ECONOMICS MRS. SURIAN FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET EXAM on WED 1/22 & TH 1/23 Bring a PENCIL & PEN NO ELECTRONIC DEVICES ALLOWED IN CLASSROOM!
MICROECONOMICS Ch 1-Life is Economics *Four factors of production- natural resources, capital, labor, entrepreneur *Scarcity- the central problem in economics; why is everything considered to be scarce? *Tradeoffs v. Opportunity costs- secondary effect = consequence (+ or -)
Choice Value of second choice (What you could have done.)
Ch 2- Economic Systems *Capitalism- 5 pillars: consumer sovereignty, free/private enterprise, private property, competition, profit motive *Types of Economies (command, market, mixed market; characteristics of each)
command market What is produced? government consumer How it is Produced? government producer For when is it government producer produced?
Ch 3- Demand (think “consumer”) *Demand-based on consumers wants and needs; demand shown when people buy . . . *Law of Demand/DemandCurve- negative slope; as price increases, demand decreases *Law of Supply/Supply Curve- positive slope; as price increases, supply increases *Elasticity/Inelasticity- Rule of thumb: “expensive, elastic . . .” amount D in Demand
Demand Supply
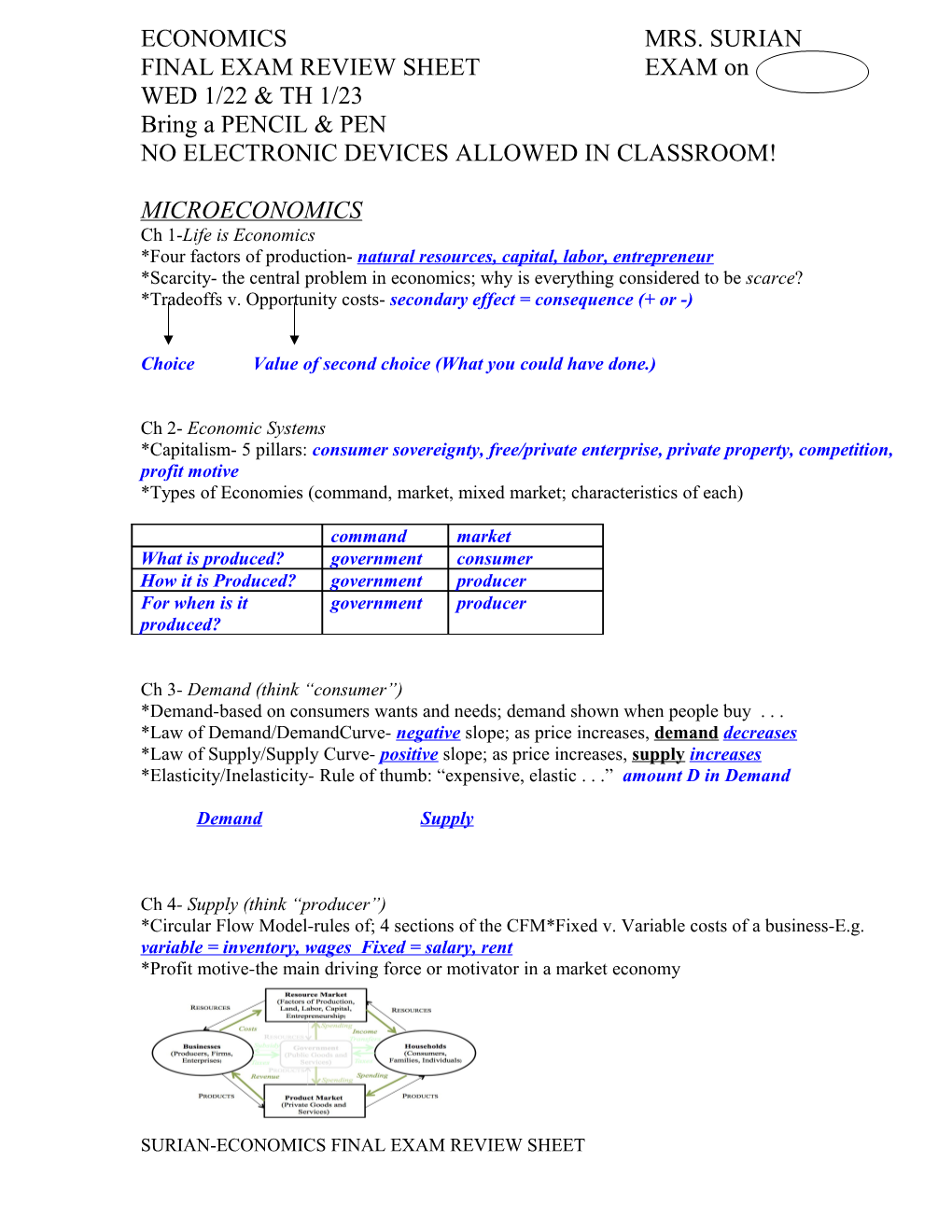
Ch 4- Supply (think “producer”) *Circular Flow Model-rules of; 4 sections of the CFM*Fixed v. Variable costs of a business-E.g. variable = inventory, wages Fixed = salary, rent *Profit motive-the main driving force or motivator in a market economy
SURIAN-ECONOMICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET Ch 5- Prices *Equilibrium price(point)-the price at which the demand and supply curves meet *Surplus/ shortage-when does each occur? Where is price forced?
