7th Grade Study Guide Answers
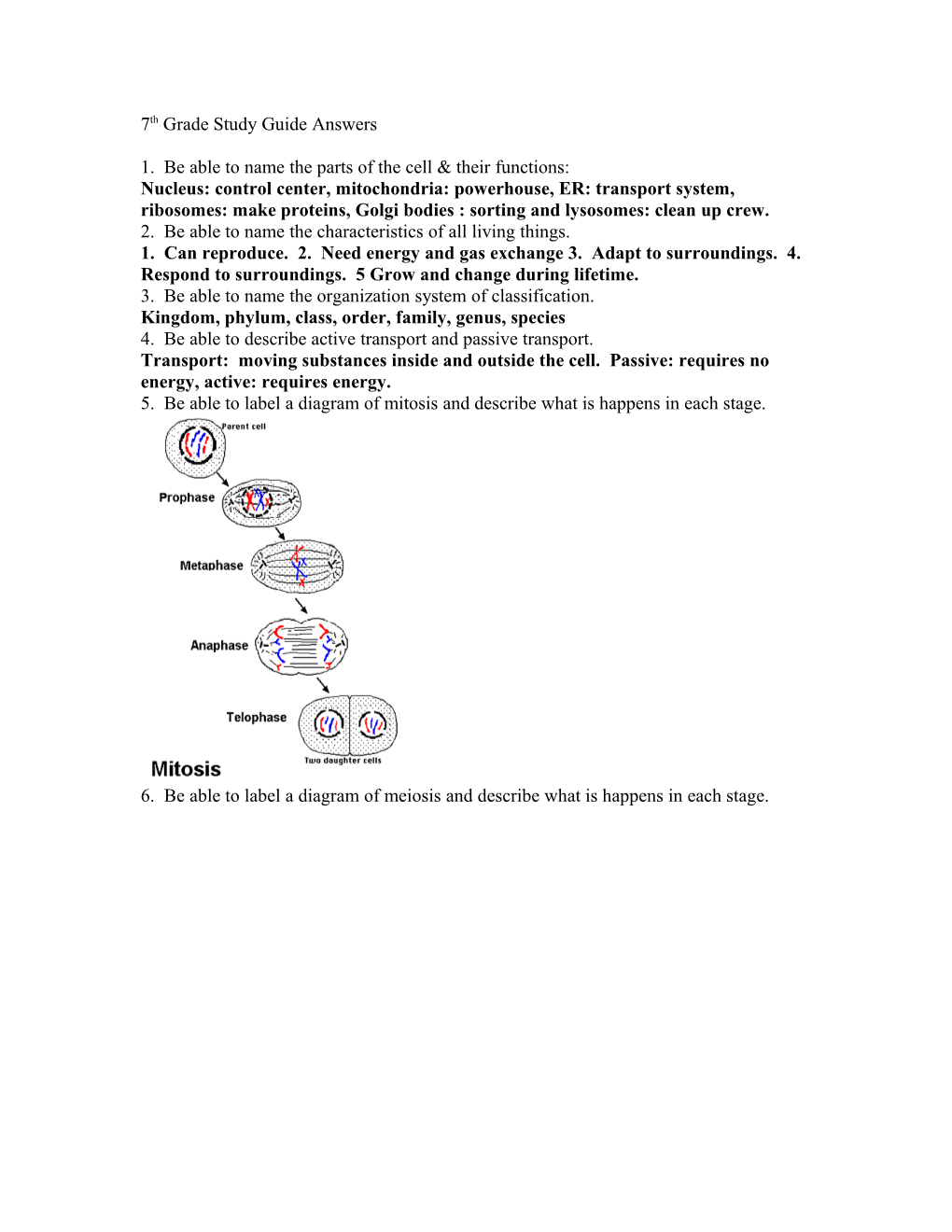
1. Be able to name the parts of the cell & their functions: Nucleus: control center, mitochondria: powerhouse, ER: transport system, ribosomes: make proteins, Golgi bodies : sorting and lysosomes: clean up crew. 2. Be able to name the characteristics of all living things. 1. Can reproduce. 2. Need energy and gas exchange 3. Adapt to surroundings. 4. Respond to surroundings. 5 Grow and change during lifetime. 3. Be able to name the organization system of classification. Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species 4. Be able to describe active transport and passive transport. Transport: moving substances inside and outside the cell. Passive: requires no energy, active: requires energy. 5. Be able to label a diagram of mitosis and describe what is happens in each stage.
6. Be able to label a diagram of meiosis and describe what is happens in each stage. 7. Be able to state the function of DNA. It is a blueprint for an organism.
