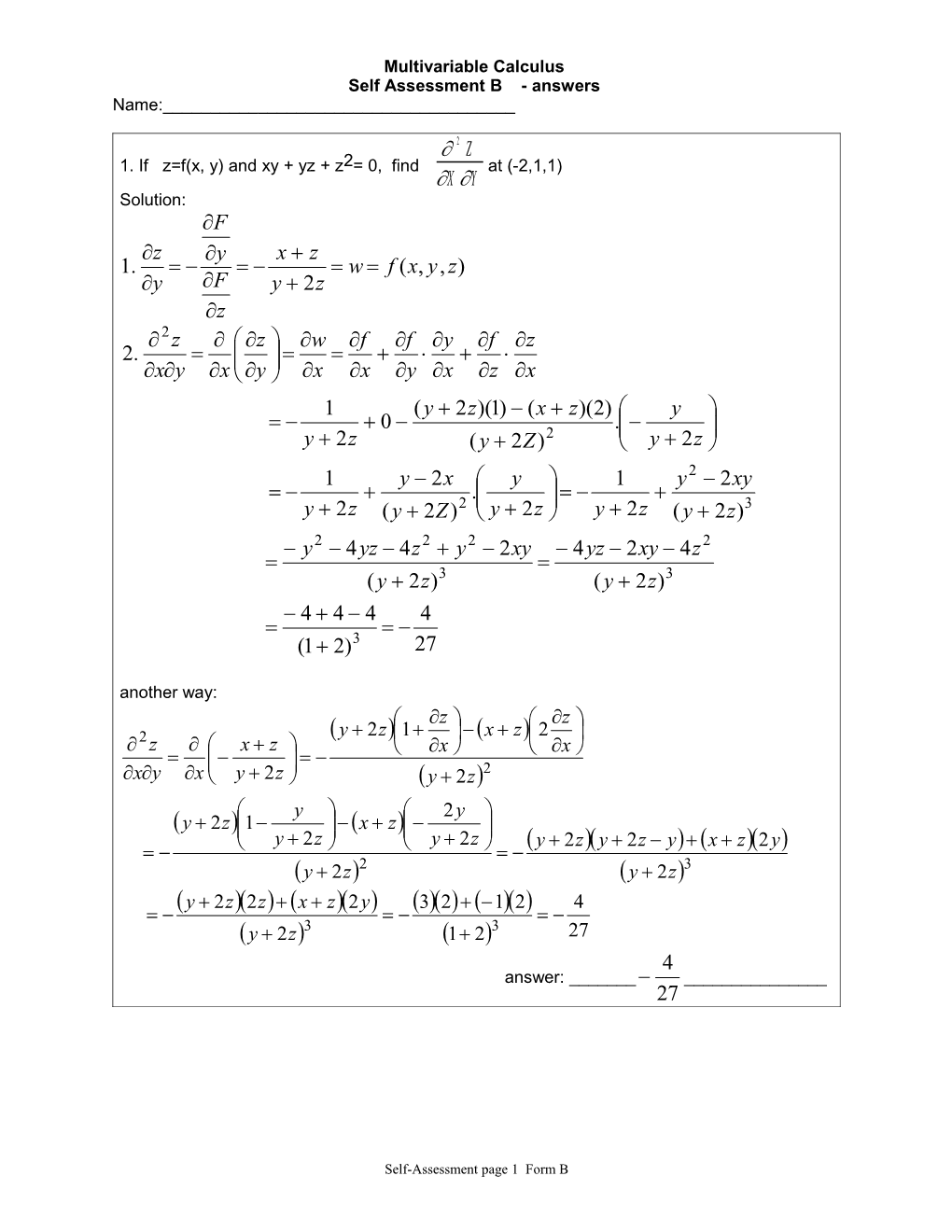
Multivariable Calculus Self Assessment B - answers Name:______
2 Z 1. If z=f(x, y) and xy + yz + z2= 0, find at (-2,1,1) X Y Solution: F z y x z 1. w f (x, y, z) y F y 2z z 2 z z w f f y f z 2. xy x y x x y x z x 1 (y 2z)(1) (x z)(2) y 0 . y 2z (y 2Z)2 y 2z 1 y 2x y 1 y2 2xy . y 2z (y 2Z)2 y 2z y 2z (y 2z)3 y2 4yz 4z 2 y2 2xy 4yz 2xy 4z 2 (y 2z)3 (y 2z)3 4 4 4 4 (1 2)3 27 another way: z z 2 y 2z1 x z2 z x z x x xy x y 2z y 2z2 y 2y y 2z1 x z y 2z y 2z y 2zy 2z y x z2y y 2z2 y 2z3 y 2z2z x z2y 32 12 4 y 2z3 1 23 27 4 answer: ______ ______27
Self-Assessment page 1 Form B dy 2. Use the Jacobian to find at (1, -1, 1) if -2xy + 3z + x2= 6 and 2x - y2 + yz = 2 dx Solution: (F,G) 2y 2x 3 4 3 dy (x, z) 2 y 2 1 10 10 10 answer: dx (F,G) 2x 3 2 3 7 7 7 (y, z) 2y z y 3 1
3. Find the directional derivative of w= 2x2yz in the direction of v=3i-4j at he point (-1, 1, 3, 6) Solution : The gradient is given by : w 4xyzi 2x2 zj 2x2 yk 12i 6 j 2k 3 4 The unit vector in the direction of v is u i j 0k 5 5 36 24 60 Dw w u 0 12 answer : 12 v 5 5 5
4. Use the Lagrangean coefficients technique to find the minimum value of w y z 2x2 subject to the condition x y2 z 2. We want to find the minimum value of w y z 2x2 for point located in the paraboloid x y2 z 2. Solution: using Lagrangean coefficients. The lagrangean equation is given by F(x, y, z,) y z 2x2 (x y2 z 2 ) F 4x 0 x x 4 F 1 1 2y 0 y y 2 F 1 1 2z 0 z z 2 F 2 2 1 1 3 3 x y z 0 0 2 2 4 42 42 Therefore, 2 1 1 3 2 1 3 4 3 4 3 4 33 4 w y z 2x2 2 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 4 2 8 2 8 8 33 4 answer: ___ ______8
Self-Assessment page 2 Form B 5. Find all critical points of f(x, y) = y3 + xy2 -2xy . Determine whether each critical point yields a relative maximum value, a relative minimum, or a saddle point. Step 1. f y2 2y 0 x y(y 2) 0 y 0 and x 0 or f 2 3y2 2xy 2x 0 3y 2xy 2x 0 y 2 and 2x 12 0 x 6 y Critical Points: The critical points are (0, 0, 0) and (-6, 2, 8)
Step 2. 2 f 0 2 x 2 f at x 0 and y 0 0 4, saddle point 2 2 f y 0 2 x2 f 2 2 f yx 6y 2x 2 2 y f 2 0 f x2 2y 2 yx 2 f at x 6 and y 2 2 4, saddle point 2 y 2 f 2 yx Answer: both (0, 0, 0) and (-6, 2, 8) are saddle points
6) An ice cone is melting in such a way that the radius is decreasing at the rate of 2 inches per minute and the height is decreasing at the rate of 3 inches per minute. At what rate is the volume changing when r=3 feet and h=5 feet.
. 1 V V dr V dh V 2 1 V r 2h rh 2 r 2 3 3 t r dt h dt t 3 3 V 2 1 (36)(60) 2 (36)2 3 2880 1296 t 3 3 V 4176 sq inches per min 29 sq ft per min 91.106 ft min t