Ch 6-Market Structures *Monopoly- one producer of a product (>90% industry) *Oligopoly-few suppliers of one type of product. E.g. 12, 20 eg. Gas stations, airlines *Laissez Faire-Gov’t “Government Hands Off” *Antitrust legislation-Sherman Antitrust Act (1890) Makes monopolies ILLEGAL! except for: **Natural monopoly = LIPA & SCWA
Ch 7-Business Organizations *Sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation (differences between them) see chart in notebook *Limited/unlimited liability-levels of responsibility in certain types of businesses
“Liability” = responsibility
“Life” = will the business still exist?
Ch 8- Labor and Wages *Federal Minimum wage- currently $7.25 What groups of people usually receive it? Youth and Elderly *NYS Min. Wage- currently $______*Salary v. wage-salary is a fixed income whereas a wage is a/an hourly income
SURIAN-ECONOMICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET Ch 9- Sources of Capital & Credit (EE bonds) *Time deposits-has a maturity date e.g. certtificate of deposit(CD) 6 months, 12 months etc… *types of banking accounts e.g. savings, checking, money market *”Rule of 72”-divide interest rate by 72 # of years to double your money in the bank *Important terms to know about Credit- e.g. grace period, Card Act of 2009, minimum pmt. APR, FICO score =credit score *Bankruptcy-aka “filing chapter 11” to improve disclosure(information) to consumers
*Loans- Mortgage loan term ______yrs, Auto/car loan term- ______Student loan term- ______*What loan NEVER gets erased? Student loans *Amortization (calculator) What does it calculate/show you? amt. of payments, # of payment, can play around and change the length (term) and interest rate to see what you can afford
MACROECONOMICS
Ch 10- Economic Performance GDP = Gross Domestic Product *GDP and problems with calculating its accuracy; durable/ non-durable goods Know formula: *4 phases of the business cycle:
Ch 11-Economic Challenges *4 types of unemployment Cyclical, structural, seasonal, frictional *Inflation- increase in price level *Hyperinflation extreme decrease in value of money How is it measured? by CPI = Consumer Price Index (Market basket of goods/services) What is the “base year?” base year = 0, general increase in price level
*Income v. Wealth- income = flow of value of value v. wealth = accumulation of value of value *Poverty threshold (poverty line)- $ amount (based on # of people in household) whereby if fall below that $, you are “poor”( according to the government) Eligible for food stamps, welfare etc.. *Minimum Wage- currently $ 7.25 hour; NYS =$8.00 per hour as of 1/1/14 *Pros/Cons of raising min. wage- Affect on worker???? Affect on business owner????
Ch 13- $Money *What is fiat money? Money that has value simply because people all believe it does=faith *3 functions of money- store of value, measure of value, medium of exchange *4 characteristics of money acceptable, portable, divisible, stable value *FDIC-Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation- currently insures $250,000 per depositor
SURIAN-ECONOMICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET Ch 14- The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy *Federal Reserve System (“The Fed”)- main function of? - to maintain a stable $ supply; raise and lower interest rates as it sees fit (if want to motivate people to spend= lower interest rates) *Reserve Requirement- banks must keep 10% of all deposits in the bank ; cannot lend out/invest *3 ways banks make money- loans (interest), invest in stock market (cap gains), circulate $
Ch 15- Fiscal Policy & Taxes (FISCAL = having to do with MONEY) *Fiscal Policy- monetary policy (having to do with money and the economy) *Federal budget-US Government spending of funds to benefit the nation *Fiscal year ( Oct 1 st to Sept 30 th) *National debt-total deficits from years past to the present day (17.3 TRILLION! As of 2014) *Deficit-yearly debt: calculated annually; when outlays exceed revenue ($ spent > $ earned) OR O>R *Taxable year ( Jan 1 st to Dec 31st) (spend income) *Taxes-types of taxation-income, property, gift, cap. gains, corporate income, “sin” taxes etc *Gross (total) vs. net pay (taxes taken out of one’s paycheck) “net is what you get” (after taxes) *FICA (Social Security) and other taxes from paycheck, etc. (medicate, unemployment insurance)
OTHER TOPICS:
*Investing Unit *Capital gain/loss-gain- money made (gain)/lost (loss) from the sale of stock *Dividend-money paid to a stock holder from corporate profits (usually a small amount per share) *Diversification-investing in various industries (stocks); lessens risk *Bull/Bear market-Bullish (high) / Bearish (low) *DOW Jones Industrial Avg. –index of 30 common stocks; represents “market health” *Job of the Securities and Exchanges Commission (SEC)- Gov’t regulatory agency; regulates insider trading, corruption in stock market etc. *401K, 403b, 529 Plan and other deferred compensation plans 401, 403b- retirement accts. 529 Plan- college savings acct. IRA= individual retirement acct. IPO-=initial public offering; when a stock is offered to the public for the first time
*Outsourcing- contracting a business function to someone else; usually outside the country *Advantages and disadvantages of outsourcing- Adv- cheap labor= lower prices, faster production, Disadv.- removes US jobs; gives jobs to other nations; less $ in/to U.S. *Who we use for outsourcing? China, India, many other nations with a willing workforce *Examples of companies that outsource- Apple (China-Foxcomm factory,) other “American” companies, most clothing companies etc
SURIAN-ECONOMICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET ADDITIONAL NOTES:
SURIAN-ECONOMICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET