Human Anatomy & Physiology 03B.2 Epi-N-Dermis
Layers of the Epidermis Leave space for the following diagram to be glued.
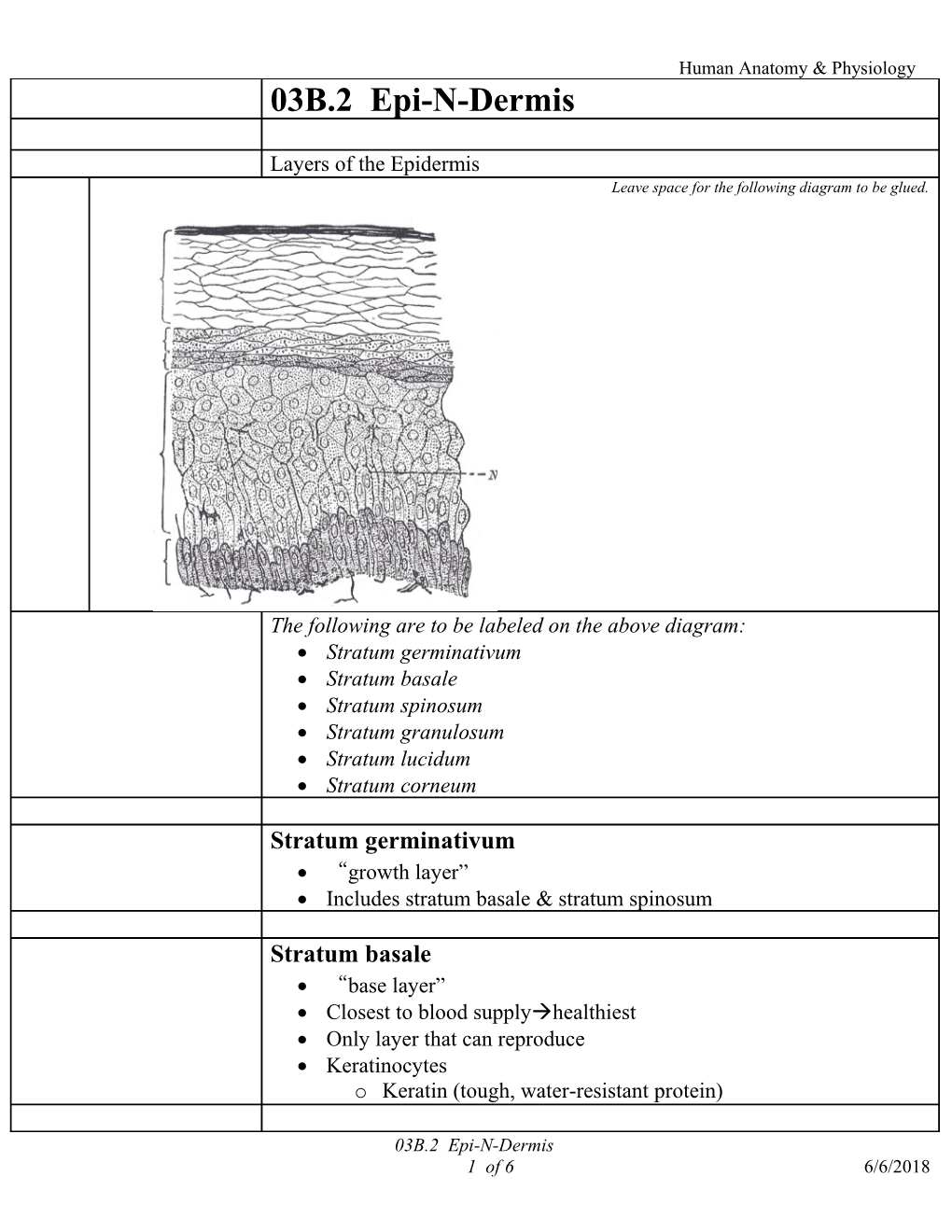
The following are to be labeled on the above diagram: Stratum germinativum Stratum basale Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum Stratum corneum
Stratum germinativum “growth layer” Includes stratum basale & stratum spinosum
Stratum basale “base layer” Closest to blood supplyhealthiest Only layer that can reproduce Keratinocytes o Keratin (tough, water-resistant protein)
03B.2 Epi-N-Dermis 1 of 6 6/6/2018 Human Anatomy & Physiology Melanocytes o Melanin (brown protein pigment) . Absorbed by surrounding keratinocytes
Two categories of melanin: o Eumelanins (dark brown) o Pheomelanins (light brown/red/orange)
Freckle o clusters of concentrated melanin which are most often visible on people with a fair complexion http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=10102 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Freckle
Mole o Clusters of concentrated melanin o Often raised http://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/guide/moles
Stratum spinosum “spiny layer” as pushed from below become “squished” & look “spiny” on cross section spot desmosomes can pull out “spines” as cells shrink away from each other, when pulled apart less healthy don’t reproduce
Stratum granulosum “grainy layer” as cells from stratum germinativum die, they enter stratum granulosum all cells are dead look grainy when stained / no nuclei
basophilic keratohyalin granules (seen on the close-up view). These granules contain lipids, which along with the desmosomal connections, help to form a waterproof barrier that functions to 03B.2 Epi-N-Dermis 2 of 6 6/6/2018 Human Anatomy & Physiology prevent fluid loss from the body.
Stratum lucidum “light layer” or “clear layer” Layer looks almost clear Gets more full of keratin
Stratum corneum “horny layer” meaning “like an animal’s horm” Keratin is fully formed, making keratinzed stratified squamous epithelium.
A complete new epidermis forms every 25-45 days.
DERMIS Your “hide” Irregular dense fibrous connective tissue
