World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
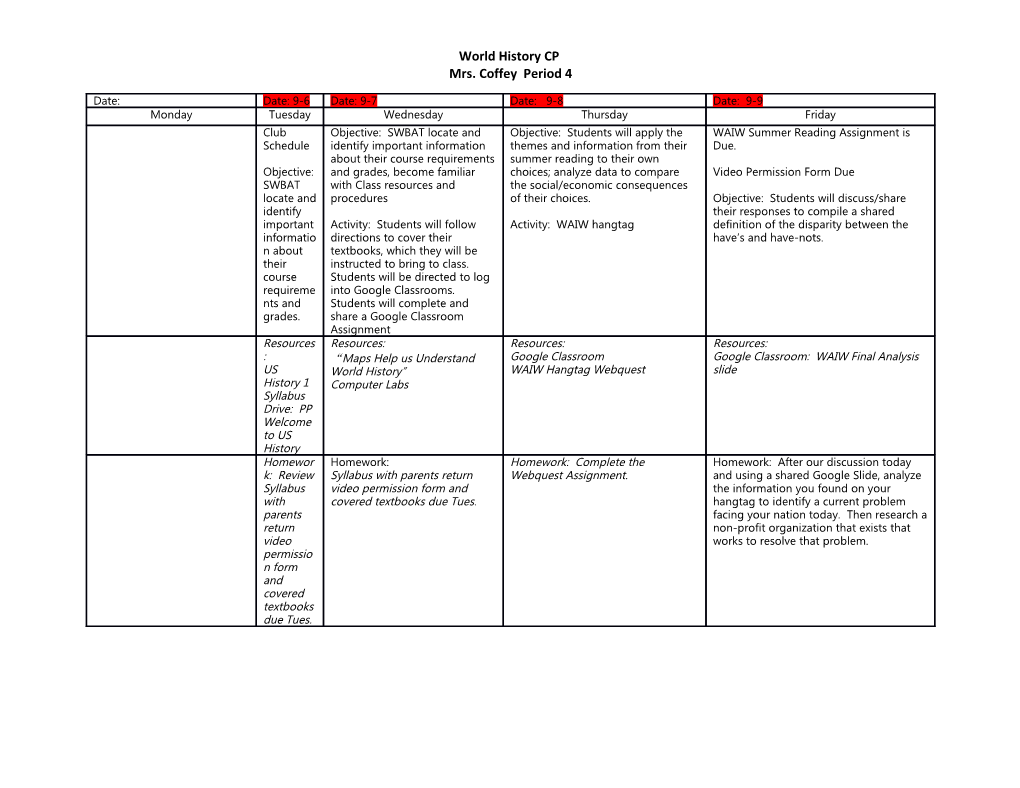
Date: Date: 9-6 Date: 9-7 Date: 9-8 Date: 9-9 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Club Objective: SWBAT locate and Objective: Students will apply the WAIW Summer Reading Assignment is Schedule identify important information themes and information from their Due. about their course requirements summer reading to their own Objective: and grades, become familiar choices; analyze data to compare Video Permission Form Due SWBAT with Class resources and the social/economic consequences locate and procedures of their choices. Objective: Students will discuss/share identify their responses to compile a shared important Activity: Students will follow Activity: WAIW hangtag definition of the disparity between the informatio directions to cover their have’s and have-nots. n about textbooks, which they will be their instructed to bring to class. course Students will be directed to log requireme into Google Classrooms. nts and Students will complete and grades. share a Google Classroom Assignment Resources Resources: Resources: Resources: : “Maps Help us Understand Google Classroom Google Classroom: WAIW Final Analysis US World History” WAIW Hangtag Webquest slide History 1 Computer Labs Syllabus Drive: PP Welcome to US History Homewor Homework: Homework: Complete the Homework: After our discussion today k: Review Syllabus with parents return Webquest Assignment. and using a shared Google Slide, analyze Syllabus video permission form and the information you found on your with covered textbooks due Tues. hangtag to identify a current problem parents facing your nation today. Then research a return non-profit organization that exists that video works to resolve that problem. permissio n form and covered textbooks due Tues. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 9-12 Date: 9-13 Date: 9-14 Date: 9-15 Date: 9-16 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Due: Covered Textbooks Focus Activity: Video: Objective: Students will Objective: SW review the key Objective: SWBAT Identify the WAIW Slides “History of the World in 7 review the key cultural cultural and political main characteristics of Minutes” characteristics; summarize the contributions of Roman Medieval Europe; evaluate the Objective: Students will political contributions of Civilization; evaluate the cultural and political review the WAIW slides and Objective: SWBAT review Greek Civilization. impact of Roman organization developments of the Middle discuss the various NGOs that characteristics of to the development of a Ages. they researched. Paleolithic/Neolithic Man; list Notes: shared Western Tradition for criteria for civilization; identify Europe. Introduce: World Atlas the 4 major centers for Activity due 9/19** civilization Paired Activity: “All Roads Lead to Rome” worksheet. Activity: Students will work on their World Atlas Activity.
Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: “ History of the World in 7 “All Roads Lead to Rome” “One Step Forward, Five Maps Help us Understand minutes”: Video PP Ancient Greece Review worksheet. Steps Back” Article from Our World History. PP Ancient Rome World’s Story. PP 1.1 Civilization Review World History Atlas Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Completed World History Completed World History Completed World History Completed World History Completed World History Atlas due 9/19. Atlas due 9/19. Atlas due 9/19. Atlas due 9/19. Atlas due 9/19. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 9/19 Date: 9/20 Date: 9/21 Date: 9/22 Date: 9/23 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Focus: “Medieval Europe: Objective: SWBAT describe Due: Geography Packets. **Assign Renaissance Man Quiz Review Unit and Lord and Vassal” the achievements of the **Assign Renaissance Man Project ** Geography of World Muslim world in the Dark Project ** Objective: SWBAT become Continents and Oceans. Objective: SWBAT describe Ages; Identify the main Objective: SWBAT become familiar with the research the achievements of the characteristics of Medieval familiar with the research process and how best to Muslim world in the Dark Europe; evaluate the cultural process and how best to utilize the NHS library Ages; Identify the main and political developments of utilize the NHS library resource; work cooperatively characteristics of Medieval the Middle Ages resource; work cooperatively to research the lives of major Europe; evaluate the cultural to research the lives of major Renaissance Era Men and and political developments of Focus Activity: Students will Renaissance Era Men and contributors; Analyze the Middle Ages. review the Middle Ages article contributors; Analyze information and Produce and and review the role of the information and Produce and present an original slide show Student Cards: Need Muslim cultures in the time present an original slide show that highlights the Students’ Name and School period through 1001 that highlights the Renaissance figures life and Inventions. Renaissance figures life and accomplishments. accomplishments. Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: “One Step Forward, Five “medieval Matchup” NHS LIBRARY NHS LIBRARY Steps Back” Article from Our Ren Man Project and Ren Man Project and World’s Story. Video“1001 Inventions” Assignment. Assignment. PP Middle Ages PP Middle Ages Chapter 1 Study Guide Chapter 1 Study Guide Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Completed World History Completed World History Student Pair will research Study Guide #1.1 Due Study Guide #1.1 Due Atlas due 9/19. Atlas due 9/19. their Renaissance figure to Monday Monday make their best possible **Ren Man Project** **Ren Man Project** selection. Tomorrow.
Date: 9/21 Date: 9/22 Date: 9/23 Date: 9/24 Date: 9/25 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Return and Review World Open Notes Quiz Objective: SWBAT explain Objective: SWBAT explain Objective: SW become History Geo Packets. why the Renaissance will why the Renaissance became familiar with High School Quiz 1: Monday 9/28 Objective: SWBAT explain occur in Italy; identify centered in Italy; explain how Library procedures including why the Renaissance will contributing factors to the the printing press impacted log-in and computer Objective: SWBAT describe occur in Italy; identify Renaissance; analyze the the spread of art and ideas in procedures, Google Drive the achievements of the contributing factors to the impact of secularism and Europe. platforms, and Google Slides Muslim world in the Dark Renaissance; analyze the humanism on the human self- through a partnered research Ages; summarize main impact of secularism and perception. Focus Activity: “The Impact of project on a Renaissance characteristics of life in the humanism on the human self- Printing” (Spielvogel) Figure. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Middle Ages. perception. Closing Activity: Geography Application: Activity: Students will review Focus Activity: #161 Trade in Renaissance Europe the Middle Ages article and Renaissance Europe: Words review the role of the Muslim to Know. cultures in the time period **Assign Renaissance Man **Assign Renaissance Man through 1001 Inventions. **Assign Renaissance Man Project ** **Assign Renaissance Man Project ** Project ** Project ** Student Cards: Need Students’ Name and School Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: “medieval Matchup” #161 Renaissance Europe: #163 Renaissance Europe: NHS Library Words to Know PP Renaissance Who’s Who? Video“1001 Inventions” PP Renaissance Geography Application: PP Renaissance 2 PP Middle Ages Trade in Renaissance Europe PP Renaissance Ren Man Project 2015
Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Study Guide #1.1 Due Wed Study Guide #1.1 Due Wed Study Guide #1.2 due Friday Study Guide #1.2 due Friday Study for Geo Quiz Monday World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 9/28 Date: 9/29 Date: 9/30 Date: 10-1 Date: 10-2 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Quiz on Current Europe Map Activity: Students will work Activity: Students will work Focus: The Importance of the Focus: Reviewing important cooperatively to research the cooperatively to research the Printing Press. concepts…What is a Activity: Students will work life and work of a major life and work of a major Protestant? cooperatively to research the Renaissance artist. Students Renaissance artist. Students Pass Back: Homework and life and work of a major will create an original Google will create an original Google Quizzes Notes: PP Protestant Renaissance artist. Students Slide project and present their Slide project and present their Reformation will create an original Google Renaissance Man for inclusion Renaissance Man for inclusion Review Renaissance Themes: Slide project and present their in the Ren Man 2015 in the Ren Man 2015 Renaissance Man for inclusion Competition. Competition. Students will work to in the Ren Man 2015 complete the Erasmus article Competition. together.
Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: NHS Library with Wendy NHS Library with Wendy NHS Library with Wendy Renaissance Man(YouTube) PP Reformation Whipple Whipple Whipple Desiderus Erasmus PBS Empires: Martin Luther
C-Level Mobile Carts Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Students will research and Students will research and Students will research and Students will research and Students will research and produce the Google Slide produce the Google Slide produce the Google Slide produce the Google Slide produce the Google Slide cooperatively. cooperatively. cooperatively. cooperatively. cooperatively. Presentations to Begin on Monday. NJCCS: 6.1.12.B.1.a NJCCS: 6.1.12.B.1.a NJCCS: 6.1.12.A.7.a; B.7.a; NJCCS: 6.1.12.A.7.a; B.7.a; NJCCS: 6.1.12.A.7.a; B.7.a; C.7.a; D.7.a C.7.a; D.7.a C.7.a; D.7.a World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 10-5 Date: 10-6 Date: 10-7 Date: 10-8 Date: 10-9 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday **Presentations** **Presentations** **Presentations** Focus: Desiderus Erasmus #1- Renaissance Quiz 3 Activity: Students will work Activity: Students will work Activity: Students will work Notes: PP Protestant cooperatively to research the cooperatively to research the cooperatively to research the Notes: PP Protestant Reformation life and work of a major life and work of a major life and work of a major Reformation Renaissance artist. Students Renaissance artist. Students Renaissance artist. Students will create an original Google will create an original Google will create an original Google Slide project and present their Slide project and present their Slide project and present their Renaissance Man for inclusion Renaissance Man for inclusion Renaissance Man for inclusion in the Ren Man 2015 in the Ren Man 2015 in the Ren Man 2015 Competition. Competition. . Competition. Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources:
PBS Empires: Martin Luther PBS Empires: Martin Luther PBS Empires: Martin Luther Desiderus Erasmus
Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: View: PBS Empires: Martin Read Section 1.3 Quiz Renaissance on Friday Read Section 1.4 due Luther: Driven to Defiance. Monday. Study Guide HW #4 Viewing Chart Due Thursday. due Tuesday. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 10-17 Date: 10-18 Date: 10-19 Date: 10-20 Date: 10-21 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Period 3/7 Period 3 **Presentations** Notes: PP Protestant Reformation Quiz Student Discussion: Scientific **Presentations** Reformation/ Scientific Revolution. Revolution Primary Source Work: Activity: Students will work Period 7 Describe science-yness of the Primary Source Work: cooperatively to research the Reformation Quiz on Renaissance. Describe science-yness of the life and work of a major Notes: PP Protestant Thursday Renaissance. Renaissance artist. Students Reformation to England Activity: Notes on Scientific will create an original Google Revolution Activity: Notes on Scientific Slide project and present Revolution their Renaissance Man for inclusion in the Ren Man 2016 Competition. Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources:
Video: Renaissance Man PP Protestant Reformation WHFUA: Scientific Video: Henry Henry Henry Revolution readings
Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Study Guide #1.5 WHFUA: Scientific Primary Sources for essay. Period 3 due Wed. Revolution readings Students Students should use the PS Period 7 due Tuesday will read the articles using to chart on a SOAPS close reading Worksheet. Chapter Test on practiceslooking for evidence Tuesday/Wed. of science and rating the science-yness of the articles. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 10-24 Date: 10-25 Date: 10-26 Date: 10-27 Date: 10-28 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday ** Essay prep for Chapter 1 Test Chapter 1 Review Chapter 2/3 Study Focus Activity: Marco Polo Standage Reading Quiz (5 Test tomorrow** Guide points) Activity: Explorers Chart and Complete Scientific Activity: Explorers Chart and Map Activity. Focus: Sea Travel Revolution Notes. Map Activity. Notes: Exploration Review and chart Scientific Obj: SWBAT identify the Portugal Revolution readings and contributions of major science-yness evidence. explorers of the period; identify the major powers of the period; evaluate the motivation of those powers in expansion; determine which technologies contributed to expansion during this period. Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: WHFUA: Scientific Exploration PP Exploration PP Exploration PP Revolution readings Standage, Tom. Seeds of Standage, Tom. Seeds of Standage, Tom. Seeds of Empire. Empire. Empire.
Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Test Ch. 1 on Tuesday Standage Article, Section 1 Standage Article, Section 2 due Friday due Monday. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 10-31 Date: 11/1 Date: 11/2 Date: 11/3 Date: 11/4 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Reading Quiz: Standage Reading Quiz: Standage Objective: SWBAT identify Focus: Bernal Diaz, “Markets Focus: Globalization video- Focus: Europe Discovers the the motivation for Europeans and Merchandise” Dutch market Focus: Sails Riches of India to explore the Indian Ocean . region; describe the Objective: SWBAT identify the Objective: SWBAT define Objective: SWBAT identify the characteristics of Portuguese key explorers in the discovery mercantilism and contributions of key explorers investment there; identify the of the New World; describe entrepreneurship; describe and the technology that made means by which Europeans the nature of Spanish how the nature of colonialism exploration possible; the were able to gain control of colonization there; evaluate expressed mercantilism and impact of the Treaty of the Indian Ocean; compare the impact of the Columbian predicated the global growth Tordesillas in creating a global the efforts to colonize of exchange; Explain how of the period of exploration. period of discovery; assess the Portugal/Netherlands slavery developed in the New impact of Europeans on the World; Evaluate Spain’s efforts African Slave Trade; evaluate Notes: Exploration in South to Christianize the new world the relative responsibility of and Southeast Asia and respond to calls for Africans and Europeans with reform. regard to the slave trade. Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources Resources: Notes: Exploration PP (Spain Notes: Exploration PP Exploration PP Spain in the Americans PP Triangular Trade PP Tordesillas) Exploration PP GA: Europe discovers the 2 Views of Spanish Conquest YouTube: Mankind “Treasure” African Trading Empires Riches of India. Bartolome de las Casas. – Dutch market YouTube: Mankind PS The Treaty of Tordesillas “Treasure” – Pieces of Eight PS King Affonso: Letter to King John III of Portugal
Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: 2 Views of Homework: Test on Read Final portion of Article Spanish Conquest Wednesday 11/9 Bartolome de las Casas. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 11/7 Date: 11/8 Date: 11/9 Date: 11/10 Date: 11/11 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Focus: Class Participation Review Chapter 1 Tests and Chapter 2 Test ** No School ** ** No School ** Rubric Chapter 2 Test Essays.