8. Be able to name the four nucleotides of DNA. Adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine
9. Be able to match nucleotide pairs. Adenine-thymine, cytosine-guanine 10. Be able to construct Punnett squares. 11. Be able to determine offspring alleles if given the parents alleles, & the percentage of offspring exhibiting the desired trait. Example, in the picture above, only 1 flower is recessive homozygous, and 25% of offspring will be white.
12. Name and recognize the three shapes of bacteria. Round- coccus, rod- bacillus, and spiral-spirillia
13. Compare Eubacteria and Archaebacteria. Eubacteria, common bacteria that resides in most types of environments. Archaebacteria: lives in extreme environments like geothermal vents and volcanoes.
14. Be able to recognize the difference between aerobes and anaerobes. Aerobe: breathes oxygen Anaerobe: lives in environments without oxygen.
15. Name 2 examples of beneficial bacteria and 2 examples of harmful bacteria. Beneficial: yogurt and recyclers. Harmful: pathogens (strep throat) and ones that produce toxins (botulism).
16. Be able to describe bioremediation, antibiotics, and pasteurization. Bioremediation- using bacteria to clean pollutants. Antibiotics- substances that harm bacteria. Pasteurization: heating food to kill bacteria but not alter the taste.
17. Describe what a protist is. A protist is a one-celled or many celled organism that lives in moist or wet places.
18. Be able to name the three kinds of protists. Animal-like, plant-like and fungus like.
19. Name at least one example of each protist group. Animal like: paramecium, amoeba. Plant-like: Euglena, algae. Fungi-like: slime molds and water molds.
20. Describe the characteristics of a fungus. Fungi do not have organs such as leaves or roots. They do not make their own food. They grow best in damp, warm areas. They get food by absorbing dead or decaying material from other organisms.
21. Be able to name the three different types of fungi. Sac fungi, club fungi and zygotic fungi.
22. Be able to describe what a lichen is. A lichen is an organism made of both a fungus and either a green algae or cyanobacteria. 23. Be able to state the differences between a plant cell and an animal cell. Animal cell: cell membrane, flagella or cilia, small vacuoles Plant cell: cell wall, chloroplasts, large central vacuole
24. be able to name the 2 groups of plants. Tracheophyte- “artery plant”; bryophyte- “moss plant”
25. Be able to list the 3 groups of nonvascular plants and their characteristics. The three kinds of plants are mosses, hornworts and liverworts. They do not have transport tubes, leaves, stems, or roots. Bryophytes grow in moist areas because they need to get water easily, have spores and rhizoids, and are restricted to a small size because they do not have roots to anchor them in soil or to take in water and nutrients; also they do not have a transport system to carry water and food to all areas of the plant.
26. Be able to recognize and label the parts of a fern. (fiddlehead, a frond, a leaflet, a rhizome, and a fern root)
27. Be able to list the 3 groups of vascular plants and describe the characteristics of each group. Ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms. Ferns are vascular, but have spores. Gymnosperms have naked seeds, look like cones. Angiosperms have covered seeds and flowers. 28. Be able to label the parts of a flower.
29. Be able to state products and reactants in photosynthesis. Products: oxygen, water, and sugar Reactants: sunlight, carbon dioxide and water 30. Be able to describe the characteristics of animals in general. Animals are made of many cells. They have a nucleus and other organelles inside their cells. They get their food from other living things. They digest their food. They move from place to place. They reproduce both sexually and asexually. They have the ability to adapt to their environment and respond to their environment.
31. Be able to name the 2 major divisions of animals. Invertebrates and vertebrates.
32. Be able to recognize an example of bilateral symmetry and radial symmetry. 33. Be able to describe the characteristics of a sponge and important structures of a sponge. (Spicules, pores, collar cells) Most sponges are asymmetrical, but a few have radial symmetry. Adults are rooted to one place. They eat food by pulling water through their pores. Spicules give the body structure and support. Collar cells have tine cilia that move the water through the pores and out the organism. 34. Be able to describe the characteristics of a jellyfish and important structures of a jellyfish. (tentacles, stinging cells, water-based support system) Jellyfish, or cnidarians, have radial symmetry. They have two layers of cells that form tissue and a digestive area. They have a nerve net that carries messages all over the body. They also have tentacles- arm like structures used for getting food. They have a mouth, where food enters and undigested food is removed. Their tentacles have stinging cells that stun or kill victims. They have a hydrostatic skeleton, which is a system of tubes that fill with water to give the organism structure and support.