Papillary region superficial region has bumps called dermal papillae bumps in the human body are often called papillae (sing. papilla = “nipple” increase surface area for glue to “hold” more tightly Arranged in rows to form "prints" of hands/fingers and feet/toes to improve grip Fingerprints http://www.reachoutmichigan.org/funexperiments/agesubject/lesson s /prints.html
Reticular region Deeper, irregular swirls of collagen fibers Nerves, nerve endings, blood vessels, sweat glands, etc. Reticular = “netlike”
Leave space for the following diagrams to be glued.
03B.2 Epi-N-Dermis 3 of 6 6/6/2018 Human Anatomy & Physiology
The following are to be labeled on the above diagram. Those not italicized need to be placed into your notes.: Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis) Stratum basale 03B.2 Epi-N-Dermis 4 of 6 6/6/2018 Human Anatomy & Physiology Stratum corneum Hair shaft
Hair follicle lined by cells derived from the epidermal (outside) layer of the skin Each follicle normally goes through a five-year cycle of growth and rest, with about 90% of the follicles growing hair at any one time
Papilla of hair bulb Provides nutrients for growth and development of the hair
Sweat gland
Sebaceous (oil) gland Lubricates the hair Keeps hair & skin from drying out
Pore
Arrector pili when contracted, causes hair to “stand up” or goose bumps
Nerve fibers (will need to draw in)
Pacinian corpuscle receptive to deep pressure
Meissner’s corpuscle sensitive to light touch
Adipose (fat) tissue
Blood vessels draw this in red = from heart (arteries); blue = back to heart (veins)
Other Items: Blisters epidermis & dermis are tightly connected. 03B.2 Epi-N-Dermis 5 of 6 6/6/2018 Human Anatomy & Physiology Sometimes when too much friction or burns occur that connection is lost & area fills with interstitial fluid http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blister
Scars form when a denser-than-usual mass of fibers are produced to replace those damaged in an injury Keloid Scars o Abnormally large scars
Stretch marks occur when the skin is overstretched and the dermis tears beneath the epidermis
Remember to: Reduce, Recite, Reflect, & Review! Make your Flashcards & Study 3 x 5!
03B.2 Epi-N-Dermis 6 of 6 6/6/2018