Objectives: SWBAT summarize the differences between Spanish, Dutch and Portuguese exploration; describe the economic, political, and social characteristics of Spanish colonization; evaluate the success of the encomienda system/mission system and Spain’s reaction to Las Casas demands. Resources: Resources: Resources: Spain in the Americans PP Triangular Trade PP YouTube: Mankind “Treasure” – Dutch market
Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Two Views and Definitions. Chapter 2 Essay World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 11/21 Date: 11/22 Date: 11/23 Date: 11/24 Date: 11/25 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Focus: Tears for Fears, Absolute Monarchs Projects Period 3 Meets only ** No School ** ** No School ** “Everybody Wants to Rule the are due today. World” Chapter 4 Crossword Puzzle. Assign Chapter 4 Study Guide. Objective: SWBAT define Absolute Monarchy and Focus: As pairs they should summarize the consequences of work on the Wars of Philip II the Religious Wars in Europe in (page 143) the 15-16th centuries. Notes: Slides 3 – 5 Hapsburg crowns… Resources: Resources: Resources: Absolutism In Europe Absolutism in Europe
Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Absolute Monarchs PROJECT Study Guide #4.1 due Tuesday due Tomorrow. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 11/30 Date: 12-1 Date: 12-2 Date: 12-3 Date: 12-4 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Due: Chapter 2/3 Essays Due Introduce Absolute Monarchs Student Research Library Student Research Library Research projects Due Report Card Project Due Or C-Level Mobile Lab Or C-Level Mobile Lab Read: Chapter 78: Mechanical December 4th. SWBAT define Absolute Galleon SW research and evaluate the Monarchy and summarize the Review Noodle-tools lives, decisions and consequences of the Religious Introduce Research project: contributions of an Absolute Wars in Europe in the 15-16th Absolute Monarchs Report Student Research Library Monarch. centuries. Card Project Due December Or C-Level Mobile Lab 7th. Chapter 4 Study Guide Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Absolutism in Europe (1-3) C-LEVEL MOBILE LAB C-LEVEL MOBILE LAB C-LEVEL MOBILE LAB C-LEVEL MOBILE LAB Tears for Fears, “Everybody Absolutism in Europe (1-3) Absolutism in Europe (1-3) Wants to Rule the World” Tears for Fears, “Everybody Tears for Fears, “Everybody Wants to Rule the World” Wants to Rule the World” Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Chapter 4.1 Due Absolute Monarchs Report Absolute Monarchs Report Absolute Monarchs Report Absolute Monarchs Report Monday. Card Card Card Card World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 12-14 Date: 12-15 Date: 12-16 Date: 12-17 Date: 12-18 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Return Chapter 3 Test Absolute Monarchs Absolute Absolute Monarchs Presentations Absolute Monarchs Presentations continue Monarchs continue Presentation SWBAT describe the struggle for power between Presentation Nobles and King in the era of Absolutism; identify SWBAT describe how s continue SWBAT describe how the Stuarts the means by which Louis XIV was able to preserve the Stuarts Kings and Kings and Tudor Kings differed in his power; predict the consequences of such power Tudor Kings differed in SWBAT their treatment of Parliament; on the European world stage their treatment of describe how describe the impact and motivation Parliament; describe the the Stuarts behind the English Civil War; and impact and motivation Kings and the consequences of the Glorious behind the English Civil Tudor Kings Revolution. War; and the differed in consequences of the their Glorious Revolution. treatment of Parliament; describe the impact and motivation behind the English Civil War; and the consequence s of the Glorious Revolution. Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Absolutely French Revolution in England Revolution Revolution in England History of the Palace of Versailles in England https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=XxIzMr2Ekpo
Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: HW #4.3 Due Today HW # 4.3 Due Thursday Test Chapter 4.1 – 4.3 on Tuesday Test Chapter 4.1 – 4.3 on Tuesday
Thirty Years War https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B18zwAVO4q0 World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 1/2 Date: 1/5 Date: 1/6 Date: 1/7 Date: 1/8 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Absolute Monarch Absolute Monarch Absolute Monarch Absolute Monarch Presentations Presentations Presentations Presentations
Objectives: SWBAT describe Objectives: SWBAT describe Objectives: SWBAT describe Objectives: SWBAT compare unique characteristics of unique characteristics of unique characteristics of and evaluate the reigns of Eastern Absolutism; Eastern Absolutism; Eastern Absolutism; absolute monarchs; identify summarize Peter the Great’s summarize Peter the Great’s summarize Peter the Great’s the key constructs of rise to power and the means rise to power and the means rise to power and the means absolutism, describe their with which he centralized with which he centralized with which he centralized successes; identify the limits power under his rule; power under his rule; power under his rule; of absolutism. summarize Catherine the summarize Catherine the summarize Catherine the Great’s rise to power and the Great’s rise to power and the Great’s rise to power and the means with which he means with which he means with which he centralized power under his centralized power under his centralized power under his rule. rule. rule. Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: PP Rise of Modern Russia PP Rise of Modern Russia PP Rise of Modern Russia Absolute Monarchs Video: Land of the Tsars – Video: Land of the Tsars – Video: Land of the Tsars – Worksheet Peter the Great #6-10 Peter the Great #6-10 Peter the Great #6-10 https://www.youtube.com/pla https://www.youtube.com/pla https://www.youtube.com/pla ylist? ylist? ylist? list=PLNBBnDp2V0QLdI0dzk list=PLNBBnDp2V0QLdI0dzk list=PLNBBnDp2V0QLdI0dzk M_XP-LK5vbiLOhF M_XP-LK5vbiLOhF M_XP-LK5vbiLOhF PS – Peter’s Decrees on PS – Peter’s Decrees on PS – Peter’s Decrees on German Clothes and shaving German Clothes and shaving German Clothes and shaving Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Essay Preparation Study Guide #5 due Friday on the Age of Absolute Monarchs OUTLINE DUE for Essay MONDAY World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 1/11 Date: 1/12 D Date: 1/14 Date: 1/15 a t e : 1 / 1 3 Monday Tuesday W Thursday Friday e d n e s d a y Absolute Monarch Presentations Quiz Sections F Focus: Enlightenment Debate Notes: PP #4.4/#4/5 o Enlightenment Objectives: SWBAT describe unique characteristics of Eastern c Objectives: SWBAT explain how the Notes (Review Absolutism; summarize Peter the Great’s rise to power and the means Objectives: SWBAT u Renaissance, Reformation, and Scientific Enlightenment with which he centralized power under his rule; summarize Catherine explain how the s Revolution contributed to the Thinkers Folders the Great’s rise to power and the means with which he centralized Renaissance, A Enlightenment; identify the ideas and responses) power under his rule. Reformation, and c beliefs of the Philosophes; describe how Scientific Revolution t economic ideas shifted during this MAP: contributed to the i period. Enlightenment Enlightenment; v Europe identify the ideas i Enlightenment Thinkers Folders and beliefs of the t Philosophes; y describe how : economic ideas P shifted during this o period. s t - i t S t u d e n World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
t O r i g i n a t e d
E n li g h t e n m e n t D e f i n i t i o n s : E n li g h t e n m World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
e n t , P h i l o s o p h e , n a t u r a l r i g h t s , a b s o l u t i s m , L i b e r World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
t y , d e i s m
O b j e c t i v e s : S W B A T e x p l a i n
h o w
t h e R e n a i World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
s s a n c e , R e f o r m a t i o n , a n d
S c i e n t i f i c R e v o l u t i o n
c World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
o n t r i b u t e d
t o
t h e E n li g h t e n m e n t ; i d e n t i f y t h e i d e a World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
s a n d
b e li e f s o f t h e P h i l o s o p h e s ; d e s c r i b e h o w
e c o n o World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
m i c i d e a s s h i f t e d
d u r i n g
t h i s p e r i o d . Resources: Resources: R Resources: Resources: PP Rise of Modern Russia Textbook e History Station Folders PP Enlightenment Video: Land of the Tsars – Peter the Great #6-10 s WHFUA: Big Era 6.6.1: Student Notes https://www.youtube.com/playlist? o Handout 3.1 and Map: list=PLNBBnDp2V0QLdI0dzkM_XP-LK5vbiLOhF u PS from NCHS and Mini-Q “Enlightenment in PS – Peter’s Decrees on German Clothes and shaving r Europe” c e s : P World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
P
E n l i g h t e n m e n t N o t e s P S : H o b b e s . L e v i a t h a n L o c k e . World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
O f C i v i l G o v e r n m e n t
Homework: Homework: H Homework: Homework: Study Study Guide #4 due Wednesday Study Guide #5.1 o Complete History Stations Responses Guide #5.2 Due due Wednesday m Tuesday e w o r k : D e b a t e
p r e p World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 1/23 Date: 1/24 Date: 1/25 Date: 1/26 Date: 1/27 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SW work cooperatively to SW work cooperatively to BAT: Chapter 5 Test Midterm Review Midterm Review BAT : describe how the ideals evaluate current social, of the enlightenment changed environmental, political, and social and political ideals of economic problems; apply the enlightened despots and evaluate ideals of the Enlightenment to their impact on diverse social the social problem. classes; evaluate current social, environmental, political, and economic problems; apply the ideals of the Enlightenment to the social problem.
Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: NCHE: Frederick II Articles; Student selected Current Events
Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: MIDTERM review distributed MIDTERM date 1/30 – 2/1
NJCCS Standards: 6.2.12.A.2.a Compare the principle ideas of the Enlightenment in Europe with similar ideas in Asia and Muslim empires of the Middle East and North Africa. 6.2.12.A.2.b Determine the reasons for, and the consequences of , the rise of powerful, centralized nation states in Europe. 6.2.12.C.2.b. Relate the development of more modern banking and financial systems to European economic influence in the world. 6.2.12.D.2.d. Analyze the impact of new intellectual, philosophical, and scientific ideas on how humans viewed themselves and how they viewed their physical and spiritual worlds. 6.2.12.D.2.e. Assess the impact of the printing press and other technologies developed on the dissemination of ideas. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4 World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 2-1 Date: 2-2 Date: 2-3 Date: 2-4 Date: 2-5 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Assign French Revolution Study Objectives: SWBAT explain how Objectives: SWBAT explain Guide and Project. Objectives: SWBAT describe the Objectives: SWBAT describe the political crisis of 1789 led to how the political crisis of 1789 social divisions of France’s Old the social divisions of France’s popular revolts; summarize the led to popular revolts; Objectives: SWBAT describe the Order; identify the reasons for Old Order; identify the reasons reforms of the National Assembly summarize the reforms of the social divisions of France’s Old France’s economic troubles in for France’s economic troubles in August 1789 and then in 1791; National Assembly in August Order; identify the reasons for 1789; describe why Louis XVI in 1789; describe why Louis Evaluate the success/limitation of 1789 and then in 1791; Evaluate France’s economic troubles in called the Estates-General and XVI called the Estates-General the National Assembly in dealing the success/limitation of the 1789; describe why Louis XVI the conditions that the Estates- and the conditions that the with the political crisis in France; National Assembly in dealing called the Estates-General and General Placed on the 3rd Estate; Estates-General Placed on the Describe the impact of the with the political crisis in France; the conditions that the Estates- summarize the events that led to 3rd Estate; summarize the events Declaration of the Rights of Man Describe the impact of the General Placed on the 3rd Estate; the Storming of the Bastille that led to the Storming of the and Citizen and the Constitution Declaration of the Rights of Man summarize the events that led to Bastille reflect Enlightenment thought; and Citizen and the Constitution the Storming of the Bastille Predict how the unfolding French reflect Enlightenment thought; Revolution will impact other Predict how the unfolding French European nations. Revolution will impact other European nations Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: PP French Revolution PP French Revolution PP French Revolution PP National Assembly 2016 PP National Assembly 2016 French Revolution 6.1 French Revolution 6.1 French Revolution 6.1 PS: Declaration of the Rights of PS: Declaration of the Rights of Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Man and Citizen Man and Citizen Student Handout 1.4 “Cahiers Student Handout 1.4 “Cahiers Student Handout 1.4 “Cahiers de Doleances” de Doleances” de Doleances” Video: History: The French Video: History: The French Video: History: The French Revolution Revolution Revolution Homework: Read Section 6.1 Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: pages ______. Be able to Study Guide #2 due Thursday Work on Timeline Study Guide #1 describe the Ancien Regime. and French Revolution Project.
NJCCS Standards: 6.2.12.A.3.a Explain how and why various ideals (e.g., liberty, popular sovereignty, natural rights, democracy, and nationalism) became driving forces for reforms and revolutions, their influence on Latin American independence movements, and evaluate their impact on government, society, and economic opportunities. 6.2.12.A.3.b Relate the responses of various governments to pressure for self-government or self-determination to subsequent reform or revolution. 6.2.12.D.3.a Explain how individuals and groups promoted revolutionary actions and brought about change during this time period. 6.2.12.D.3.b Explain how industrialization and urbanization affected class structure, family life, the daily lives of men, women, and children, and the environment. Date: 2-8 Date: 2-9 Date: 2-10 Date: 2-11 Date: 2-12 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Objectives: SWBAT explain Objectives: SWBAT explain Objectives: SWBAT explain Objectives: SWBAT explain why Quiz Sections 1 – 3 how the political crisis of 1789 why radicals moved to abolish why radicals moved to abolish radicals moved to abolish the led to popular revolts; the monarchy in France; Explain the monarchy in France; Explain monarchy in France; Explain why Objectives: SWBAT describe summarize the reforms of the why the Committee on Public why the Committee on Public the Committee on Public Safety Napoleons rise to power explain National Assembly in August Safety was created and why the Safety was created and why the was created and why the Reign of why the French so strongly World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
1789 and then in 1791; Evaluate Reign of Terror resulted; explain Reign of Terror resulted; Terror resulted; explain how the supported him; summarize how the success/limitation of the how the actions of The explain how the actions of The actions of The Convention led to Napoleon built an empire and National Assembly in dealing Convention led to the creation of Convention led to the creation the creation of The Directory; identify the challenges that his with the political crisis in France; The Directory; Predict the of The Directory; Predict the Predict the impact of excess on empire faced; predict how other Describe the impact of the impact of excess on the French impact of excess on the French the French people; evaluate the European nations will perceive Declaration of the Rights of Man people; evaluate the need for people; evaluate the need for need for freedom vs. the need for his rise; analyze the events that and Citizen and the Constitution freedom vs. the need for security freedom vs. the need for security led to Napoleon’s fall; Outline reflect Enlightenment thought; security the purpose of the Congress of Predict how the unfolding Vienna and evaluate its success. French Revolution will impact other European nations Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: PP National Assembly 2016 PP Radical Phase of the French PP Radical Phase of the French PP Radical Phase of the French PP The End of the FR and the PS: Declaration of the Rights of Revolution Revolution Revolution Rise of Napoleon Man and Citizen PS “Viewpoints: Two Views of PS “Viewpoints: Two Views of PS “Viewpoints: Two Views of Article: Reaction and the French Revolution” the French Revolution” the French Revolution” Revolution – Video: HC: TFR - King Louis Video: HC: TFR - King Louis Video: HC: TFR - King Louis Article: Napoleon XVI escapes? XVI escapes? XVI escapes?
Homework: Study Guide # 3 due Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Thursday. French Revolution Work on Timeline Study Guide #1 Quiz on Friday. and French Revolution Project.
