087a1ac7b86cb348a00e0438a5e3d863.doc SCH4C – Organic Chemistry
Date: ______Alkenes
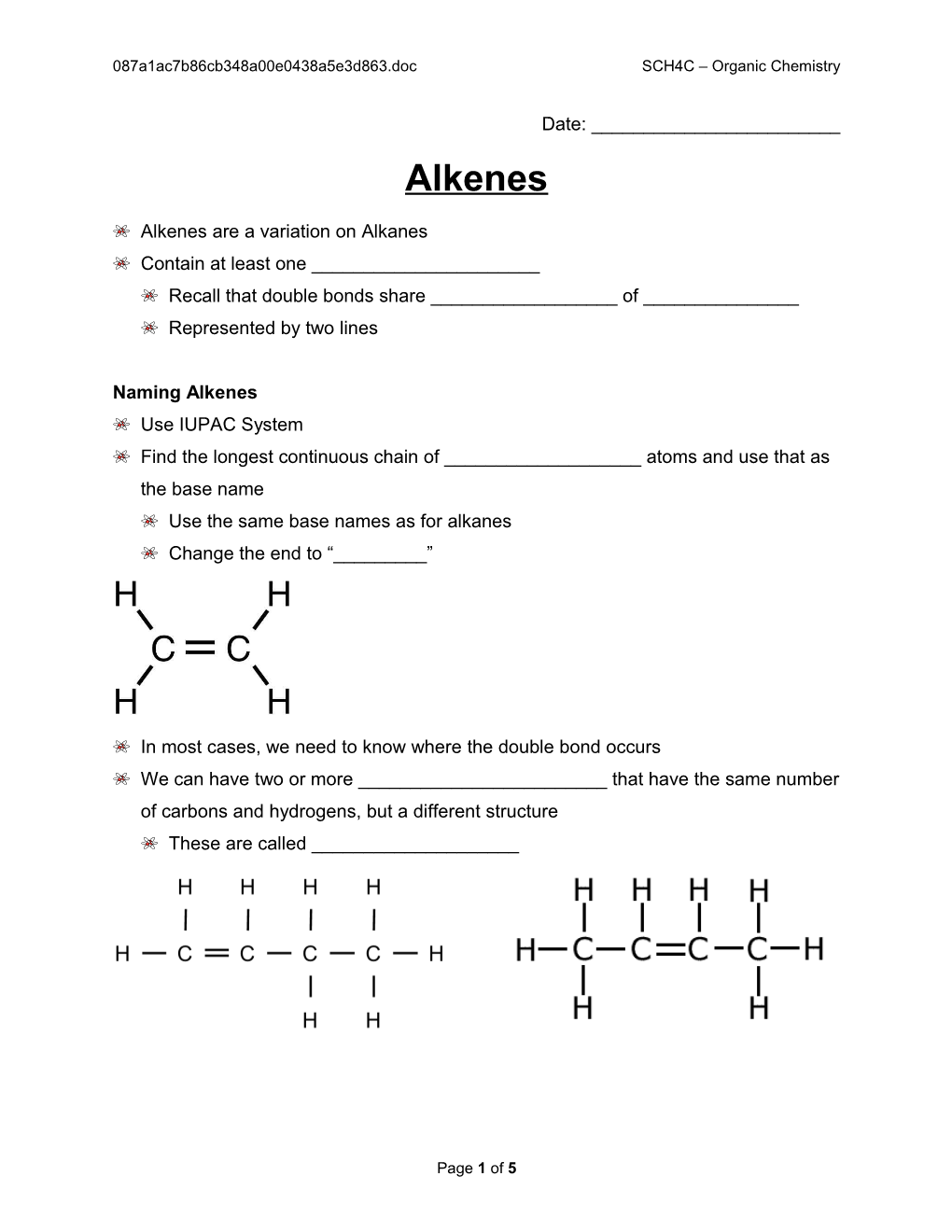
Alkenes are a variation on Alkanes Contain at least one ______Recall that double bonds share ______of ______Represented by two lines
Naming Alkenes Use IUPAC System Find the longest continuous chain of ______atoms and use that as the base name Use the same base names as for alkanes Change the end to “______”
In most cases, we need to know where the double bond occurs We can have two or more ______that have the same number of carbons and hydrogens, but a different structure These are called ______
Page 1 of 5 087a1ac7b86cb348a00e0438a5e3d863.doc SCH4C – Organic Chemistry
These two isomers have different ______and ______properties It is important to differentiate these two We need to note where the ______is Count from the end Use the one that has the ______
Drawing Alkenes Same as the alkanes for structural drawings Use extra line to show the place of the double bond Examples
4-decene
Page 2 of 5 087a1ac7b86cb348a00e0438a5e3d863.doc SCH4C – Organic Chemistry cis and trans Alkenes There are two forms of alkenes Depends on the ______of the double bond If the larger groups are on the same side of the double bond, it is ______If the larger groups are on the opposite side of the double bond, it is ______Examples:
Page 3 of 5 087a1ac7b86cb348a00e0438a5e3d863.doc SCH4C – Organic Chemistry
Cyclic Alkenes
With a cyclic alkene, we can chose the starting carbon So we know that the double bond is at position 1
Page 4 of 5 087a1ac7b86cb348a00e0438a5e3d863.doc SCH4C – Organic Chemistry
Draw structures for the following compounds.
1.cis-4-ethyl-2-heptene
2.2-methyl-2-butene
3.2,4,6-octatriene
4.3,4-dimethyl-2-pentene
5.5-ethyl-3,6-dimethyl-1,7-nonadiene
6.2-methylpropene
7.7-propyl-3-decene
8.5-ethyl-3-heptene
9.5,6-dipropyl-2-nonene
10. trans-3-hexene
Name the following structures.
1. 5. CH2 CH2CH2CH3 || | CH3-CH2-C-CH2-CH2CH3 CH3CH=CHCH2CH2CHCH3
2. 6.
CH3CH=CHCH-CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH=CHCH2CH2CH3 | CH3
3. 7. CH3 CH3 | | CH3CH2CH2C=CH3 CH3CHCH2C=CHCH3 | CH2CH3
4. 8. CH2CH3 CH3 CH2CH3 | | | CH3CHCHCH=CH2 CH3CHCHCH=C | | | CH2CH3 CH3 CH3
Page 5 of 5