teaching/Learning Strategy Resources Assessment of Evaluation able to) Reference Ref/Map. including ILT Learning Outcomes n/a p/t course identify suitable uses of the storage NA Floppy discs Use internet for Formative 11 media describing the advantages and Explain that floppy discs are reference assessment disadvantages. Understand types of fast falling out of favour with access and access speeds the advent of CDs, DVDs and memory sticks. They are still used however where small files such as word processing, small spreadsheets and databases need to be moved from one computer to another. They are useful to backup small data files. Computers tend not to be fitted with floppy drives as standard anymore, however. See Unit 2 for more
Identify suitable uses of portable NA Mobile phones Use mobile Formative 12 communication devices, stating the Explain how they are used phone web Assessment advantages and disadvantages. for communicating sites personally and for business use in remote areas and whilst traveling. Uses of sending photos and videos as well as video calls in addition to voice calls. Used for sending urgent messages which don’t necessarily interrupt business conferences.
Supporting Guidance for completion of Schemes of Work
SOW - VERSION One – Design Colin McGahan-Cunliffe Page 5 of 6 15/09/09 Scheme of Work Learning Outcomes Resources including ILT Teaching and i.e. – what types of activities/approaches will you use to deliver and achieve the learning outcomes identified? Learning Strategy L = Lecture, W = Workshop, Re=Research R = Roleplay, S = Simulation, G = Games, Di = Discussion, CS = Case Study, PA=Practical Activity, De = Demonstration, MM = MindMap, V = Visit, QA = Question & Answer, GW = Group Work, TM = Training Manual, SV = Sound and Vision, IW = Individual Work, Ob= Observation, Li = Listening Assessment of Learning Ob= Observation, Li = Listening, QA = Question & Answer, Q = Quiz, T = Test, As = Assessment, ILP = Individual Learning Plan Outcomes
SOW - VERSION One – Design Colin McGahan-Cunliffe Page 6 of 6 15/09/09