35. Be able to describe the characteristics of flatworms and name 2 examples. Flatworms are bilateral and have soft bodies. They have three layers of tissue. Their bodies are flat. They have a mouth and a digestive tract. 2 examples are planarians and tapeworms. 36. Be able to describe the characteristics of roundworms and name 2 examples. Roundworms are long and thin like a piece of thread. Their body tapers like a carrot tip at both ends. They are a tube with another tube inside. They have a mouth and an anus. Two examples are pinworms and hookworms. 37. Be able to describe the characteristics of segmented worms and label important structures (setae, gizzard, crop, aortic arches, esophagus, brain, mouth, nerve, intestine) They have tube shaped bodies divided into many segments. They use setae, bristle- like structures, to move and hold on to soil. They have bilateral symmetry, and a body cavity that holds organs. They contract two sets of muscles to move. They take in food and it moves to the crop, where it is stored. Then the gizzard grinds the soil, which is then passed to the intestine. They have a closed circulatory system, where blood is pumped by the aortic arches into two blood vessels. They exchange gas through their skin, so they must always be moist.
38. Be able to name two examples of segmented worms and their uses. 2 examples: Earthworms- break down soil, and leeches- suck blood for medicinal purposes.
39. Be able to describe the general characteristics of molluscs. Molluscs are soft bodied invertebrates that have bilateral symmetry. Some have a shell, and some don’t. They have a thin layer of tissue called the mantle that covers the body. It protects the body, or secretes a shell. Molluscs also have gills, where gas exchange occurs. They have an open circulatory system, meaning the heart moves the blood out into the open spaces around the organs. They all have a head with a mouth and some sensory organs. Some have tentacles, and others have a foot.
40. be able to name the three main groups of molluscs and their specific characteristics of each, and be able to name examples of each. Gastropods- have a foot, and all except slugs have a single shell. They have a radula which is a tongue-like organ with rows of teeth. They use this to get food. Snails are an example. Bivalves are another group. They have two shells that are joined by extremely strong muscles. Clams and oysters are examples. Cephalopods have tentacles and a well-developed eye. They are predators. They have a closed circulatory system, and propel themselves using jet propulsion. Octopus and squid are examples. 41. Be able to label the mantle.
42. Be able to state if the mollusk has an open or closed circulatory system. All except cephalopods have an open circulatory system.
43. Be able to describe the general characteristics of arthropods. Arthropods have jointed appendages, bilateral symmetry, and a segmented body. They also have an exoskeleton. To grow, they need to molt, or shed the old exoskeleton and then grow a new one. They can live in most environments.
44. Be able to label diagrams of complete and incomplete metamorphosis. 45. Be able to name the different groups of arthropods. Insects, arachnids, and crustaceans
46. Be able to describe the characteristics of echinoderms. Echinoderms are found in the ocean. They have a hard endoskeleton. They have radial symmetry. They have a mouth, stomach, and intestines. They feed on plants and animals. They have a nerve ring, but no brain. They have a water-vascular system, like the jellyfish. They also have tube feet, which are tubes with little suction cups.
47. Be able to name examples of echinoderms. Star fish, sea urchins\
48. Be able to describe the characteristics of chordates and vertebrates. Chordates- has four characteristics at some point in its development: a notochord, a postanal tail, a nerve chord, and pharyngeal pouches. Vertebrates have the characteristics of a chordate, but also have endoskeletons, vertebrae and cartilage.
49. Be able to name the 5 classes of vertebrates. Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.
50. Be able to describe the characteristics of fish. Fish are cold-blodded and live in water. They have a tail and fins. Scales cover their body. They have a lateral line to detect movement. They have a two chambered heart and gills. 51. Be able to describe how fish get oxygen from their gills. Fish get oxygen from their gills by moving the blood in the opposite direction from the water flowing through their gills. The oxygen moves from the water into the blood cells. This is through passive transport.
52. How many chambers does a fish heart have? Is the circulatory system open or closed? 2 chambers. They have a closed circulatory system. 53. What two ways do fish stay afloat? Swim bladders and oil in their bodies.
54. What is the counter-current exchange system? When one substance (water) moves in the opposite direction from the other substance (blood), so that the concentration is always higher of one molecule (oxygen) so it will transfer easily to the other substance.
55. What salt problem do fresh water fish have? What salt problem do salt-water fish have? Fresh water fish need more salt. Salt water fish have too much.
56. Describe the characteristics of amphibians. Amphibians and cold-blooded. They breathe both through lungs and their skin. Theyhave three chambered hearts. They have two circuits through which their blood passes through, one to the lungs and the other around their body. They also go through some sort of metamorphosis.
57. How many chambers does an amphibian heart have? Three
58. Which have a longer digestive tract, herbivores or carnivores? Herbivores, so they have more time to break down plant material and absorb nutrients. Those pesky cell walls!
59. What is positive pressure breathing? When air is gulped and forced down into the lungs.
60. How many circuits does an amphibian circulatory system have? Two. One to the lungs, the other around the body.
61. Is there any mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood? Yes.
62. Be able to describe the differences between an tadpole and a frog. A tadpole has gills, fins, and a two chambered heart. A frog has a three chambered heart., legs, and lungs.