answer: ______ 91.106 ft min ______
Self-Assessment page 3 Form B 2 z 7. If z = x2 +y2 , x=r+2s and y = 3r +s, find r s Solution: z z x z y 2x 2 2y 1 4x 2y w s x s y s 2 z w x w y (w) 41 2(3) 10 rs r x r y r answer: __ 10______
2 z 8. If f(x, y) = x2 -xy + y2 find x y Solution: 2 z z x 2y 1 x y x y x answer:____-1 ______
x y2 9. If x=f(y, z), 4 = x3 -y3 -z3 , find answer: : ______y x2
Solution: F x y 3y2 y2 y F 3x2 x2 x
10. Use differentials to approximate 3 6 . 3 3 7 . 6 Solution: Let f (x, y) x3 y , x 36, x 0.3, y 8, y 0.4 f (36,8) 363 812 f f 3 y x f df x y x y x y 2 x 33 x2 2 6 6 24 18 3 0.3 0.4 0.15 12 12 120 120 120 20 Therefore, 36.33 7.6 12 0.15 11.85 answer :11.85
Self-Assessment page 4 Form B 11. Find the maximum value of w= x2 +3y2 +2z2 subject to the condition 2x-3y+5z=1. Solution: using Lagrangean coefficients. The lagrangean equation is given by F(x, y, z,) x2 3y2 2z 2 (2x 3y 5z 1) F 39 4 2x 2 0 x 1 x 4 39 F 4 6y 3 0 y x y 2 39 F 5 2 4z 5 0 z y z 4 39 F 3 25 5 2x 3y 5z 1 0 2 1 0 z 2 4 39 2 2 2 16 12 50 78 2 Therefore, w x 3y 2z answer 392 392 392 392 39
12. Find the point on the plane 2x-y +3z -5 =0 that is closest to the origin. Solution: We want to minimize d x2 y2 z 2 or D d 2 x2 y2 z 2 subject to the constraint that 2x - y + 3z -5 =0. The lagrangean equation is given by F(x, y, z,) x2 y2 z 2 (2x y 3z 5) F 5 2x 2 0 x 14 10 x 7 F 5 2y 0 y x y 2 7 F 3 5 2z 3 0 z y z 2 14 F 1 9 15 2x y 3z 5 0 2 5 0 z 2 2 14 5 5 15 Therefore, the closest point is , , 7 14 14
Self-Assessment page 5 Form B 13. The gradient is normal to the level surface F(x, y, z) =0. It is because of this normality of the gradient that the maximum directional derivative ( which is ) at a point is often called the normal d f derivative at Normal Derivative at that point. We use the notation for the normal derivative of a d n function f.
Find the normal derivative of z = x3 y at the point (-1, 2, 2) and the corresponding unit vector. Solution: df z 3x2 yi x3 j 6i j z 62 (1)2 37 dn 6 1 u i j 37 37
x 2 y 14. Show that l i m 4 2 0 along any line y=mx, for any m. What is x 0 x y y 0 x 2 y x 2 y l i m 4 2 along y=x2 . Does l i m 4 2 exist?. Explain. x 0 x y x 0 x y y 0 y 0
Solution: x2 y mx3 mx 0 y mx, m 0 lim lim lim 0 x0 x4 y2 x0 x4 m2 x2 x0 x2 m2 m2 y0 y0 y0 x2 y 0 m 0 y 0 and lim lim 0 x0 x4 y2 x0 x4 y0 y0 x2 y x4 1 y x2 lim lim x0 x4 y2 x0 x4 x4 2 y0 y0 Therefore the limit does not exist because it is not unique
Self-Assessment page 6 Form B