NJCCS Standards: 6.2.12.A.3.a Explain how and why various ideals (e.g., liberty, popular sovereignty, natural rights, democracy, and nationalism) became driving forces for reforms and revolutions, their influence on Latin American independence movements, and evaluate their impact on government, society, and economic opportunities. 6.2.12.A.3.b Relate the responses of various governments to pressure for self-government or self-determination to subsequent reform or revolution. 6.2.12.D.3.a Explain how individuals and groups promoted revolutionary actions and brought about change during this time period. 6.2.12.D.3.b Explain how industrialization and urbanization affected class structure, family life, the daily lives of men, women, and children, and the environment. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 2-15 Date: 2-16 Date: 2-17 Date: 2-18 Date: 2-19 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday President’s Day Schools Closed Objectives: SWBAT describe Objectives: SWBAT describe Catchup day/ Test Review Quiz Sections 1 – 3 Napoleons rise to power explain Napoleons rise to power explain why the French so strongly why the French so strongly Objectives: SWBAT describe supported him; summarize how supported him; summarize how Napoleons rise to power explain Napoleon built an empire and Napoleon built an empire and why the French so strongly identify the challenges that his identify the challenges that his supported him; summarize how empire faced; predict how other empire faced; predict how other Napoleon built an empire and European nations will perceive European nations will perceive identify the challenges that his his rise; analyze the events that his rise; analyze the events that empire faced; predict how other led to Napoleon’s fall; Outline led to Napoleon’s fall; Outline European nations will perceive the purpose of the Congress of the purpose of the Congress of his rise; analyze the events that Vienna and evaluate its success. Vienna and evaluate its success. led to Napoleon’s fall; Outline the purpose of the Congress of Vienna and evaluate its success. Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: PP The End of the FR and the PP The End of the FR and the PP The End of the FR and the PP The End of the FR and the Rise of Napoleon Rise of Napoleon Rise of Napoleon Rise of Napoleon Article: Reaction and Article: Reaction and Article: Reaction and Revolution Article: Reaction and Revolution – Revolution – – Revolution – Article: Napoleon Article: Napoleon Article: Napoleon Article: Napoleon
Homework: Homework: Study Guide #4 Due Homework: Homework: Homework: Thursday
NJCCS Standards: 6.2.12.A.3.a Explain how and why various ideals (e.g., liberty, popular sovereignty, natural rights, democracy, and nationalism) became driving forces for reforms and revolutions, their influence on Latin American independence movements, and evaluate their impact on government, society, and economic opportunities. 6.2.12.A.3.b Relate the responses of various governments to pressure for self-government or self-determination to subsequent reform or revolution. 6.2.12.D.3.a Explain how individuals and groups promoted revolutionary actions and brought about change during this time period. 6.2.12.D.3.b Explain how industrialization and urbanization affected class structure, family life, the daily lives of men, women, and children, and the environment. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 2-22 Date: 2-23 Date: 2-25 Date: 2-26 Date: 2-27 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Chapter 6 Test Objectives: SWBAT identify Objectives: SWBAT identify Quiz Section 1 Objectives: SWBAT French Revolution the technologies that the technologies that understand why Britain was contributed to the Industrial contributed to the Industrial Objectives: SWBAT the starting point for the Revolution; summarize how Revolution; summarize how understand why Britain was Revolution; describe the the agricultural revolution the agricultural revolution the starting point for the changes that transformed led to the growth of new led to the growth of new Revolution; describe the the textile industry; explain industries; list factors that industries; list factors that changes that transformed the the significance of the steam contributed to the IR contributed to the IR textile industry; explain the engine in the transportation significance of the steam revolution. Activity: Students will use Activity: Students will use engine in the transportation Flocabulary to identify the Flocabulary to identify the revolution. changes characteristic of the changes characteristic of IR. Students will work the IR. Students will work cooperatively to identify cooperatively to identify factors to the growth of factors to the growth of Industrial cities in this Industrial cities in this period. period. Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: PP Industrial Revolution PP Industrial Revolution PP Industrial Revolution PP Industrial Revolution IR Focus Packet IR Focus Packet IR Focus Packet IR Focus Packet YouTube: Flocabulary – YouTube: Flocabulary – YouTube: BBC: The YouTube: BBC: The Industrial Revolution Industrial Revolution Children who Built Children who Built Mapwork: “Industrial Cities Mapwork: “Industrial Cities Victorian Britain Victorian Britain in Great Britain and Ireland, in Great Britain and Ireland, 1800-1850” 1800-1850”
Homework: Homework: Study Guide Homework: Homework: Homework: #7.1 Due Thursday Study Guide #7.2
6.2.12.A.3.c Analyze the relationship between industrialization and the rise of democratic and social reforms, including the expansion of parliamentary democracy. 6.2.12.A.3.d Compare and contrast the struggles for women’s suffrage and workers’ rights in Europe and North America, and evaluate the degree to which each movement achieved its goals. 6.2.12.C.3.a Analyze interrelationships among the “agricultural revolution,” population growth, industrialization, specification of labor, and patterns of land-holding. 6.2.12.C.3.b Analyze interrelationships among the Industrial Revolution, nationalism, competition for global markets, imperialism, and natural resources. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4 6.2.12.C.3.c Compare the characteristics of capitalism, communism, and socialism to determine why each system emerged in different world regions. 6.2.12.C.3.d Determine how, and the extent to which, scientific and technological changes, transportation, and new forms of energy brought about massive social, economic, and cultural changes. 6.2.12.D.3.a Explain how individuals and groups promoted revolutionary actions and brought about change during this time period. 6.2.12.D.3.b Explain how industrialization and urbanization affected class structure, family life, the daily lives of men, women, children and the environment. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 3/13 Date: 3/14 Date: 3/15 Date: 3/16 Date: 3/17 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Quiz Sections 7.1 and 7.2 **Probable Snow Day** Industrial Focus Packet Industrial Focus Packet Quiz Sections 7.3
Activity: Complete Map Objectives: SWBAT Objectives: SWBAT Objectives: SWBAT Work Activity understand why Britain was the understand why Britain understand Laissez-Faire starting point for the Revolution; was the starting point for economics and summarize the Objectives: SWBAT describe how the IR impacted the Revolution; describe beliefs of those who support it; understand why Britain was the social and cultural history of how the IR impacted the describe the doctrine of the starting point for the Britain ; explain how IR social and cultural history utilitarianism; summarize the Revolution; describe how contributed to urbanization. of Britain ; explain how IR theories of socialism; explain the IR impacted the social contributed to urbanization, Marx’s views of the working and cultural history of describe the impact of classes; compare/contrast the Britain ; explain how IR Laissez-Faire economics on three dominant economic contributed to urbanization. the working poor. systems; predict which system will meet the needs of dominant regional powers.
Primary Sources: Adam Smith and Thomas Malthus Quotes
Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: PP Industrial Revolution PP Industrial Revolution PP Industrial Revolution PP Industrial Revolution IR Focus Packet IR Focus Packet 19 - 23) IR Focus Packet 2012 London Olympics Video
Homework: #7.3 a HW: 7.3b Homework: **2 Views on Child Labor
6.2.12.A.3.c Analyze the relationship between industrialization and the rise of democratic and social reforms, including the expansion of parliamentary democracy. 6.2.12.A.3.d Compare and contrast the struggles for women’s suffrage and workers’ rights in Europe and North America, and evaluate the degree to which each movement achieved its goals. 6.2.12.C.3.b Analyze interrelationships among the Industrial Revolution, nationalism, competition for global markets, imperialism, and natural resources. 6.2.12.C.3.c Compare the characteristics of capitalism, communism, and socialism to determine why each system emerged in different world regions. 6.2.12.C.3.d Determine how, and the extent to which, scientific and technological changes, transportation, and new forms of energy brought World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4 about massive social, economic, and cultural changes. 6.2.12.D.3.a Explain how individuals and groups promoted revolutionary actions and brought about change during this time period. 6.2.12.D.3.b Explain how industrialization and urbanization affected class structure, family life, the daily lives of men, women, children and the environment. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 3/13 Date: 3/14 Date: 3/15 Date: 3/16 Date: 3/17 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Objectives: SWBAT Objectives: SWBAT Objectives: SWBAT Quiz Sections 7.1 – 7.3 Quiz Sections 7.1 – 7.3 understand Laissez-Faire understand Laissez-Faire understand why Britain was economics and summarize economics and summarize the starting point for the Objectives: SWBAT understand the beliefs of those who the beliefs of those who Industrial Revolution; Laissez-Faire economics and support it; describe the support it; describe the describe the changes that summarize the beliefs of those doctrine of utilitarianism; doctrine of utilitarianism; transformed the textile who support it; describe the summarize the theories of summarize the theories of industry; explain the doctrine of utilitarianism; socialism; explain Marx’s socialism; explain Marx’s significance of the steam summarize the theories of views of the working classes; views of the working classes; engine in the transportation socialism; explain Marx’s views of compare/contrast the three compare/contrast the three revolution. the working classes; dominant economic systems; dominant economic systems; compare/contrast the three predict which system will predict which system will Focus: Industrial Quote dominant economic systems; meet the needs of dominant meet the needs of dominant Game predict which system will meet regional powers. regional powers. the needs of dominant regional European Map powers. Review: Primary Sources: Adam Smith and Thomas Malthus.
Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: PP Industrial Revolution 19 - PP Industrial Revolution 19 - PP Industrial Revolution PP Industrial Revolution 23) 23) PS Marx and Engels, The Communist Manifesto
Articles: “Poverty Rate Still High..”; “Nearly 1/3 of Americans…” Homework: #7.4 due Homework: Homework: Study Guide Homework: Homework: Wednesday #9.1 Due Thursday World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 3/14 Date: 3/15 Date: 3/16 Date: 3/17 Date: 3/18 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Chapter 7/9 Test Objectives: SWBAT review Objectives: SWBAT identify Objectives: SWBAT identify Quiz Section 2 Industrial Revolution Napoleon’s impact on Otto Von Bismarck, Otto Von Bismarck, Europe; evaluate the impact realpolitik, ems dispatch, realpolitik, ems dispatch, Objectives: SWBAT of the Congress of Vienna; blood and iron; zollverein; blood and iron; zollverein; understand why Britain was predict the places that will describe his role in unifying describe his role in unifying the starting point for the experience revolution in Germany; summarize the Germany; summarize the Revolution; describe the 1848; Identify liberalism, steps toward German steps toward German changes that transformed nationalism, civil liberties, Unification; explain how Unification; explain how the textile industry; explain principle of legitimacy, Bismarck used realpolitik in Bismarck used realpolitik in the significance of the steam Concert of Europe. the Prussian Wars to unify the Prussian Wars to unify engine in the transportation Germany; describe the Germany; describe the revolution. Activity: Review Chapter 10 political character of the political character of the Big Ideas unified German Reich. unified German Reich.
Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: PP Ch. 10 Notes PP Ch. 10 Notes PP Ch. 10 Notes PP Industrial Revolution Map #37 German Map #37 German Map #37 German Unification IR Focus Packet Unification Unification Youtube: OVB YouTube: BBC: The Youtube: OVB Children who Built Victorian Britain
Homework: Homework: Study Guide Homework: Homework: Homework: #10.1 Due Thursday Study Guide #7.2
6.2.12.A.3.a Explain how and why various ideals (e.g., liberty, popular sovereignty, natural rights, democracy, and nationalism) became driving forces for reforms and revolutions, their influence on Latin American independence movements, and evaluate their impact on government, society, and economic opportunities. 6.2.12.A.3.b Relate the responses of various governments to pressure for self-government or selfdetermination to subsequent reform or revolution. 6.2.12.B.3.a Assess the impact of imperialism by comparing and contrasting the political boundaries of the world in 1815 and 1914. 6.2.12.D.3.a Explain how individuals and groups promoted revolutionary actions and brought about change during this time period. 6.2.12.C.3.b Analyze interrelationships among the Industrial Revolution, nationalism, competition for global markets, imperialism, and natural resources. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 3/21 Date: 3/22 Date: 3/23 Date: 3/24 Date: 3/25 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Objectives: SWBAT identify Objectives: SWBAT identify Quiz Chapter 10 Sections 1-3 **Spring Break** the contributions of Camillo the contributions of Camillo diCavour, Victor Emmanuel diCavour, Victor Emmanuel II, Garibaldi and Mazzini in II, Garibaldi and Mazzini in fostering Italian nationalism; fostering Italian summarize the steps toward nationalism; summarize the Italian unification, steps toward Italian Compare/Contrast the Italian unification, and German efforts toward Compare/Contrast the unification in this period of Italian and German efforts nationalism. toward unification in this period of nationalism. Activity: Students will work cooperatively to read Activity: Students will work through simulation individually to evaluate Primary Sources on Nationalism
Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Ward, Katherine. Unification of Italy Italian Unification Map
Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: HW #10.3 Read Postscript Unification Essay. for Unification of Italy. Q. What problems did Italy experience after unification? 6.2.12.A.3.a Explain how and why various ideals (e.g., liberty, popular sovereignty, natural rights, democracy, and nationalism) became driving forces for reforms and revolutions, their influence on Latin American independence movements, and evaluate their impact on government, society, and economic opportunities. 6.2.12.A.3.b Relate the responses of various governments to pressure for self-government or selfdetermination to subsequent reform or revolution. 6.2.12.B.3.a Assess the impact of imperialism by comparing and contrasting the political boundaries of the world in 1815 and 1914. 6.2.12.D.3.a Explain how individuals and groups promoted revolutionary actions and brought about change during this time period. 6.2.12.C.3.b Analyze interrelationships among the Industrial Revolution, nationalism, competition for global markets, imperialism, and natural resources. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4 World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 4/4 Date: 4/5 Date: 4/6 Date: 4/7 Date: 4/8 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Section 10.4 Homework Due Chapter 10 Test Review and Test Chapter 10 Test Chapter 10 Essay Objective: SWBAT identify and DBQ Form Complete Outline for Essay (½ period) explain the factors that contributed to “new Objectives: SWBAT describe Introduce Chapter 12: imperialism”; explain why how nationalism impacted the Imperialism Activity: Main Ideas imperialism spread; describe the rise of revolution against and Map. different methods of government multinational empires; evaluate utilized by Western powers. the response of Austria and the Objectives: SWBAT identify the Ottoman Empire to calls for countries, regions, and continents Focus: Rudyard Kipling, White reform; evaluate the impact of impacted by imperialism in the Man’s Burden industrialism on the national 19th century; start to compare the identity. experiences of the imperial powers to those they impacted. Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Notes: PP Chapter 10 PP Chapter 12 Notes Notes pp Chapter 12 PS Ottomans/Austro-Hungary Chapter 12 Graphic Organizer Cartoon and map Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Use PS to complete the DBQ Study for Chapter 10 Test, #12.1a due Friday #12 complete outline for the Essay.
6.2.12.A.3.b Relate the responses of various governments to pressure for self-government or self-determination to subsequent reform or revolution. 6.2.12.A.3.e Analyze the motives for and methods by which European nations, Japan, and the United States expanded their imperialistic practices in Africa and Asia during this era, and evaluate the impact of these actions on their relations. 6.2.12.B.3.a Assess the impact of imperialism by comparing and contrasting the political boundaries of the world in 1815 and 1914. 6.2.12.D.3.a Explain how individuals and groups promoted revolutionary actions and brought about change during this time period. 6.2.12.C.3.b Analyze interrelationships among the Industrial Revolution, nationalism, competition for global markets, imperialism, and natural resources. 6.2.12.C.3.c Compare the characteristics of capitalism, communism, and socialism to determine why each system emerged in different world regions. 6.2.12.C.3.d Determine how, and the extent to which, scientific and technological changes, transportation, and new forms of energy brought about massive social, economic, and cultural changes. 6.2.12.C.3.e Compare the impact of imperialism on economic development in Africa, Asia, and Latin America regarding barriers or opportunities for future development and political independence. 6.2.12.D.3.c Compare and contrast China’s and Japan’s views of and responses to imperialism, and determine the effects of imperialism on the development and prosperity of each country in the 20th century. 6.2.12.D.3.d Analyze the extent to which racism was both a cause and consequence of imperialism, and evaluate the impact of imperialism from multiple perspectives. 6.2.12.D.3.e Analyze the impact of the policies of different European colonizers on indigenous societies, and explain the responses of these societies to imperialistic rule. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 4/18 Date: 4/19 Date: 4/20 Date: 4/21 Date: 4/22 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday ** PARCC TESTING** ** PARCC TESTING** ** PARCC TESTING** ** PARCC TESTING** Focus Activity: The British SCHEDULE SCHEDULE SCHEDULE SCHEDULE Official’s Home in India
To Do: Review quiz To Do: Outline Map of the To Do: Outline Map of the Focus Activity: Compare Objective: SWBAT identify questions. Return Homeworks Ottoman Empire in the late Ottoman Empire in the late images of the Imperialization the factors that motivated and Complete Africa Notes. 1800s. 1800s. of India to predict the western imperialism; Evaluate characteristics of British rule. the benefits/consequences of Activity: Review White Man’s Focus Activity: Partner Focus Activity: Partner private control of the Indian Burden. Working with a define: fundamentalism; define: fundamentalism; Objective: SWBAT identify the Colony; Describe the partner, evaluate how reform, concessions reform, concessions factors that motivated western characteristics of British colonizers viewed their role in imperialism; Evaluate the Colonial Rule in India; Identify the Colonies? How does that Objective: SWBAT identify Objective: SWBAT identify benefits/consequences of the causes of Indian compare to the Contracts and the motivation for interest of the motivation for interest of private control of the Indian Nationalism; Predict Britain’s experience of the Natives? Western imperialism in this Western imperialism in this Colony; Describe the response to calls for self-rule. region; compare the response region; compare the characteristics of British Objectives: SWBAT compare of Ottomans, Egyptians and response of Ottomans, Colonial Rule in India; Identify the impact of Belgium, British Persians to outside influence; Egyptians and Persians to the causes of Indian on African continent, Evaluate evaluate their success in outside influence; evaluate Nationalism; Predict Britain’s the impact of Menelik II in retaining autonomy during this their success in retaining response to calls for self-rule. securing independence for period. autonomy during this period. Ethiopia.
Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: Notes: PP Chapter 12 Africa Notes: PP Muslim Regions Notes: PP Muslim Regions Notes: Chapter 12: India Notes: Chapter 12: India FOF “Suez Canal’ World History for Us All. George Orwell, Shooting the “Architecture, Labor, Citites” Elephant “Gandhi” “The British Official’s Home in India” Burnett, FH, “The Secret Garden”. Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Study Guide #3 due Tuesday Read Suez Canal. Study Guide #12.4 **Movie Club: Gandhi** Read “Shooting the Elephant”. Reading Quiz on Monday. **Movie Club: Gandhi** 6.2.12.A.3.b Relate the responses of various governments to pressure for self-government or self-determination to subsequent reform or revolution. 6.2.12.A.3.e Analyze the motives for and methods by which European nations, Japan, and the United States expanded their imperialistic practices in Africa and Asia during this era, and evaluate the impact of these actions on their relations. 6.2.12.B.3.a Assess the impact of imperialism by comparing and contrasting the political boundaries of the world in 1815 and 1914. 6.2.12.D.3.a Explain how individuals and groups promoted revolutionary actions and brought about change during this time period. 6.2.12.C.3.b Analyze interrelationships among the Industrial Revolution, nationalism, competition for global markets, imperialism, and natural resources. 6.2.12.C.3.c Compare the characteristics of capitalism, communism, and socialism to determine why each system emerged in different world regions. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
6.2.12.C.3.d Determine how, and the extent to which, scientific and technological changes, transportation, and new forms of energy brought about massive social, economic, and cultural changes. 6.2.12.C.3.e Compare the impact of imperialism on economic development in Africa, Asia, and Latin America regarding barriers or opportunities for future development and political independence. 6.2.12.D.3.c Compare and contrast China’s and Japan’s views of and responses to imperialism, and determine the effects of imperialism on the development and prosperity of each country in the 20th century. 6.2.12.D.3.d Analyze the extent to which racism was both a cause and consequence of imperialism, and evaluate the impact of imperialism from multiple perspectives. 6.2.12.D.3.e Analyze the impact of the policies of different European colonizers on indigenous societies, and explain the responses of these societies to imperialistic rule. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 4/25 Date: 4/26 Date: 4/27 Date: 4/28 Date: 4/29 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday ** CLUB SCHEDULE** Objective: SWBAT identify/define major trends in Chinese traditional history including the Objective: SWBAT compare Activity: Compare “White dynastic cycle, mandate of heaven and Confucianism/legalism; explain the nature of the Great the efforts to imperialize Man’s Burden” and “Shooting Wall and how it influenced the Chinese world view; identify the major advancements developed China by the West; Evaluate the Elephant”. during the Chinese Golden Age; Evaluate the motivations and consequences of the decisions of the response by the Qing Q. What does this say about the Modern Chinese Dynasties Dynasty to the West; identify how colonizers viewed their the opportunity presented in role in the Colonies? Activity: the Chinese Republic pre- Q. What does this say about WWI. the experience of the Natives? Q. What does this say about the imperial relationship? (consider justification for the right to rule and who has power itself.)
Objective: SWBAT identify the factors that motivated western imperialism; Evaluate the benefits/consequences of private control of the Indian Colony; Describe the characteristics of British Colonial Rule in India; Identify the causes of Indian Nationalism; Predict Britain’s response to calls for self-rule.
Resources: Resources: Resources: Notes: Chapter 12: India Notes: PP Reviewing Chinese History Notes: PP New Imperialism in China George Orwell, Shooting the Spielvogel. “The Development of the Chinese Traditions.” “Excerpts from The Treaty of Nanjing, Aug. 1842” Elephant (100-103) “Boxer Uprising” “The British Official’s Home “Two Edicts from the Qianlong Emperor on the Occasion of in India”Africa Lord Macartney’s Mission to China, Sept. 1793” Coffey Corner Spotlight – Mohandas K. Gandhi Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Spielvogel. “The Study Guide 12.5 Due Friday “Treaty of Nanjing” handout Study for Chapter 12 Test Development of the Chinese “Two Edicts” Handout Monday. Traditions.” (100-103) World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
6.2.12.A.3.b Relate the responses of various governments to pressure for self-government or self-determination to subsequent reform or revolution. 6.2.12.A.3.e Analyze the motives for and methods by which European nations, Japan, and the United States expanded their imperialistic practices in Africa and Asia during this era, and evaluate the impact of these actions on their relations. 6.2.12.B.3.a Assess the impact of imperialism by comparing and contrasting the political boundaries of the world in 1815 and 1914. 6.2.12.D.3.a Explain how individuals and groups promoted revolutionary actions and brought about change during this time period. 6.2.12.C.3.b Analyze interrelationships among the Industrial Revolution, nationalism, competition for global markets, imperialism, and natural resources. 6.2.12.C.3.c Compare the characteristics of capitalism, communism, and socialism to determine why each system emerged in different world regions. 6.2.12.C.3.d Determine how, and the extent to which, scientific and technological changes, transportation, and new forms of energy brought about massive social, economic, and cultural changes. 6.2.12.C.3.e Compare the impact of imperialism on economic development in Africa, Asia, and Latin America regarding barriers or opportunities for future development and political independence. 6.2.12.D.3.c Compare and contrast China’s and Japan’s views of and responses to imperialism, and determine the effects of imperialism on the development and prosperity of each country in the 20th century. 6.2.12.D.3.d Analyze the extent to which racism was both a cause and consequence of imperialism, and evaluate the impact of imperialism from multiple perspectives. 6.2.12.D.3.e Analyze the impact of the policies of different European colonizers on indigenous societies, and explain the responses of these societies to imperialistic rule. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 5-22 Date: 5-23 Date: 5-24 Date: 5-25 Date: 5-26 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Focus Activity: Compare Objective: SWBAT compare Objective: SWBAT compare Objective: SWBAT compare Test Chapter 12 images of the Imperialization the efforts to imperialize the efforts to imperialize the efforts to imperialize of India to predict the China by the West; Evaluate China by the West; Evaluate China by the West; Evaluate characteristics of British rule. the response by the Qing the response by the Qing the response by the Qing Dynasty to the West; identify Dynasty to the West; identify Dynasty to the West; identify Objective: SWBAT identify the opportunity presented in the opportunity presented in the opportunity presented in the factors that motivated the Chinese Republic pre- the Chinese Republic pre- the Chinese Republic pre- western imperialism; Evaluate WWI. WWI. WWI the benefits/consequences of private control of the Indian Imperialism Travelogue Colony; Describe the Project. Due Tuesday characteristics of British Colonial Rule in India; Identify the causes of Indian Nationalism; Predict Britain’s response to calls for self-rule.
Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources:
Homework: HW #12.5 B Homework: Test Review Homework: Homework: Homework:
6.2.12.A.3.b Relate the responses of various governments to pressure for self-government or self-determination to subsequent reform or revolution. 6.2.12.A.3.e Analyze the motives for and methods by which European nations, Japan, and the United States expanded their imperialistic practices in Africa and Asia during this era, and evaluate the impact of these actions on their relations. 6.2.12.B.3.a Assess the impact of imperialism by comparing and contrasting the political boundaries of the world in 1815 and 1914. 6.2.12.D.3.a Explain how individuals and groups promoted revolutionary actions and brought about change during this time period. 6.2.12.C.3.b Analyze interrelationships among the Industrial Revolution, nationalism, competition for global markets, imperialism, and natural resources. 6.2.12.C.3.c Compare the characteristics of capitalism, communism, and socialism to determine why each system emerged in different world regions. 6.2.12.C.3.d Determine how, and the extent to which, scientific and technological changes, transportation, and new forms of energy brought about massive social, economic, and cultural changes. 6.2.12.C.3.e Compare the impact of imperialism on economic development in Africa, Asia, and Latin America regarding barriers or opportunities for future development and political independence. 6.2.12.D.3.c Compare and contrast China’s and Japan’s views of and responses to imperialism, and determine the effects of imperialism on the development and prosperity of each country in the 20th century. 6.2.12.D.3.d Analyze the extent to which racism was both a cause and consequence of imperialism, and evaluate the impact of imperialism from multiple perspectives. 6.2.12.D.3.e Analyze the impact of the policies of different European colonizers on indigenous societies, and explain the responses of these societies to imperialistic rule. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 5-9 Date: 5-10 Date: 5-11 Date: 5-12 Date: 5-13 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Objectives: SWBAT identify Activity: Fishbowl discussion Objectives: SWBAT identify Objectives: SWBAT identify Objective: SW work the Main causes of the First re: Schools of Thought the fronts in World War I; the fronts in World War I; cooperatively to research the World War; describe the chain describe a stalemate and describe a stalemate and motivations and impact of the of events that lead to the Objectives: SWBAT identify identify the technological identify the technological period of imperialism on a outbreak of war in 1914; and the Main causes of the First changes that resulted in the changes that resulted in the specific nation/region and assess liability in the outbreak World War; describe the chain stalemate in the Western stalemate in the Western produce a GSP detailing the of war. of events that lead to the Front Front consequences to this native outbreak of war in 1914; and region. Activity: Read Causes of assess liability in the outbreak Focus Activity: Stefan Zwieg World War I of war. article Activity: Review the project, Break into small groups to due dates and processes. read Schools of Thought Resources: Resources: Resources: NHS Library Thursday - Everyday Life: World War I Stefan Zwieg, “The Excitement of War” Monday Schools of Thought: Causes of World War I YouTube: 14 Diaries PP War in Europe Map: Major European Powers YouTube: Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Homework: Imperialism Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Travelogue Project Study Guide # 14.1 due Study Guide #14.2 Due Thursday Friday 6.2.12.B.4.a Determine the geographic impact of World War I by comparing and contrasting the political boundaries of the world in 1914 and 1939. 6.2.12.B.4.b Determine how geography impacted military strategies and major turning points during World War II. 6.2.12.C.4.a Analyze government responses to the Great Depression and their consequences, including the growth of fascist, socialist, and communist movements and the effects on capitalist economic theory and practice. 6.2.12.C.4.b Compare and contrast World Wars I and II in terms of technological innovations (i.e., industrial production, scientific research, war tactics) and social impact (i.e., national mobilization, loss of life, and destruction of property). 6.2.12.D.4.a Analyze the extent to which nationalism, industrialization, territory disputes, imperialism, militarism, and alliances led to World War I. 6.2.12.D.4.b Analyze the Treaty of Versailles and the League of Nations from the perspectives of different nations. 6.2.12.D.4.d Analyze the extent to which the legacy of World War I, the global depression, ethnic and ideological conflicts, imperialism, and traditional political or economic rivalries caused World War II. 6.2.12.D.4.e Compare how Allied countries responded to the expansionist actions of Germany and Italy. 6.2.12.D.4.f Explain the role of colonial peoples in the war efforts of the Allies and the Central/Axis Powers in both World Wars. 6.2.12.D.4.g Analyze the role of racial bias, nationalism, and propaganda in mobilizing civilian populations in support of “total war”. 6.2.12.D.4.j Analyze how the social, economic, and political roles of women were transformed during this time period. 6.2.12.D.4.k Assess the cultural impact of World War I, the Great Depression, and World War II by analyzing the values and social ideas in the arts. World History CP Mrs. Coffey Period 4
Date: 5-16 Date: 5-17 Date: 5-18 Date: 5-19 Date: 5-20 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Objectives: SWBAT identify Quiz Sections 14.1 – 14.2 Objectives: SWBAT analyze the cause and effect of American No School the fronts in World War I; entry into WWI in 1917; summarize the factors that led to Allied describe a stalemate and Objectives: SWBAT describe Victory identify the technological how WWI became a TOTAL Objectives: changes that resulted in the WAR; explain the impact of stalemate in the Western WWI on minorities and Front colonized peoples.
Resources: Resources: Resources: Resources: PP 14.2 War in Europe WWI Mobilization Packet Zimmerman Note PP Total War PP End to War
Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Study Guide #14.3 due Friday Study Guide #14.4 due Tuesday 6.2.12.B.4.a Determine the geographic impact of World War I by comparing and contrasting the political boundaries of the world in 1914 and 1939. 6.2.12.B.4.b Determine how geography impacted military strategies and major turning points during World War II. 6.2.12.C.4.a Analyze government responses to the Great Depression and their consequences, including the growth of fascist, socialist, and communist movements and the effects on capitalist economic theory and practice. 6.2.12.C.4.b Compare and contrast World Wars I and II in terms of technological innovations (i.e., industrial production, scientific research, war tactics) and social impact (i.e., national mobilization, loss of life, and destruction of property). 6.2.12.D.4.a Analyze the extent to which nationalism, industrialization, territory disputes, imperialism, militarism, and alliances led to World War I. 6.2.12.D.4.b Analyze the Treaty of Versailles and the League of Nations from the perspectives of different nations. 6.2.12.D.4.d Analyze the extent to which the legacy of World War I, the global depression, ethnic and ideological conflicts, imperialism, and traditional political or economic rivalries caused World War II. 6.2.12.D.4.e Compare how Allied countries responded to the expansionist actions of Germany and Italy. 6.2.12.D.4.f Explain the role of colonial peoples in the war efforts of the Allies and the Central/Axis Powers in both World Wars. 6.2.12.D.4.g Analyze the role of racial bias, nationalism, and propaganda in mobilizing civilian populations in support of “total war”. 6.2.12.D.4.j Analyze how the social, economic, and political roles of women were transformed during this time period. 6.2.12.D.4.k Assess the cultural impact of World War I, the Great Depression, and World War II by analyzing the values and social ideas in the arts.