63. Be able to describe the difference between a young and an adult salamander. Baby salamanders are more aquatic, have gills, are carnivorous. Adults are more terrestrial, have lungs, and are herbivores.
64. be able to state which (frog or salamander) has complete metamorphosis and which has incomplete metamorphosis. Frogs have complete, salamanders are incomplete.
65. Be able to describe the characteristics of reptiles. Reptiles have thick, waterproof skin. Their skin is covered in scales. They are cold- blooded. They have a three-chambered heart, except for crocodilians. They have legs except for snakes. They lay eggs.
66. What function do scales have? For protection and to keep from losing too much water.
67. What are Jacobson’s organs? These are special receptors inside the snakes mouth that receives smell molecules.
68. Which reptile has a four-chambered heart? Crocodilians.
69. How do reptiles get rid of excess salt? Through their salt glands.
70. Be able to describe the characteristics of birds. What is their defining characteristic? Birds are warm blooded and have hollow bones. All birds have feathers and this is their defining characteristic. Birds have wings and beaks.
71. Which two classes of vertebrates are warm-blooded? Birds and mammals.
72. Describe the features of bird bones. Bird bones are hollow with struts for support.
73. Compare and contrast red meat and white meat. Red meat is meat from muscle that is meant for long, sustained activity. White meat is from short-burst activity muscle. In flying birds, the breast is red (dark) meat. In chickens, the breast is white meat.
74. How many chambers does a bird heart have? How many circuits? Birds have 4 chambers and two circuits.
75. Describe the characteristics of a bird’s digestive system. A bird’s digestive system moves very quickly. First the food goes into the crop, where it is stored. Then it is partially digested in the stomach, and then moves to the gizzard that grinds it up with small stones. Then the food moves to the intestine.
76. Describe the cycle of air flow in a bird’s respiratory system. Birds get air both during inhalation and exhalation.
77. Why is sight and sound important to birds? Because they use sound to communicate and vision to navigate during flight.
78. Be able to describe the characteristics of mammals. What is their defining characteristic? The defining characteristic is that they have mammary glands. They also have hair, and teeth. They have a four chambered heart and two circuits. They have lungs and are warm blooded.
79. Compare and contrast horns & antlers. Antlers are shed, horns stay during the lifetime. Horns are also straight, and antlers are branched.
80. Be able to name and describe the four glands in mammals. The four glands are sweat glands (to maintain temp control), Sebaceous (oil) glands- lubricates and waterproofs skin and hair, scent glands-defense and territory, and mammary glands(milk) to feed young.
81. Know the functions of the different types of teeth. Incisors- biting and gnawing, chisel-like Canines: piercing and tearing (conical) Premolars- shearing and tearing (flat with an edge) Molars- grinding and chewing (flat)
82. What is nasal scrolling? Cartilage tunnels in the nasal cavities to retain water in the body. 83. What are the five functions of the skeletal system? 1. Support and shape 2. protect the internal organs 3. to attach muscles 4. To make red blood cells 5. Storage of phosphorus and calcium.
84. What are the three types of muscle? Skeletal- to move bones Smooth- involuntary like intestine and digestive tract Cardiac- heart
85. Describe how muscles move in the body. Muscles move the bones by contracting and pulling. To move in the opposite direction, another set contracts and pulls. Muscles never push.
86. Be able to recognize what different types of joints are located throughout the body. Immovable- skull Pivot- arm Ball-and-socket – shoulder Hinge – knee Gliding- vertebrae 87. What are the three types of levers in the body? 1st class- head and neck 2nd class- foot walking 3rd class- lifting something with the arm
88. What is the largest organ in the body? The skin
89. What are the functions of skin? To make vitamin D, to protect the body, sensory response (touch) , to control body temp, and to get rid of wastes (sweat).
90. Be able to name the organs of the digestive system. Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
91. What are ventricles and atriums? Atriums are the upper chambers of the heart, and the ventricles are the lower chambers of the heart. Atriums send blood, and the ventricles take in blood.
92. Describe pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation. Pulmonary goes to the lungs, systemic goes throughout the body
93. What is the function of red blood cells and what is the function of white blood cells? Red blood cells distribute oxygen, white blood cells kill intruders
94. Name three diseases that your lungs can have. Emphysema, asthma, cancer 95. Describe the functions of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. Central nervous system- decisions brain, spinal cord Peripheral- take in information and transmit messages (nerves)
96. What are reflexes Movements caused before the brain has made a decision
97. Name the five senses. Touch, taste, sight, smell, hearing
98. Be able to recognize an organism and classify its kingdom and phylum (or class). Ex: mushroom: kingdom – fungi, phylum- club fungus.